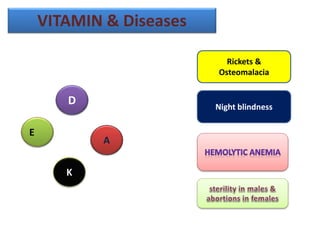
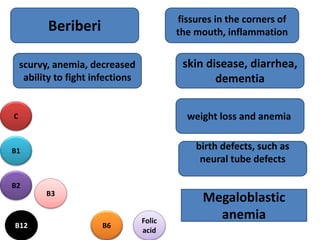
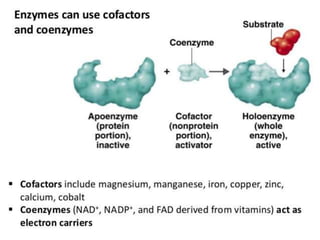
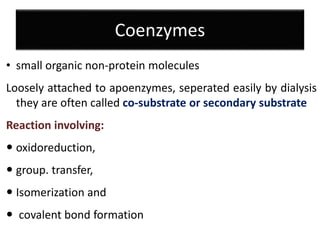
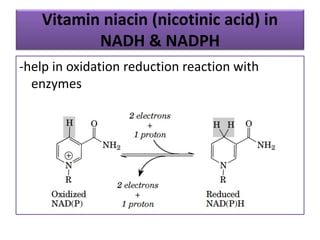
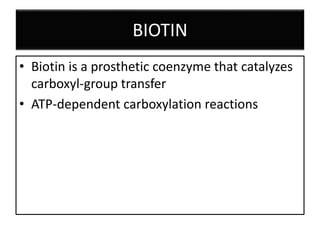
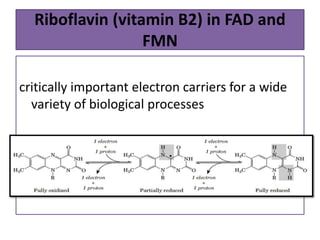
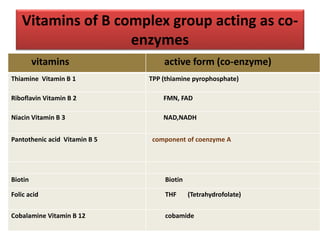
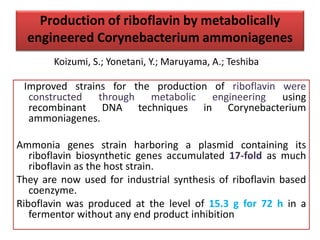
Vitamins are essential organic compounds required in small quantities for life and primarily obtained from food due to the body's limited ability to produce them. They function as coenzymes in various biochemical processes and their deficiencies can lead to specific diseases, such as rickets and scurvy. Additionally, advances in metabolic engineering have enabled the production of riboflavin, a key coenzyme, at industrial scales using genetically modified bacteria.