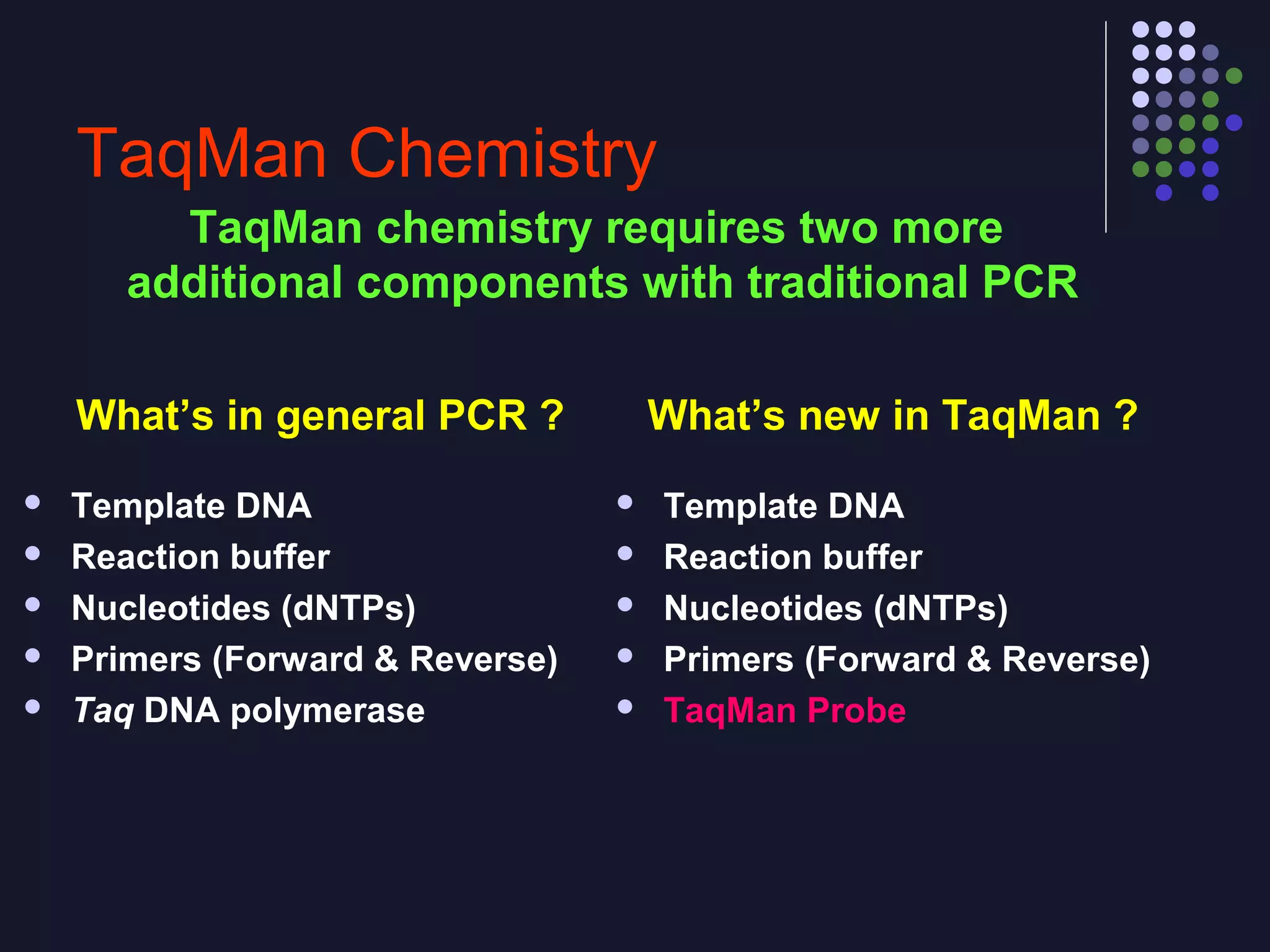
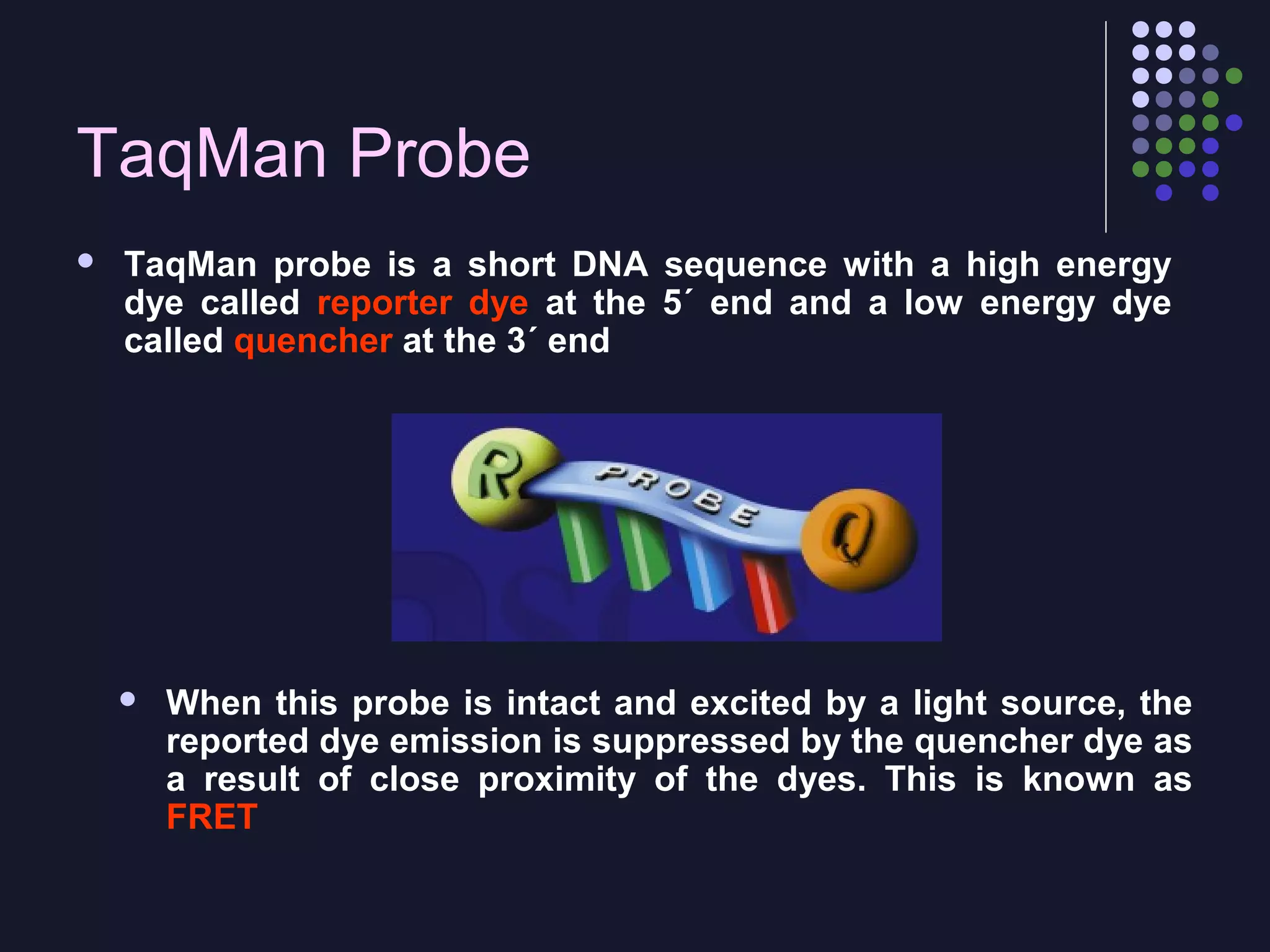
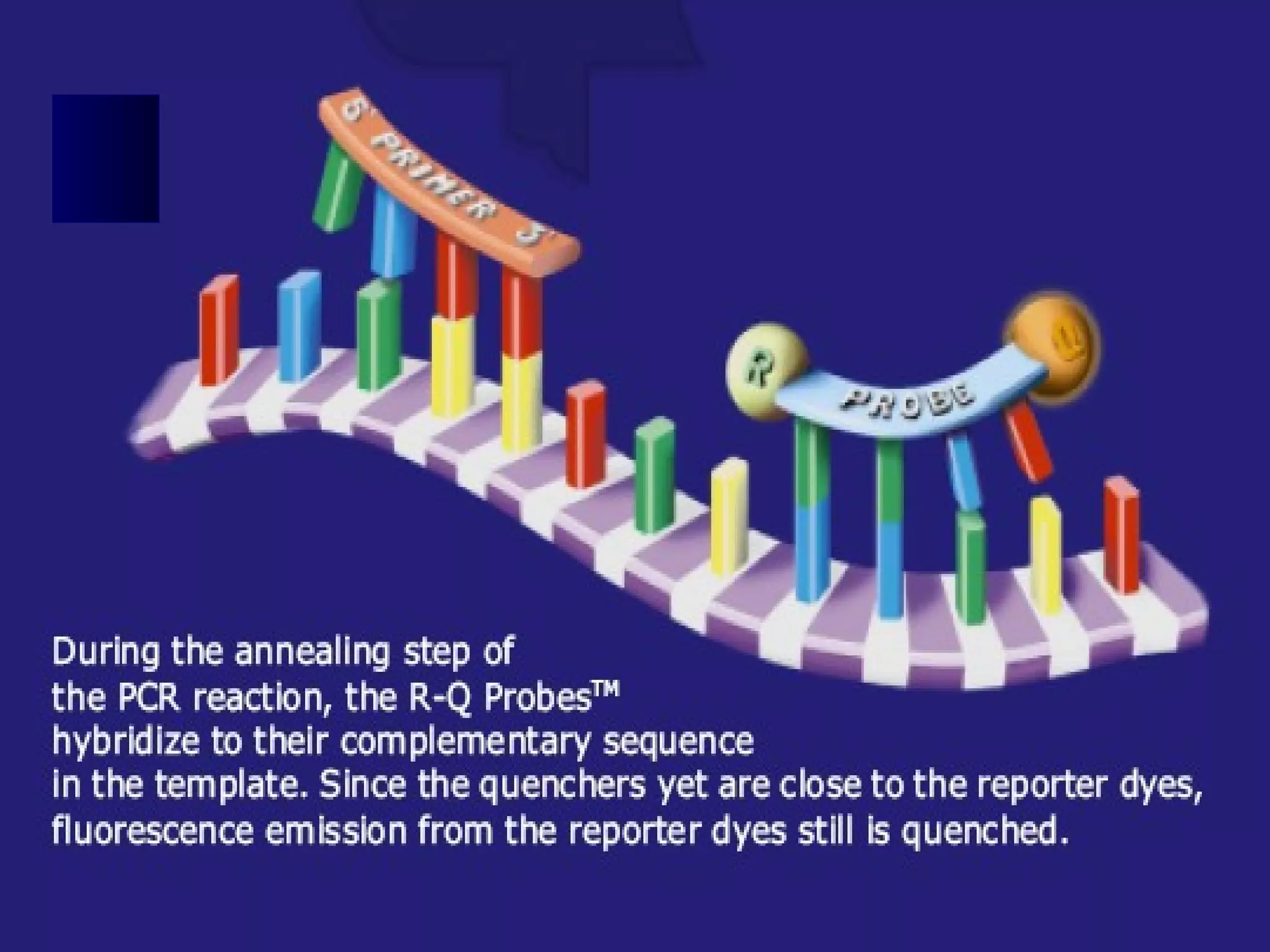
