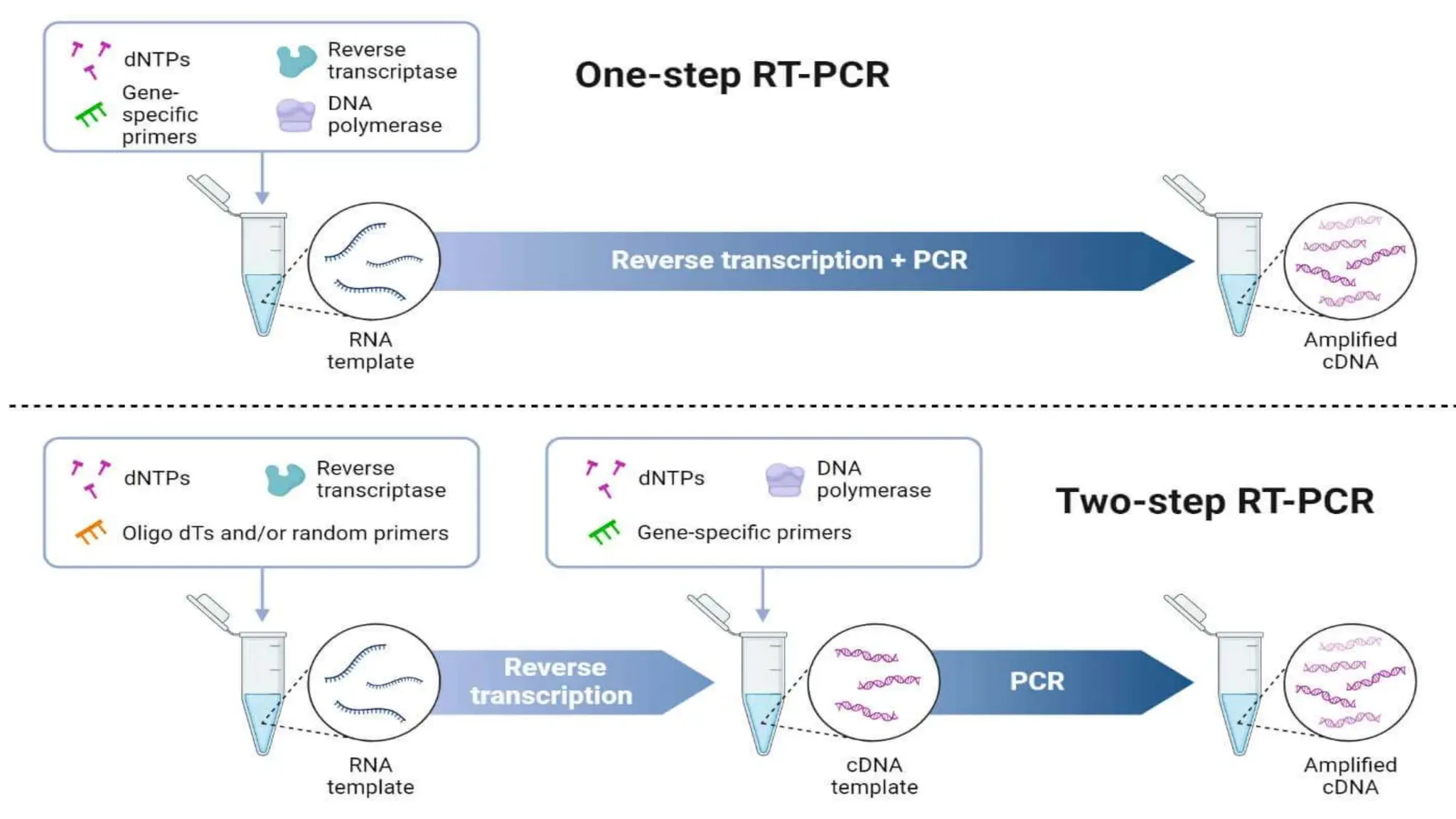
Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a technique that amplifies RNA in vitro by first converting it into complementary DNA (cDNA) using reverse transcriptase, then using PCR to amplify the cDNA. It is widely used for analyzing mRNA, studying gene expression, diagnosing infections, and genetic research. RT-PCR can be performed as one-step or two-step procedures, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages.