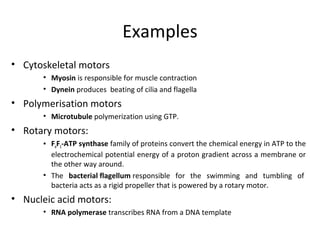
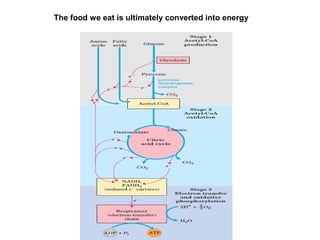
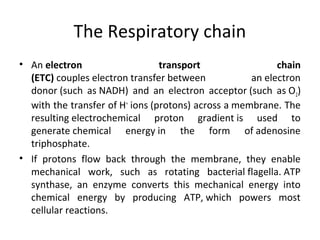
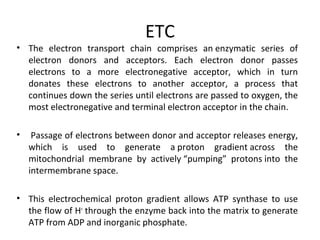
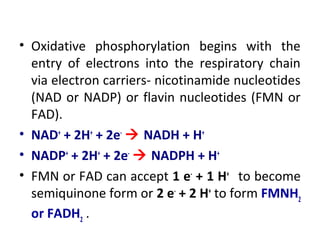
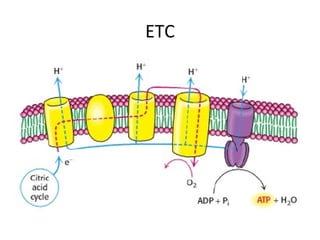
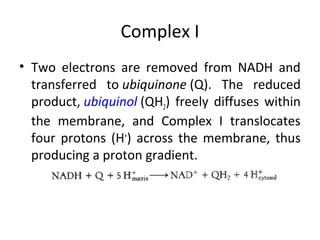
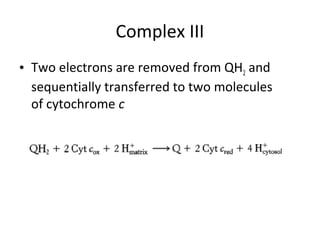
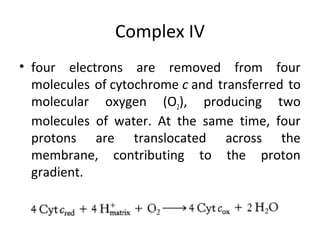
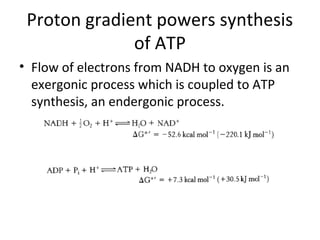
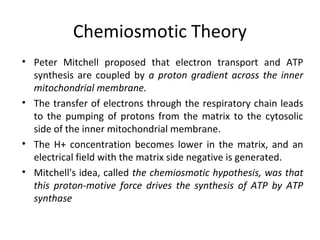
- Mechanochemistry involves the coupling of mechanical and chemical phenomena on a molecular scale. Molecular motors harness chemical energy, like from ATP hydrolysis, to perform mechanical work.
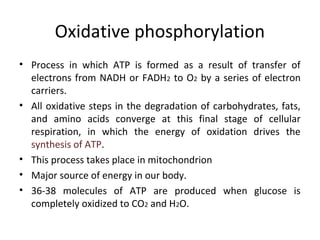
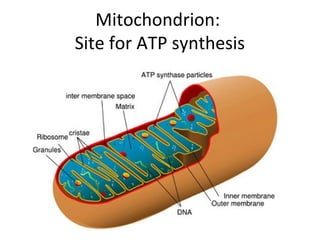
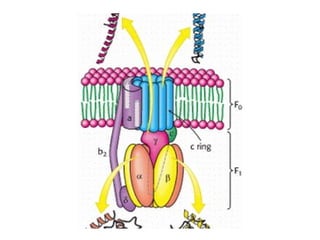
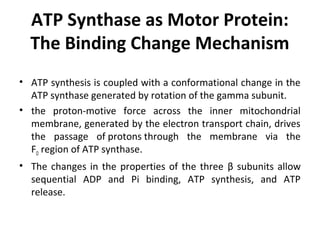
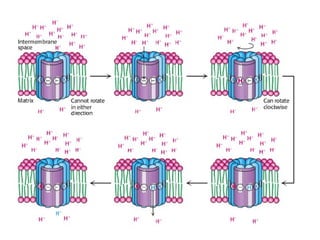
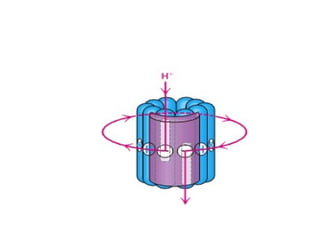
- ATP synthase is a molecular motor that uses the proton gradient generated by oxidative phosphorylation to drive the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. It rotates at around 6,000 revolutions per minute.
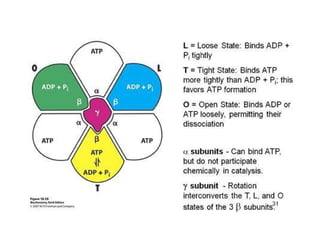
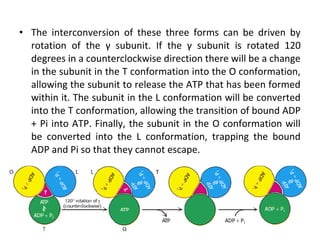
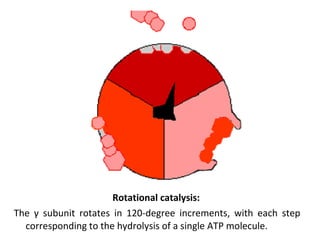
- The flow of protons through ATP synthase causes the gamma subunit to rotate, triggering conformational changes in the three beta subunits that allow for sequential binding of substrates and production of ATP.