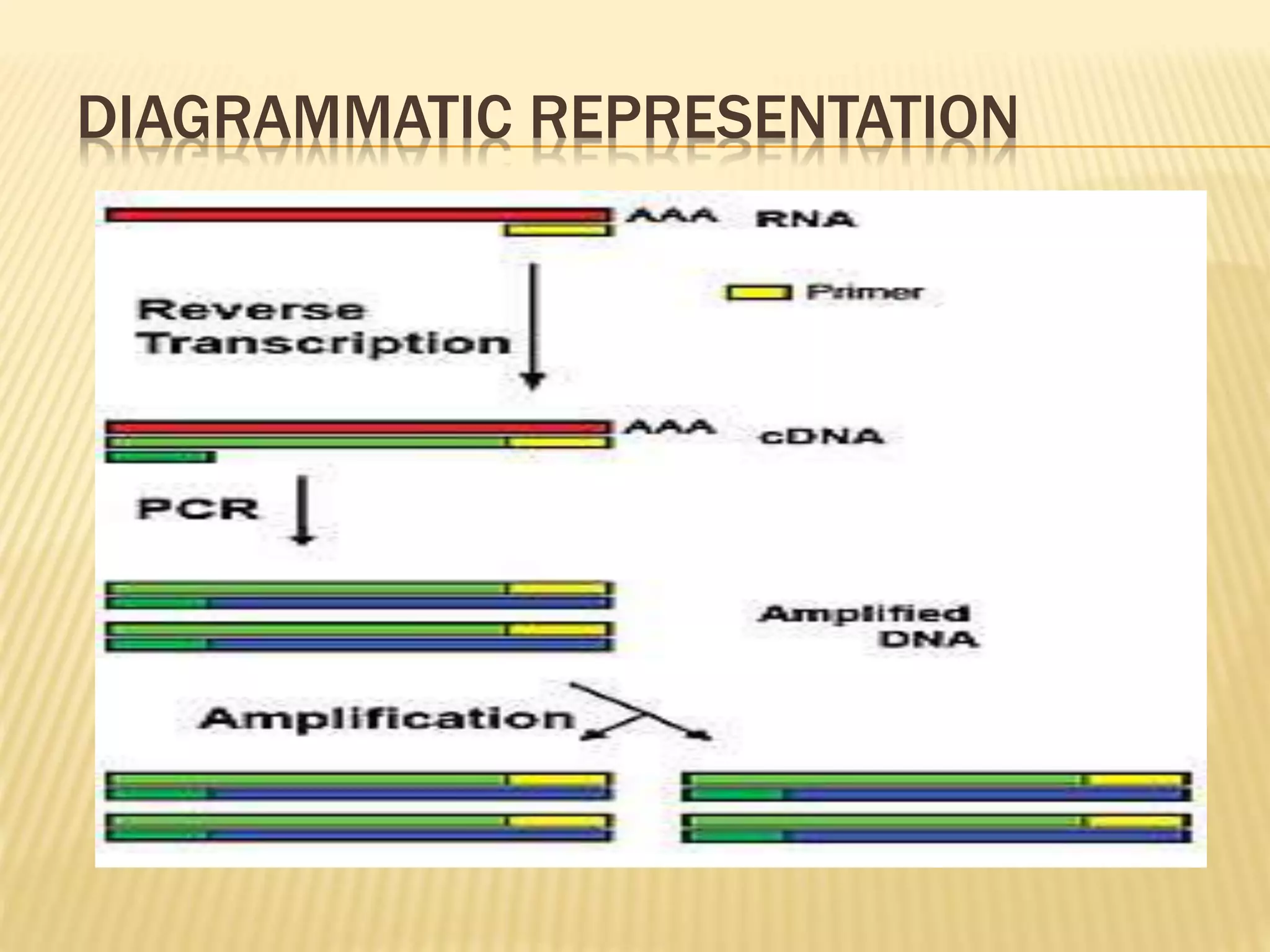
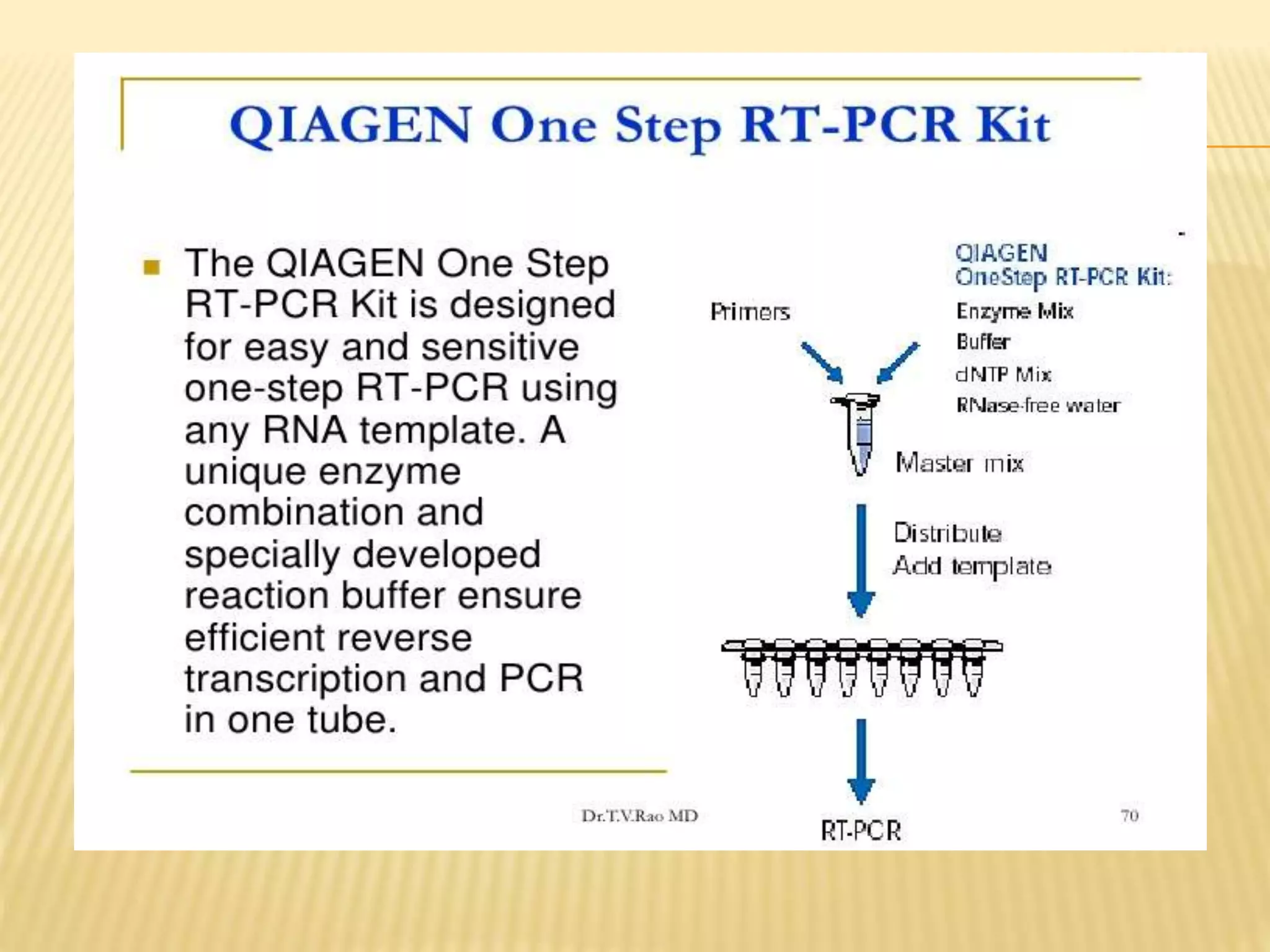
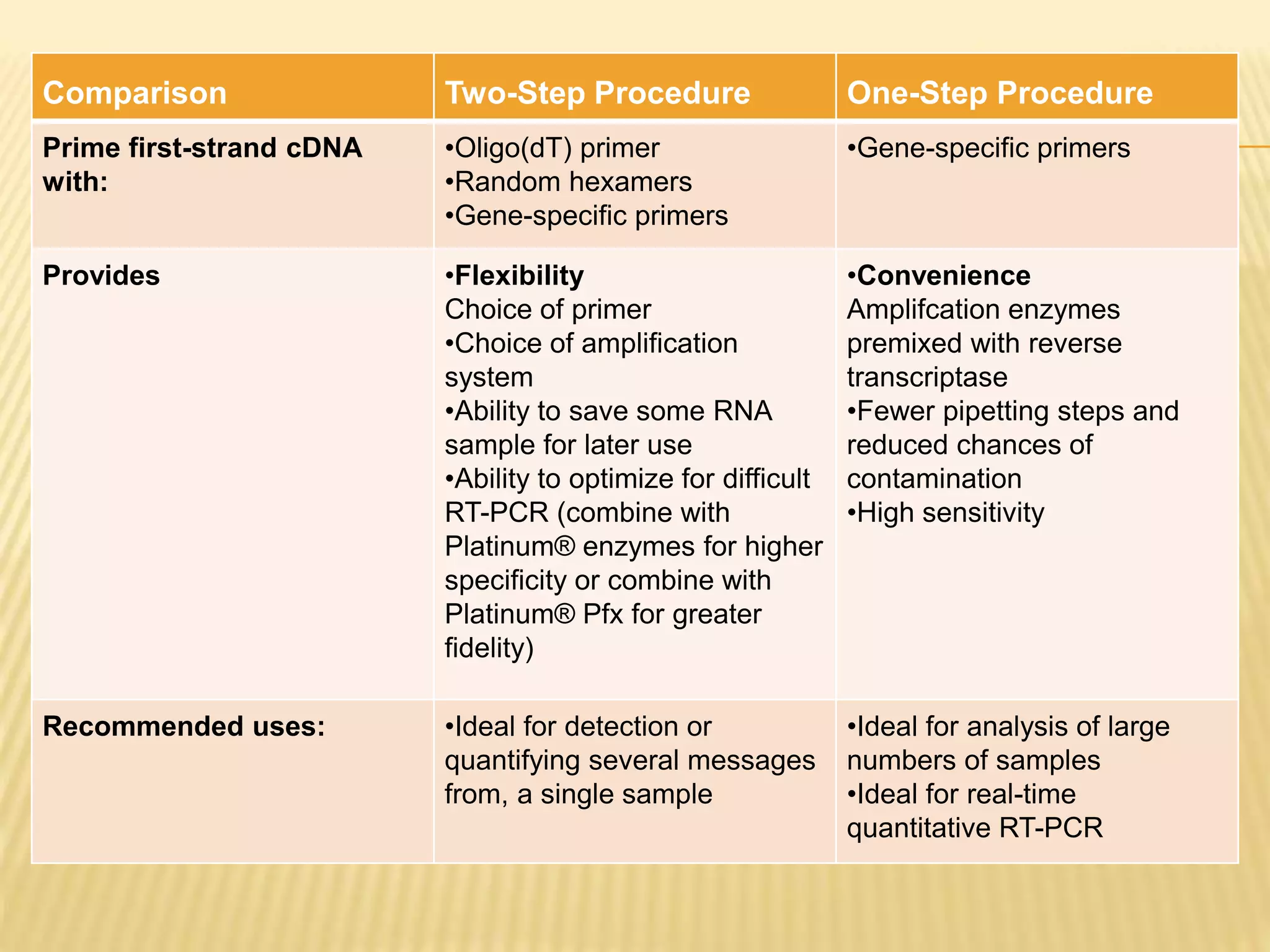
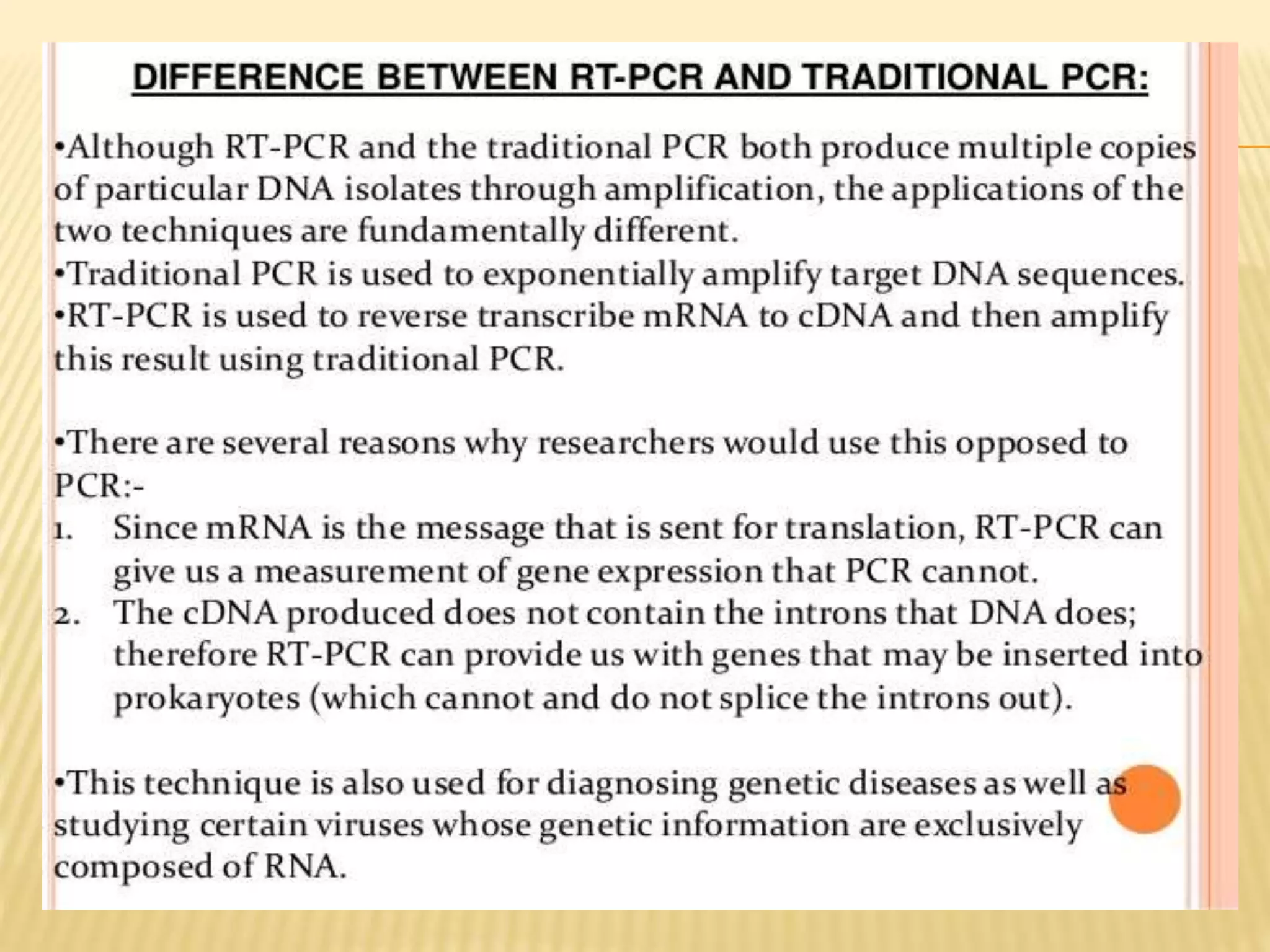
This document provides an overview of reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), including its objectives, introduction, history, principle, protocol for one-step and two-step RT-PCR, technical issues, and literature applications. RT-PCR is a technique that allows detection and quantification of mRNA by first converting RNA to cDNA using reverse transcriptase, then exponentially amplifying the cDNA using PCR. It is often used to detect gene expression and distinguish between infectious and non-infectious viruses or variants in samples. Care must be taken to prevent contamination during sample preparation and RT-PCR.