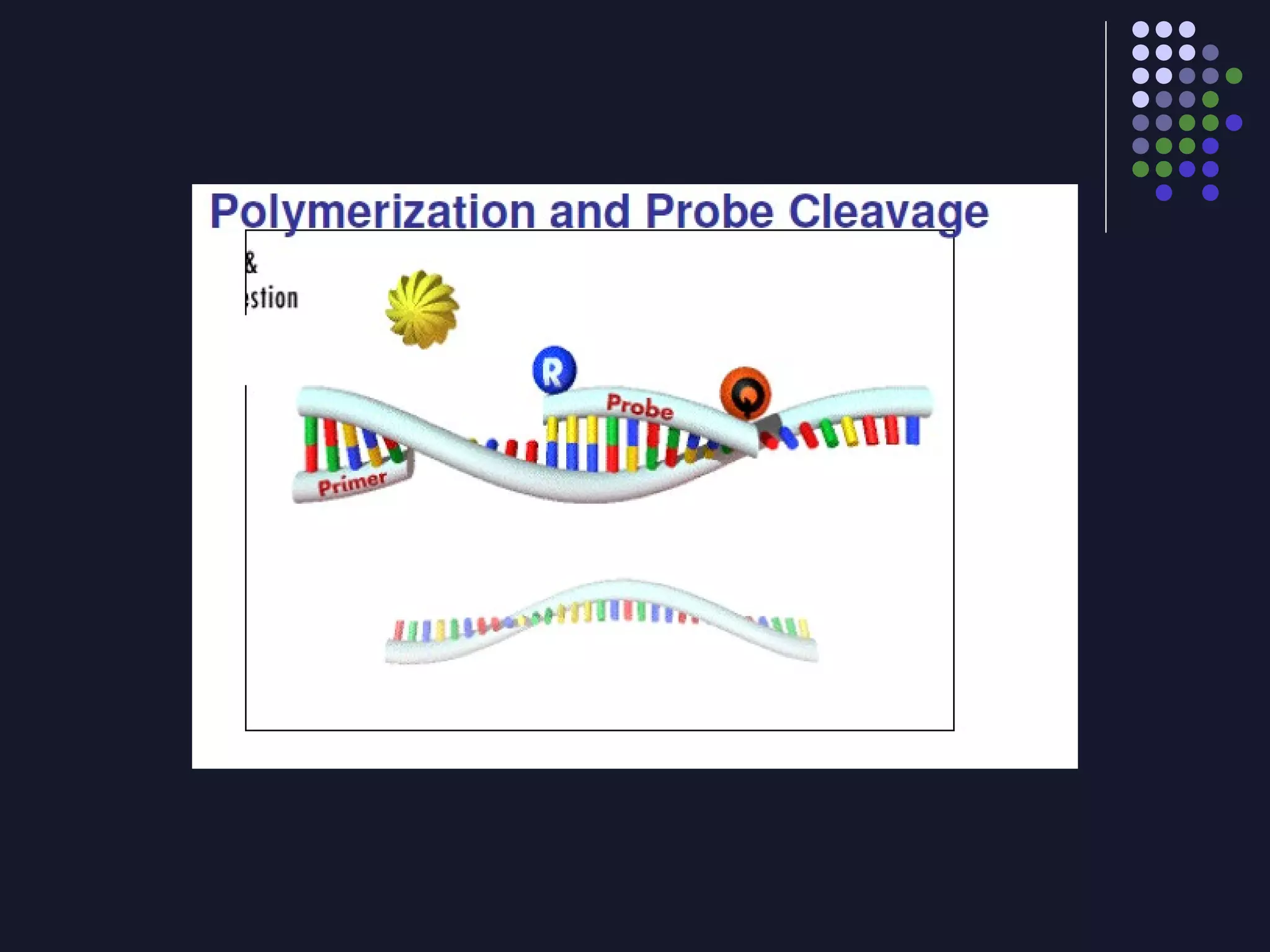
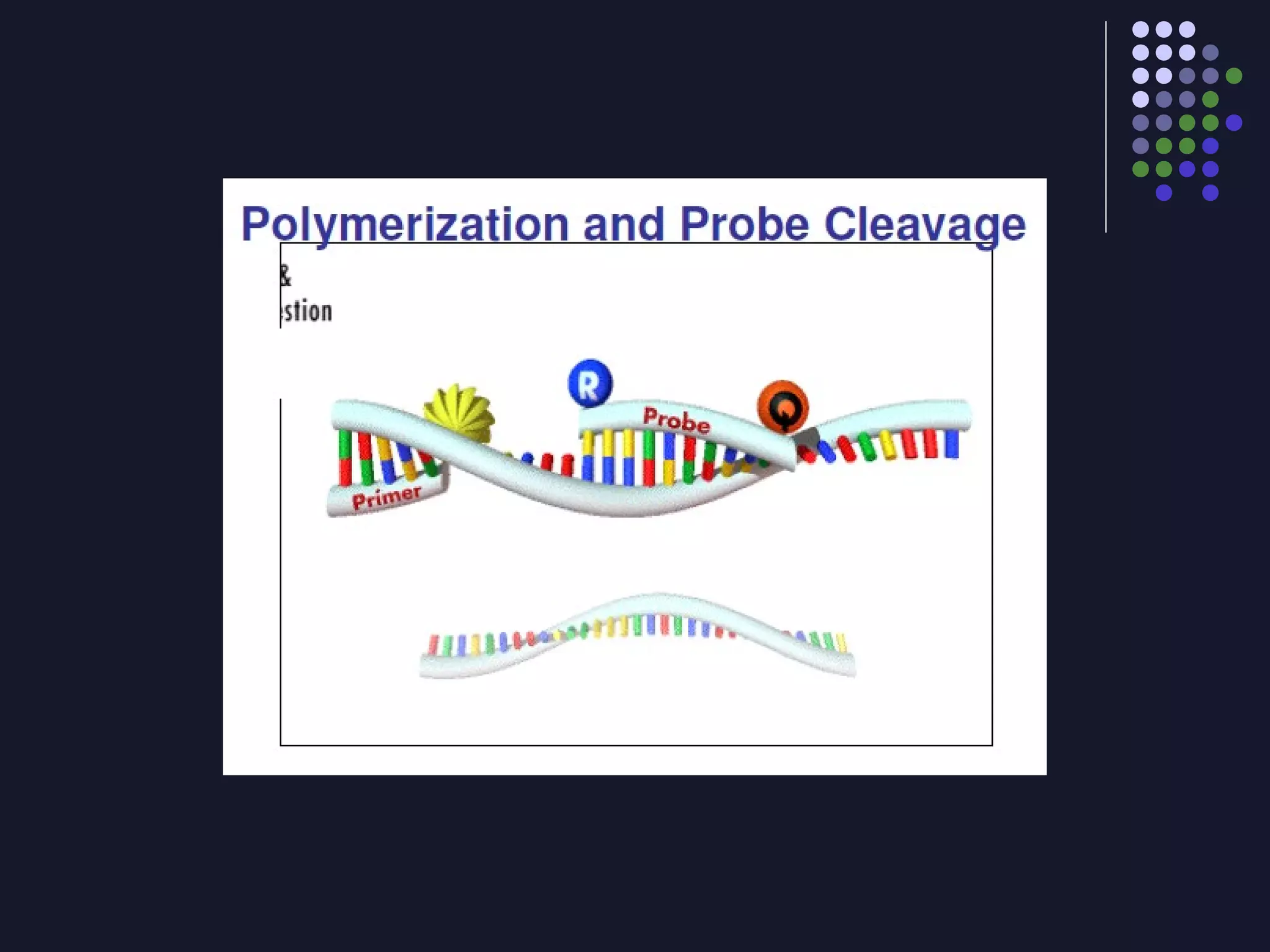
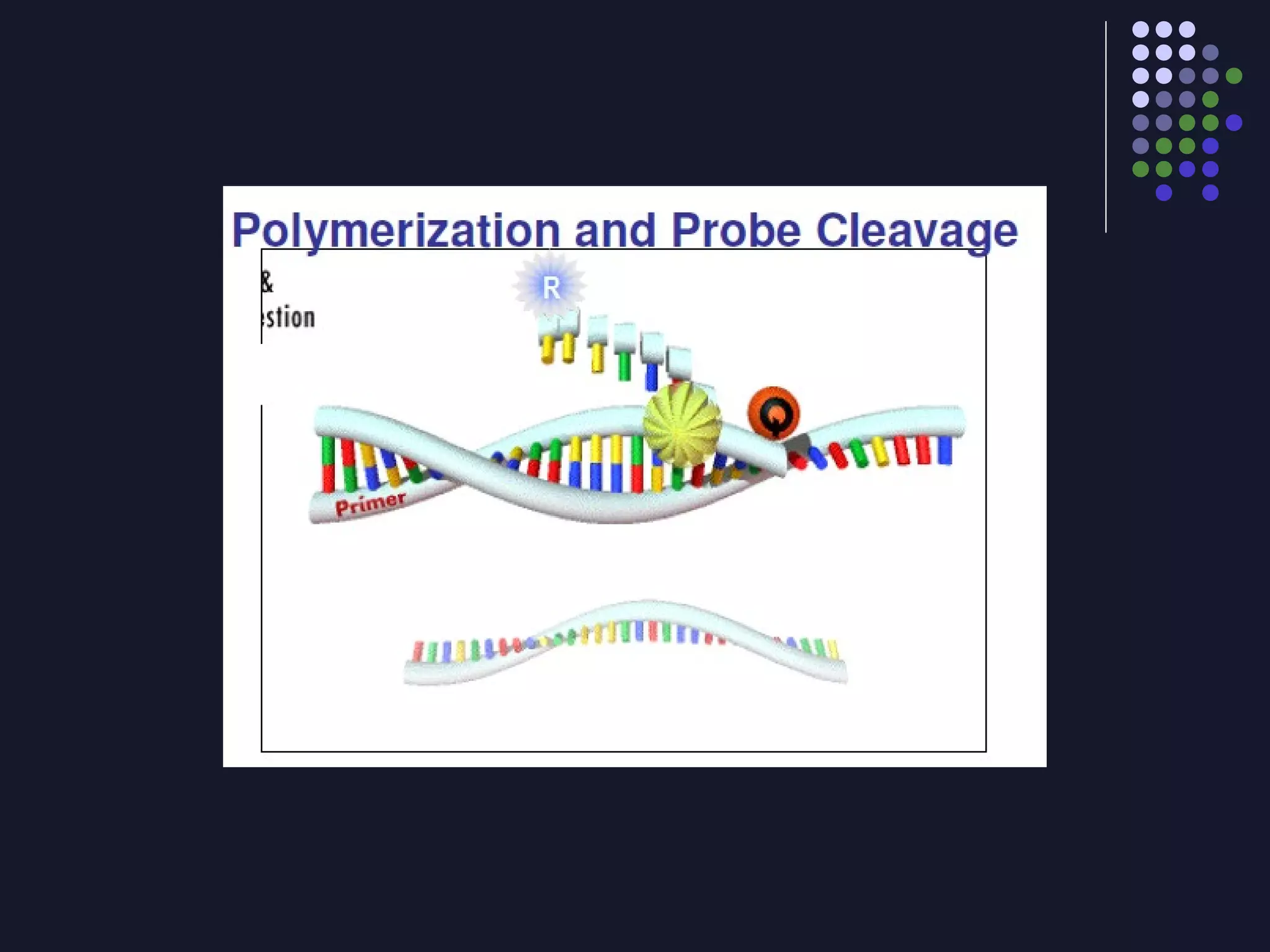
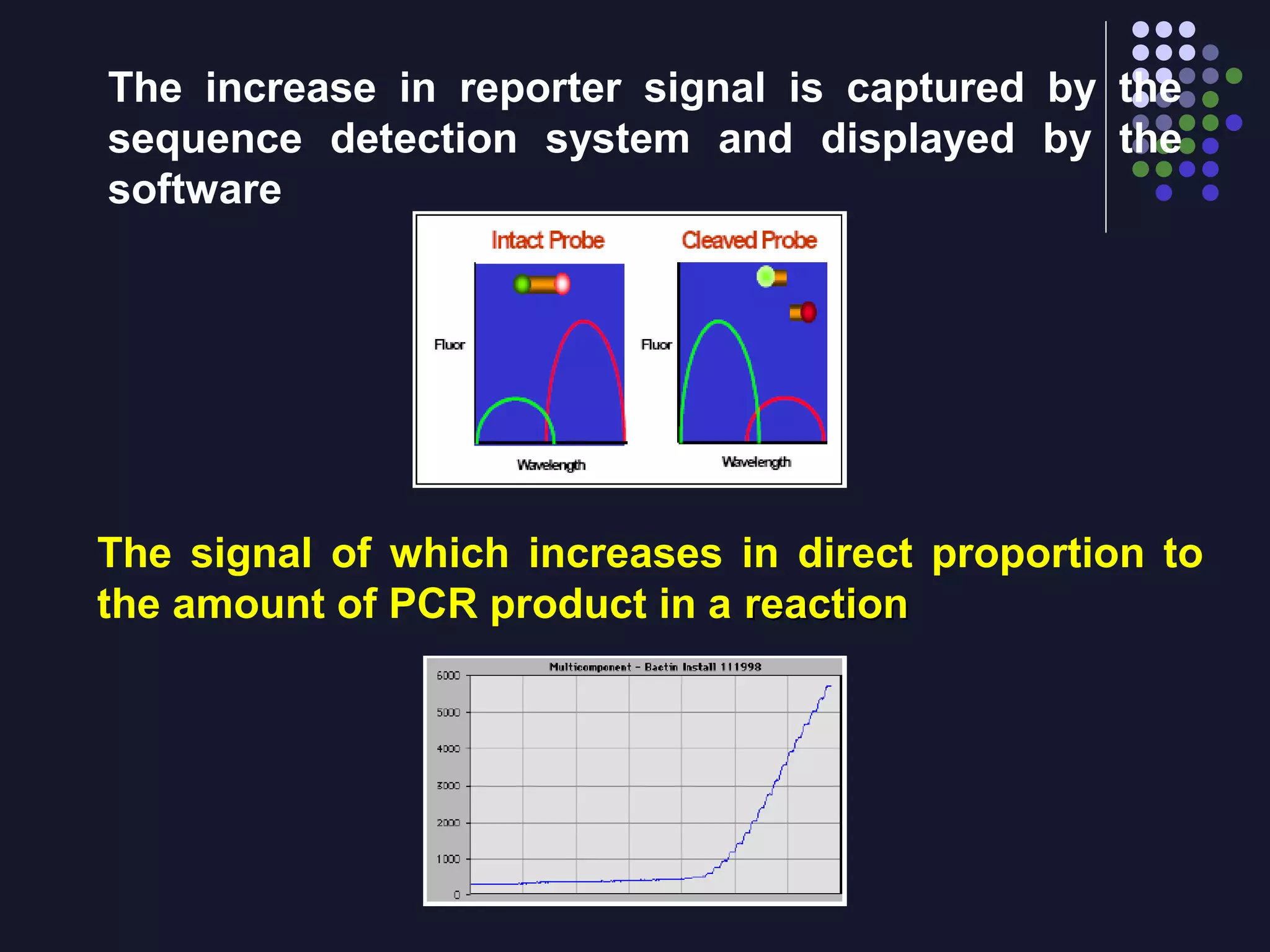
