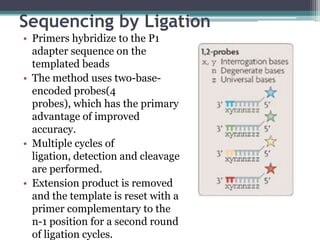
The document discusses sequencing methods in biology, focusing on traditional methods like Maxam-Gilbert and Sanger sequencing, as well as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and its advantages such as speed and cost-effectiveness. NGS technologies enable the high-throughput sequencing of millions of DNA fragments simultaneously, using techniques like emulsion PCR and cyclic reversible termination. It also outlines various NGS platforms, applications, and bioinformatics challenges related to genome alignment and assembly.