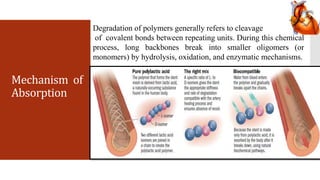
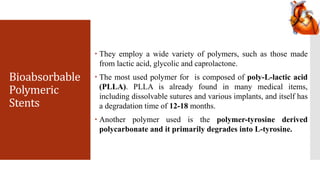
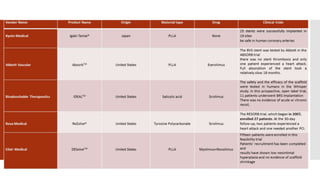
Bioabsorbable stents are manufactured from materials that dissolve in the body over time. They serve the same purpose as traditional metal stents by expanding a blocked blood vessel, but eventually degrade so the vessel is freed from the scaffold. Polymer-based materials like PLLA and absorbable metals such as magnesium alloys are being tested. Bioabsorbable stents could overcome limitations of permanent metal stents by eliminating risk of late thrombosis and local inflammation once dissolved. Several types are currently in clinical trials and projected to gain significant market share as they receive FDA approval.