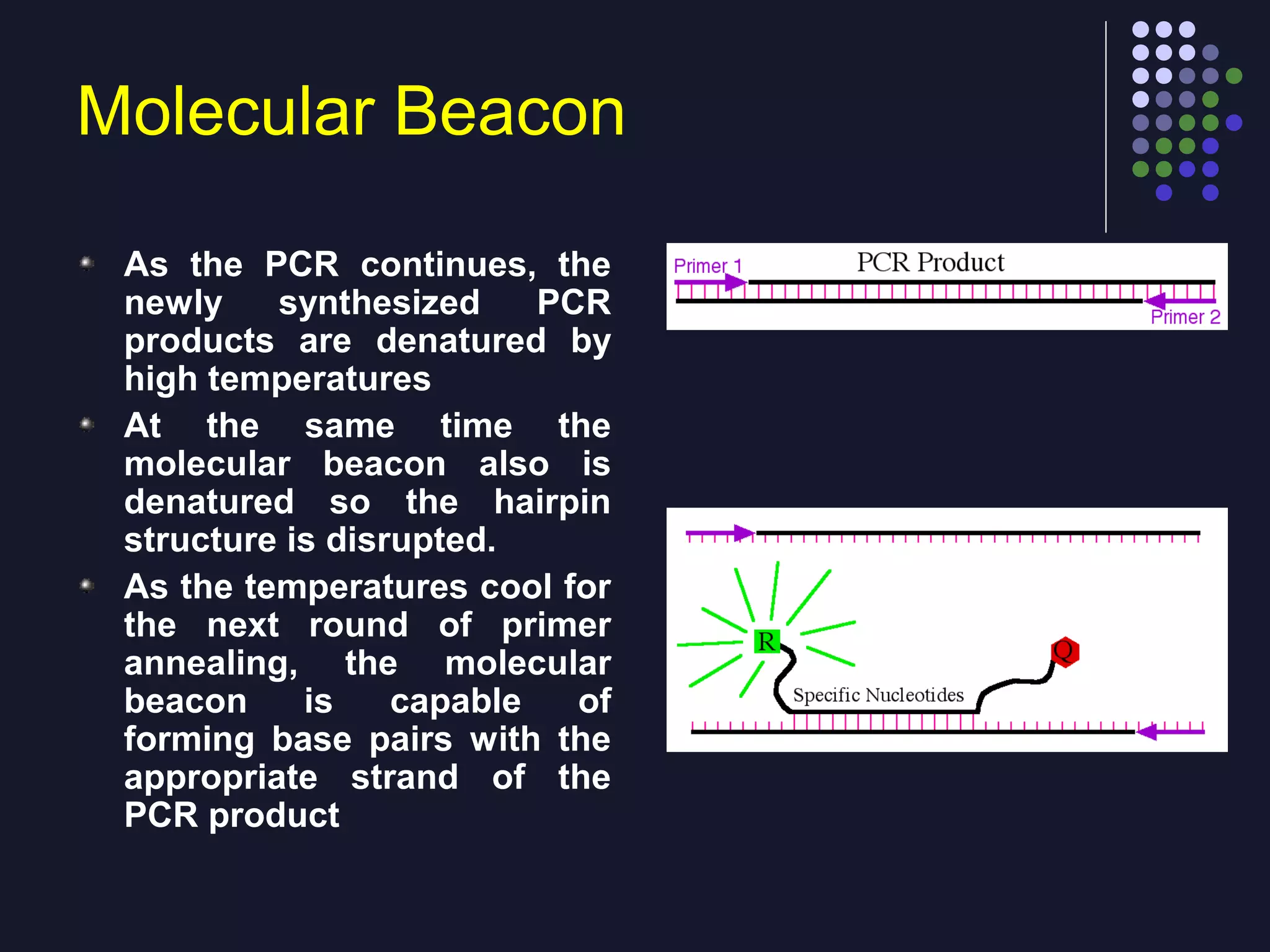
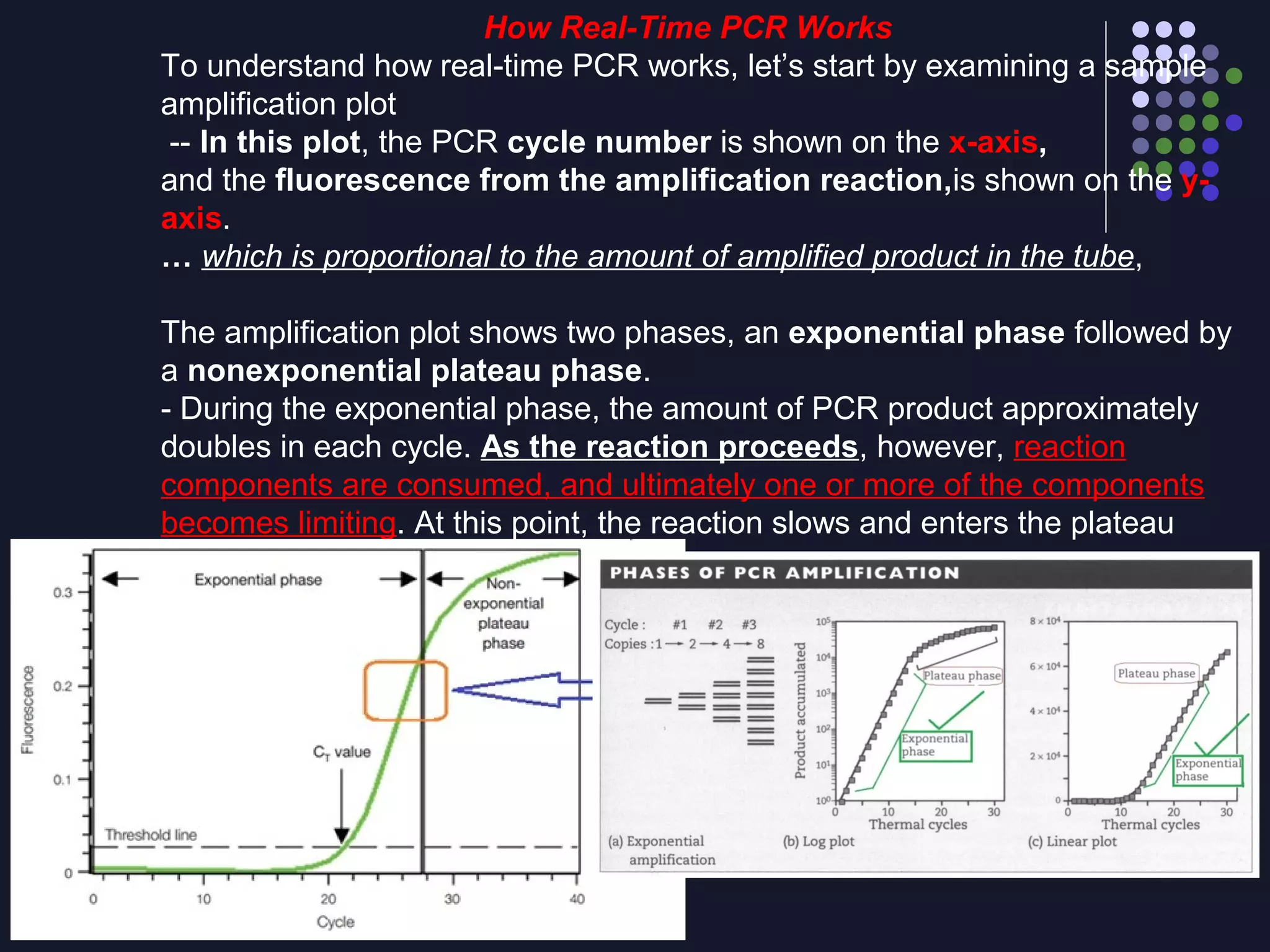
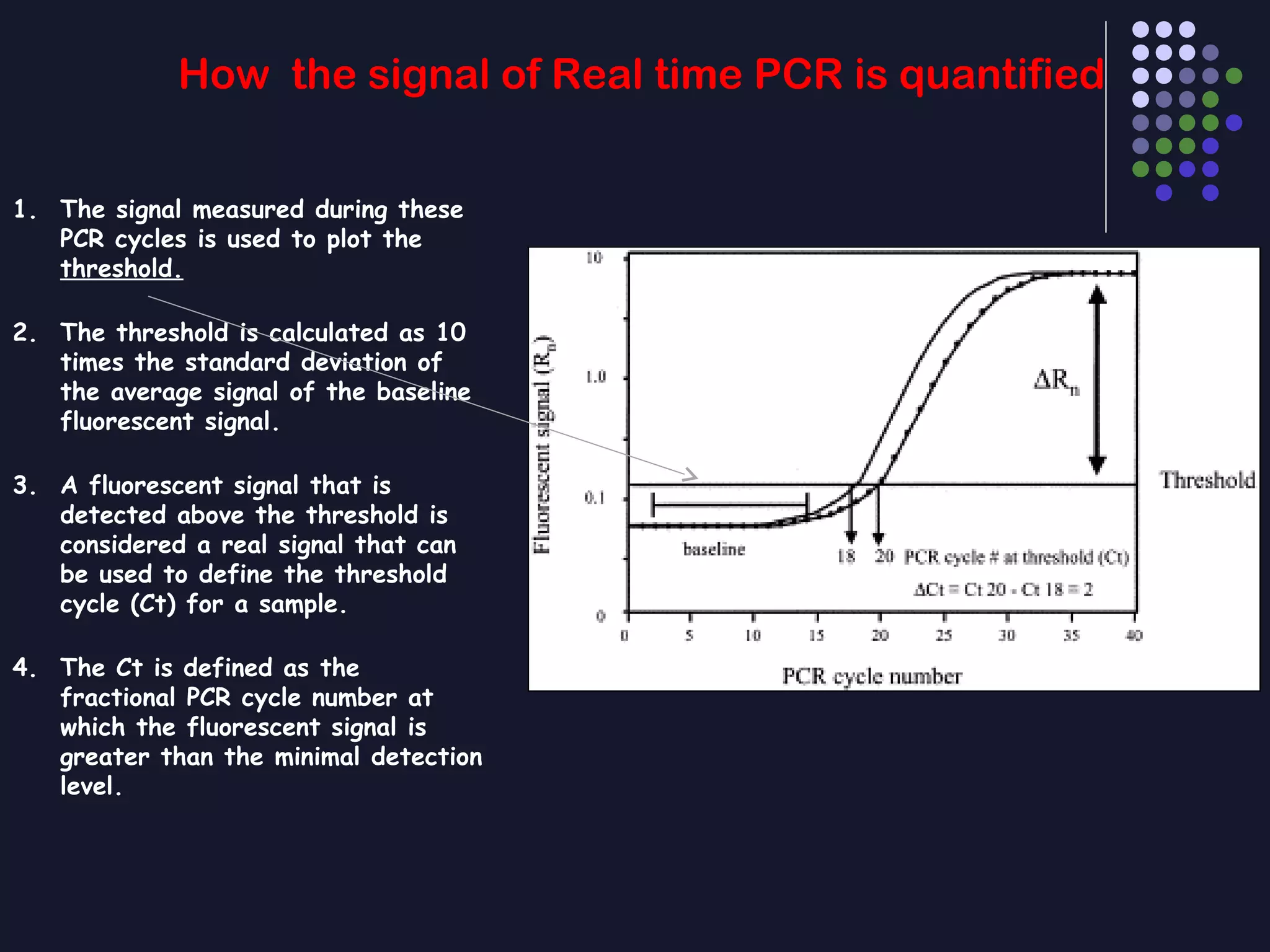
