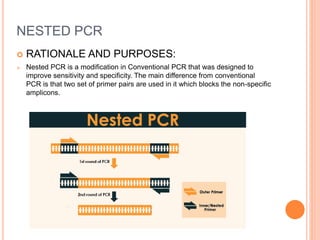
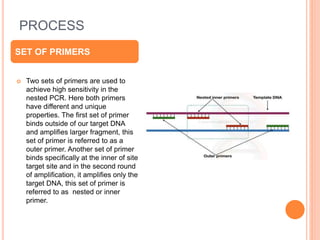
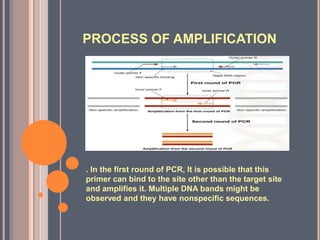
Nested PCR is a modification of conventional PCR that uses two sets of primers to improve sensitivity and specificity. It involves two rounds of amplification, where the first round uses outer primers that bind outside the target DNA to amplify a larger fragment. The second round uses inner primers that bind within the first amplified fragment to specifically amplify the target DNA. This blocks non-specific amplification. Nested PCR allows for the accurate detection of pathogens or genes present at low levels. While more sensitive and specific than conventional PCR, it is also more time-consuming and prone to contamination due to the use of two primer sets.