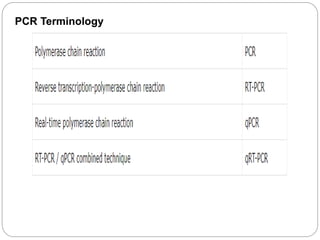
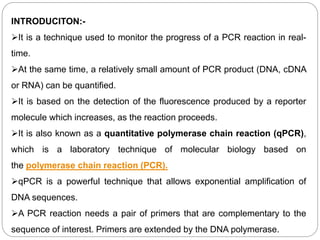
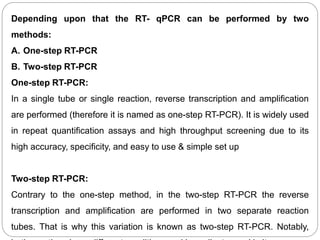
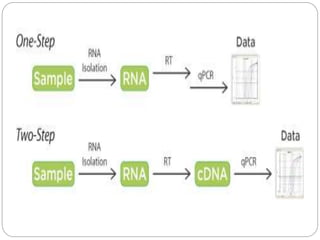
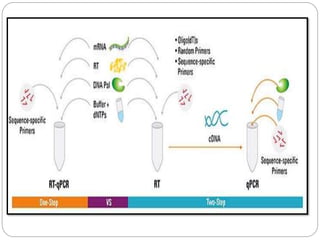
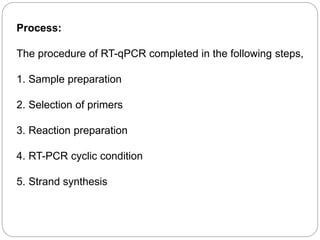
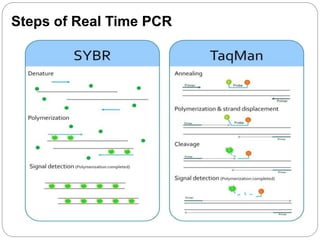
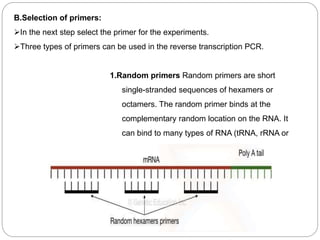
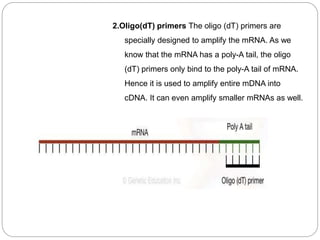
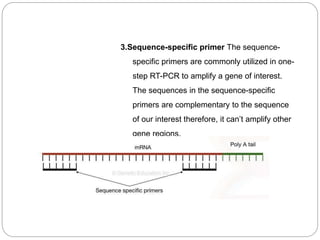
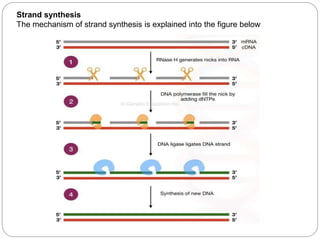
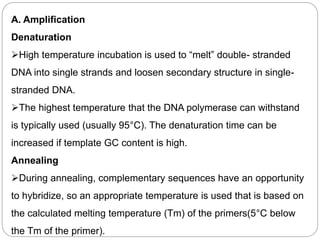
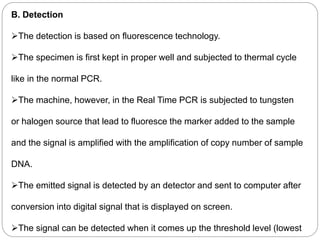
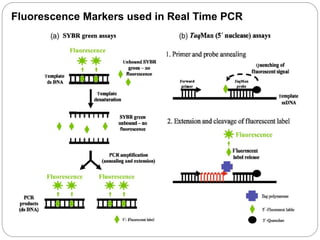
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is used to quantify RNA levels in a sample. It involves first synthesizing cDNA from RNA using reverse transcriptase. Real-time PCR then monitors the amplification of this cDNA in real-time using fluorescence, allowing for both amplification and quantification. It has several advantages over traditional PCR, including being faster and allowing for truly quantitative analysis of gene expression levels. The process involves reverse transcribing RNA to cDNA, then amplifying and detecting this cDNA using fluorescence across multiple temperature cycles.