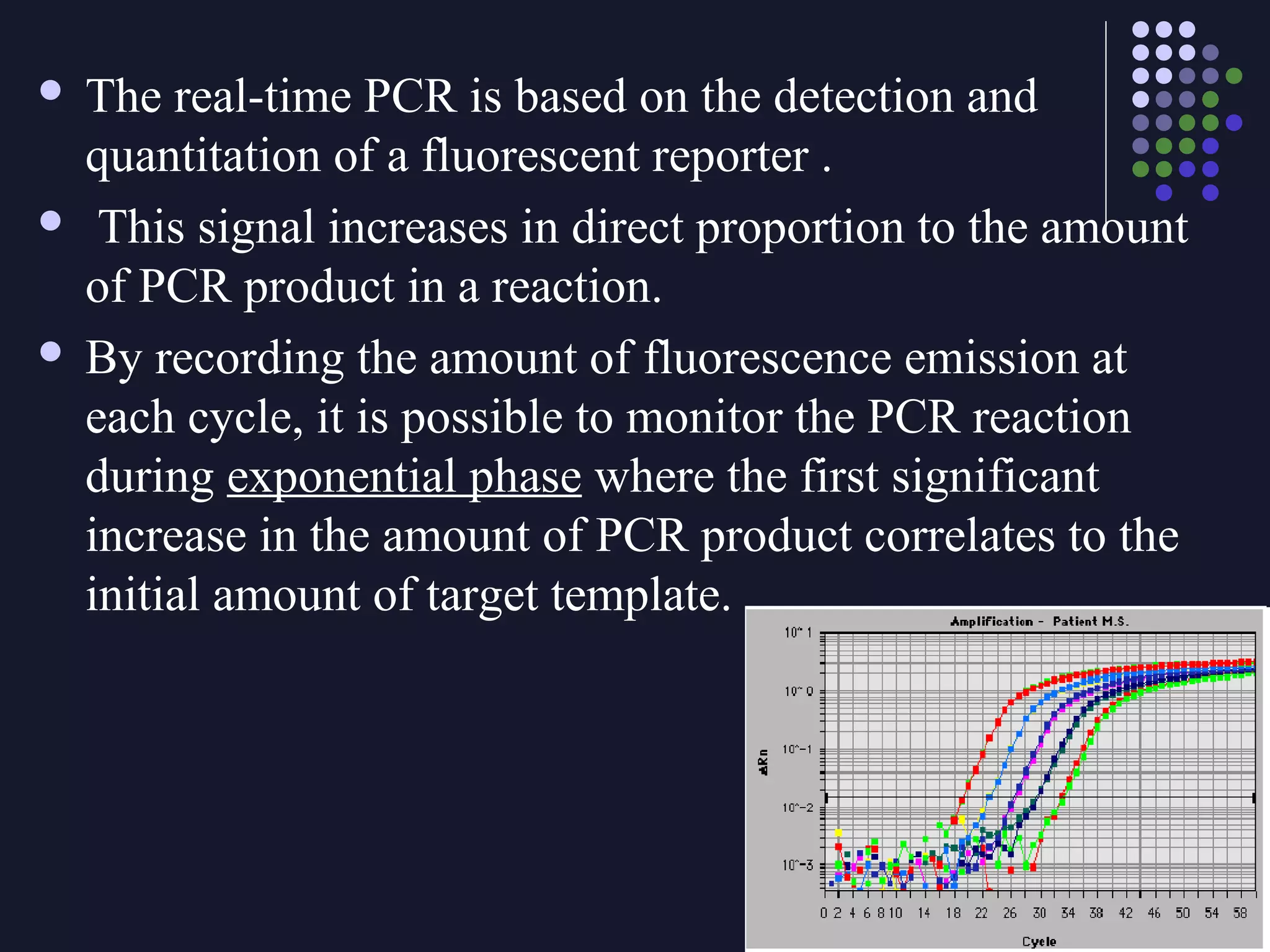
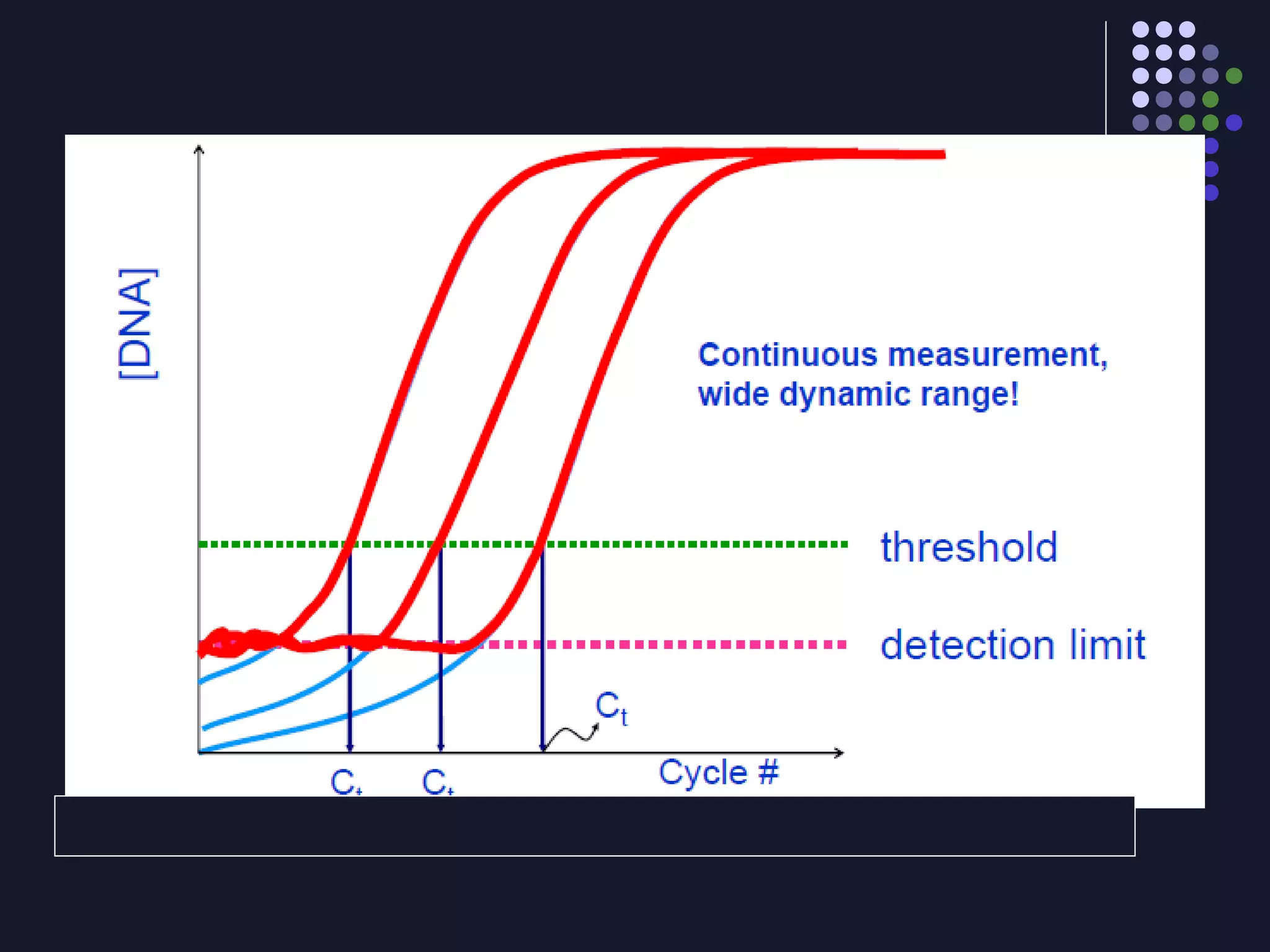
Real-time PCR allows for the continuous collection of fluorescent data during the PCR process, allowing for quantification of the amount of PCR product accumulated in each cycle. It provides advantages over conventional PCR such as increased precision, sensitivity, and automation. Various chemistries can be used including SYBR Green, TaqMan probes, molecular beacons, and scorpion primers, which rely on fluorescent dyes and quenchers. Real-time PCR finds applications in gene expression analysis, pathogen detection, and DNA damage measurement by allowing quantitative analysis.