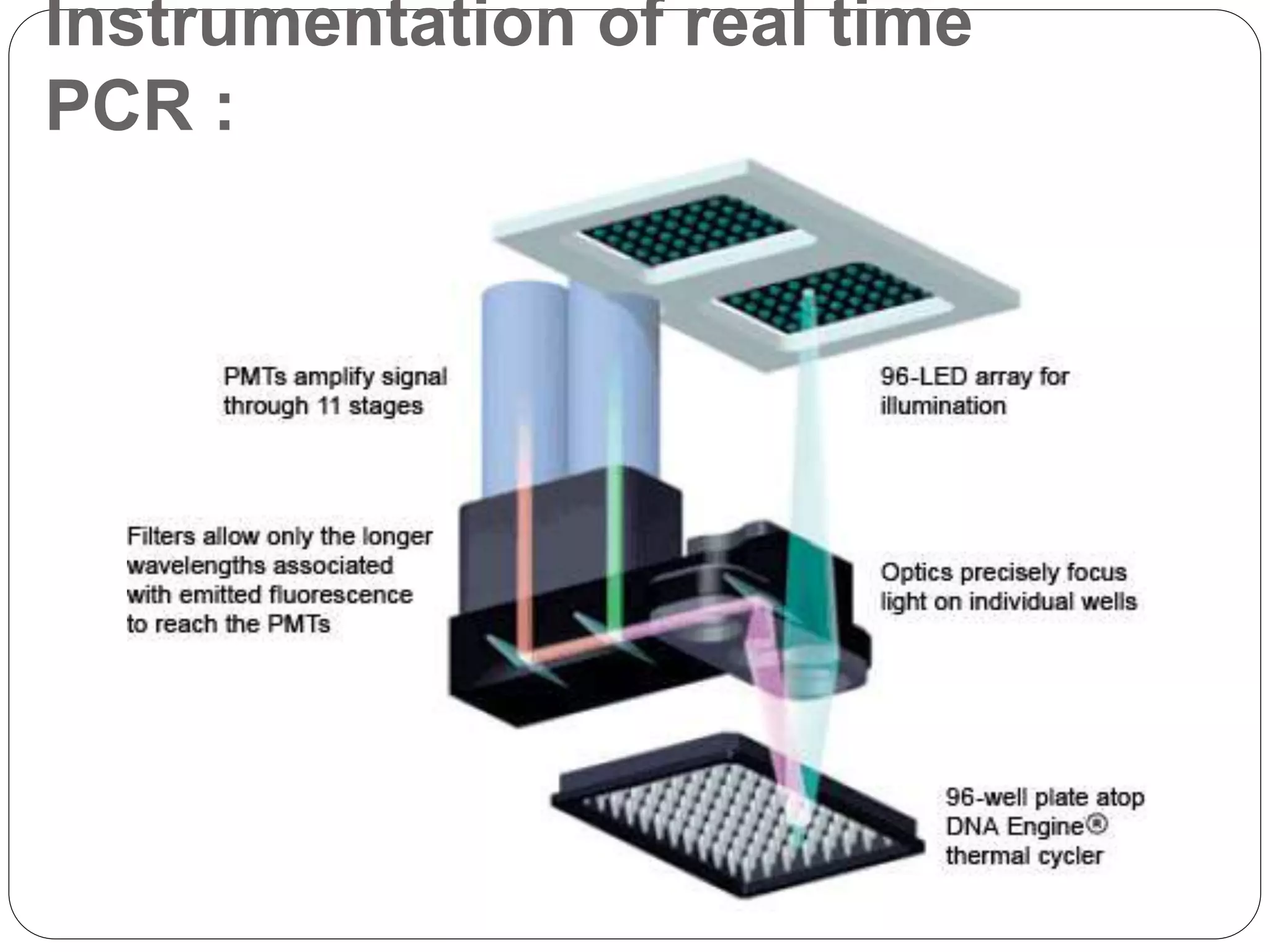
Real time PCR allows for monitoring of DNA amplification during polymerase chain reaction (PCR), rather than just at the end. There are two main detection methods: using non-specific fluorescent dyes that bind to double stranded DNA, and using sequence-specific fluorescent probes. Common non-specific dyes include SYBR Green I, while TaqMan probes are an example of sequence-specific probes that use fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Real time PCR has applications in disease diagnosis, microbiology research on food and water safety, and quantifying gene expression levels.