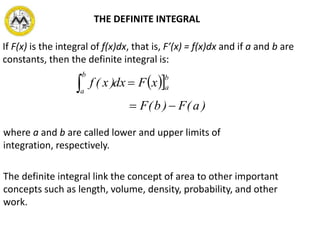
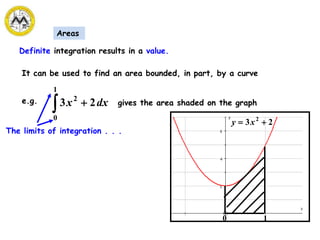
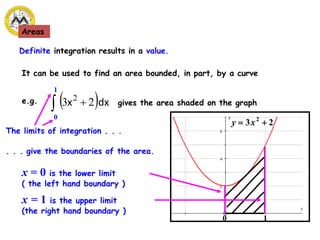
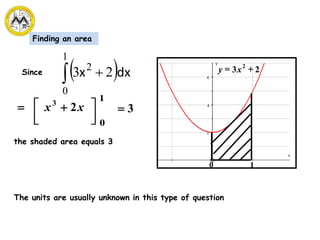
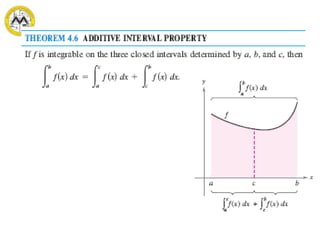
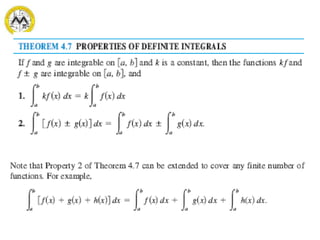
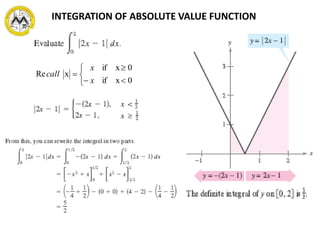
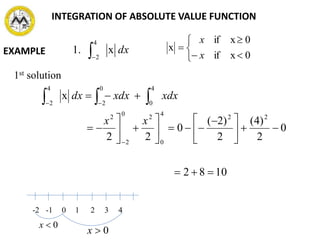
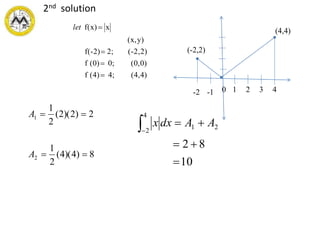
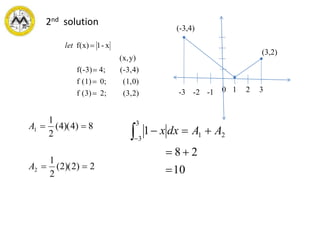
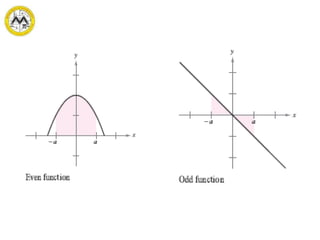
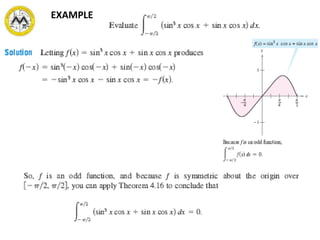
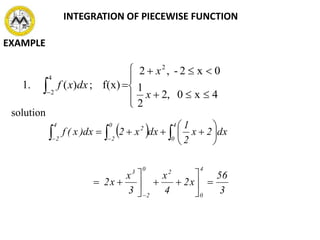
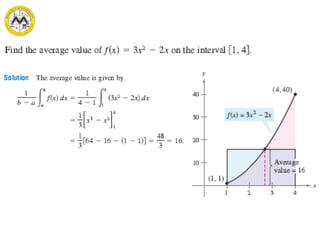
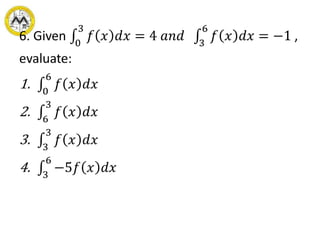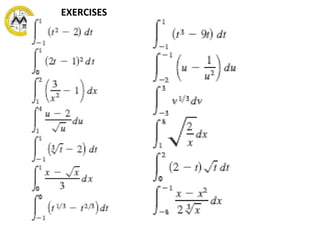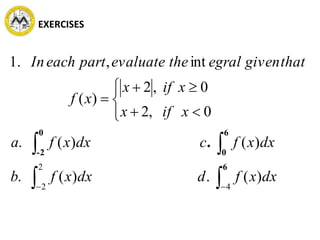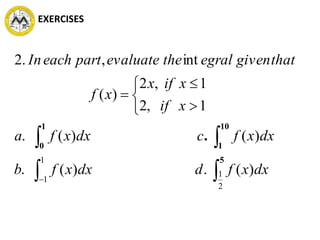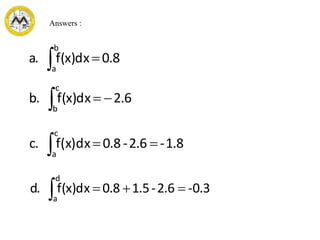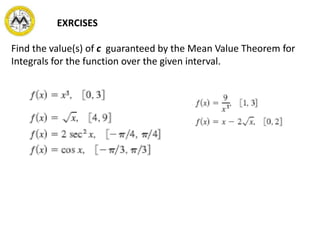The document defines definite integrals and discusses their properties. It states that a definite integral evaluates to a single number by integrating a function over a closed interval from a lower limit to an upper limit. It gives examples of using definite integrals to find areas bounded by curves. The mean value theorem for integrals is also introduced, which states that there is a rectangle between the inscribed and circumscribed rectangles with an area equal to the region under the curve. Exercises are provided on evaluating definite integrals and applying the mean value theorem.