Embed presentation
Downloaded 111 times



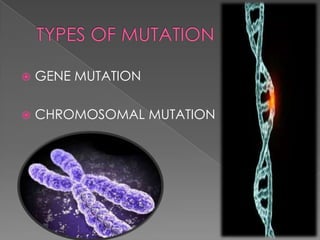


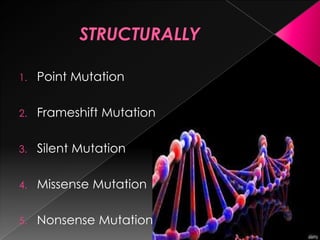
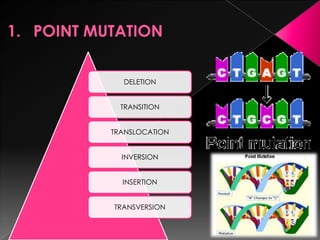
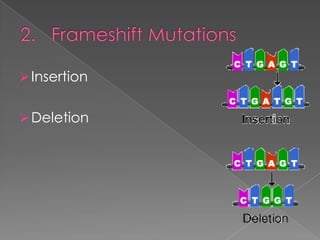
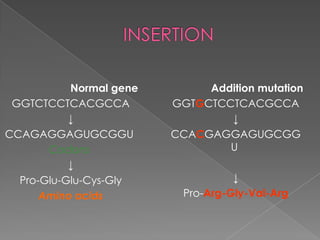
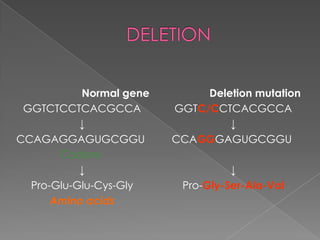

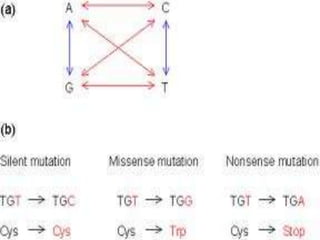
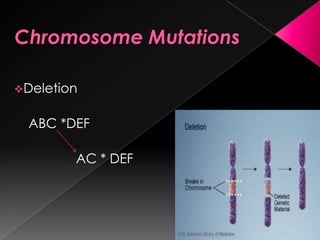

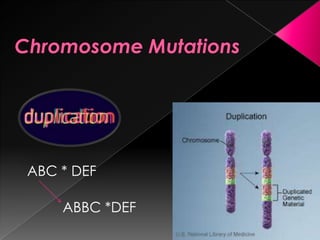
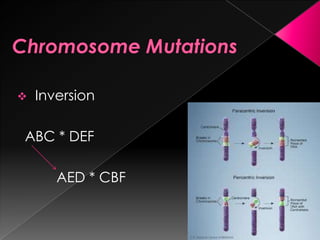
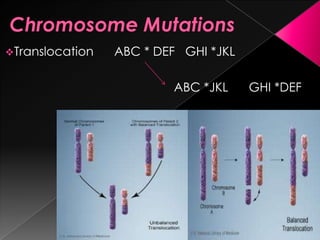
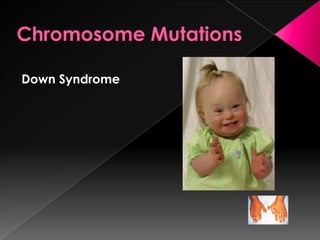





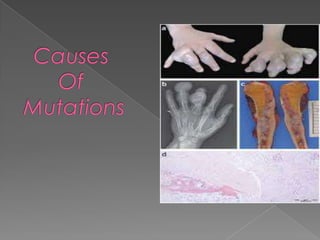
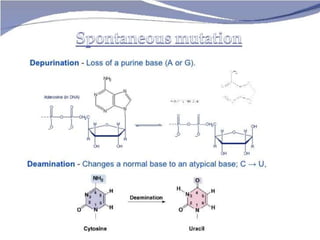
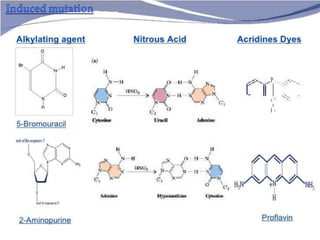





This document discusses different types of gene and chromosomal mutations. It describes point mutations like silent, missense, and nonsense mutations. It also discusses chromosomal mutations such as deletions, transitions, translocations, inversions, and insertions. Examples are given of genetic disorders caused by different mutations, including Down Syndrome, Klinefelter's Syndrome, XYY Syndrome, Turner's Syndrome, and XXX Syndrome.





































