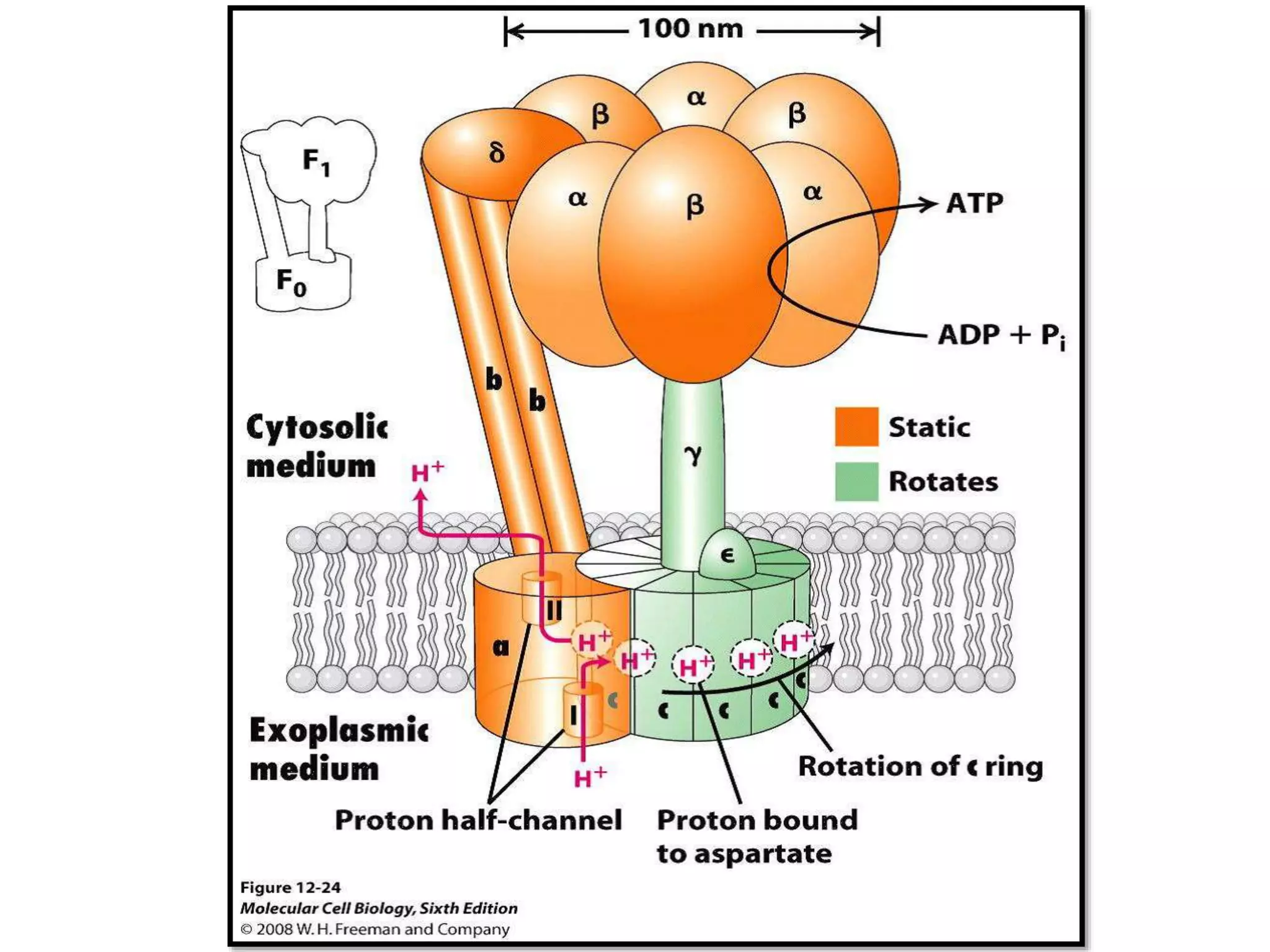
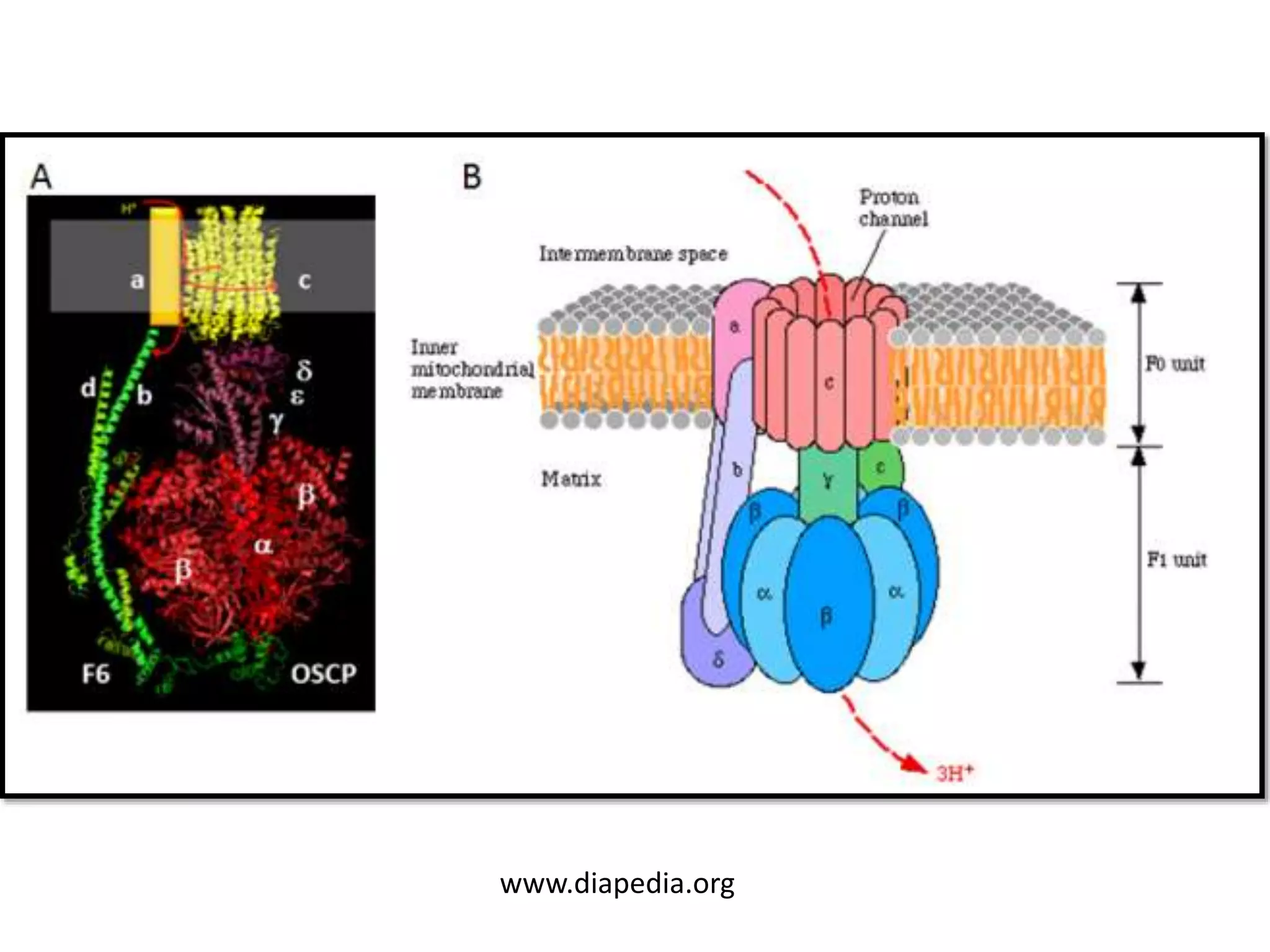
ATP synthase is a crucial enzyme in cellular metabolism that synthesizes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate, utilizing energy from an electrochemical gradient. Composed of eight subunit types, its structure includes a soluble F1 portion and a membrane-embedded FO portion, with proton movement driving ATP production. This process highlights the role of ATP as the primary energy currency in all living organisms.