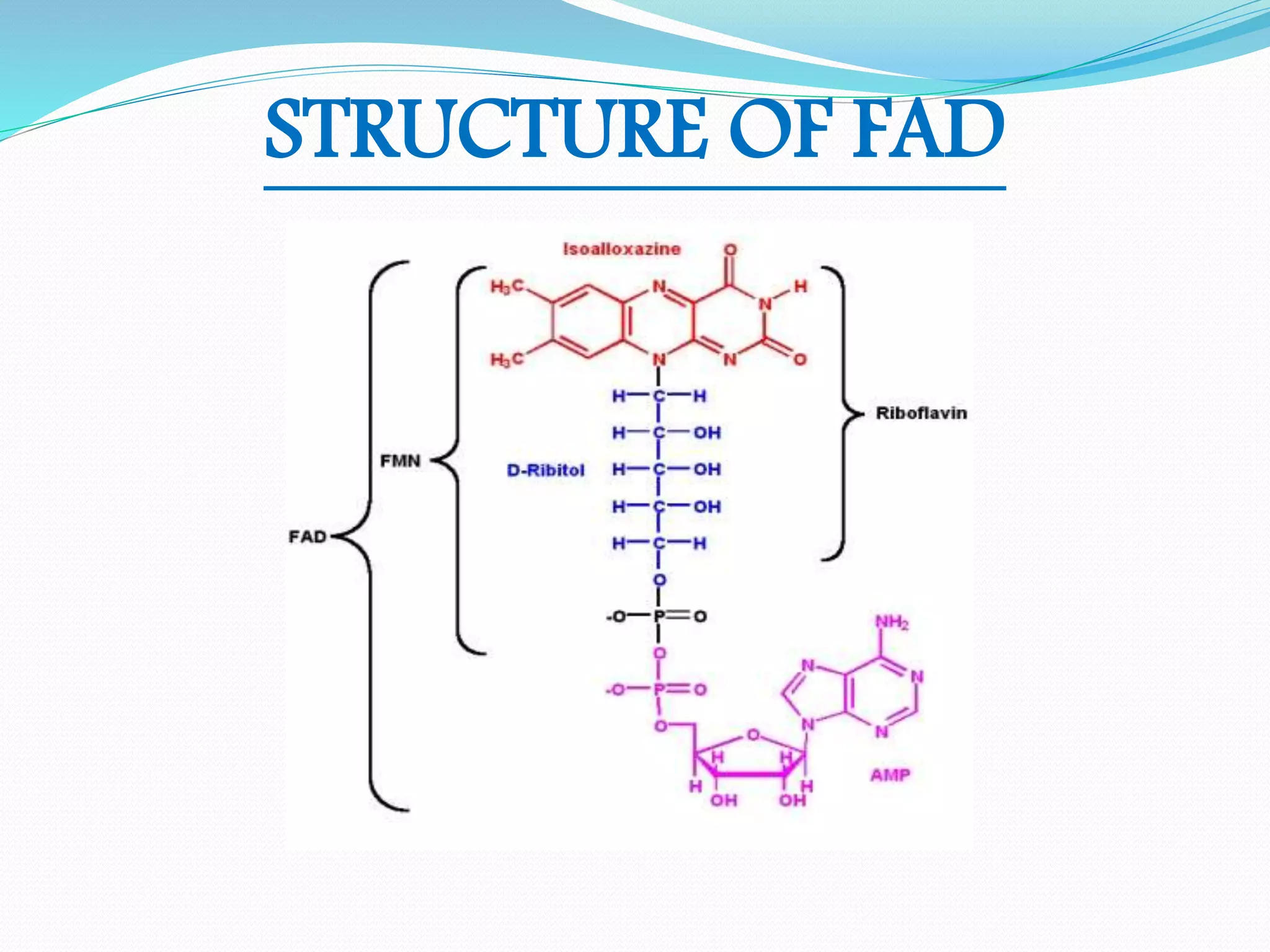
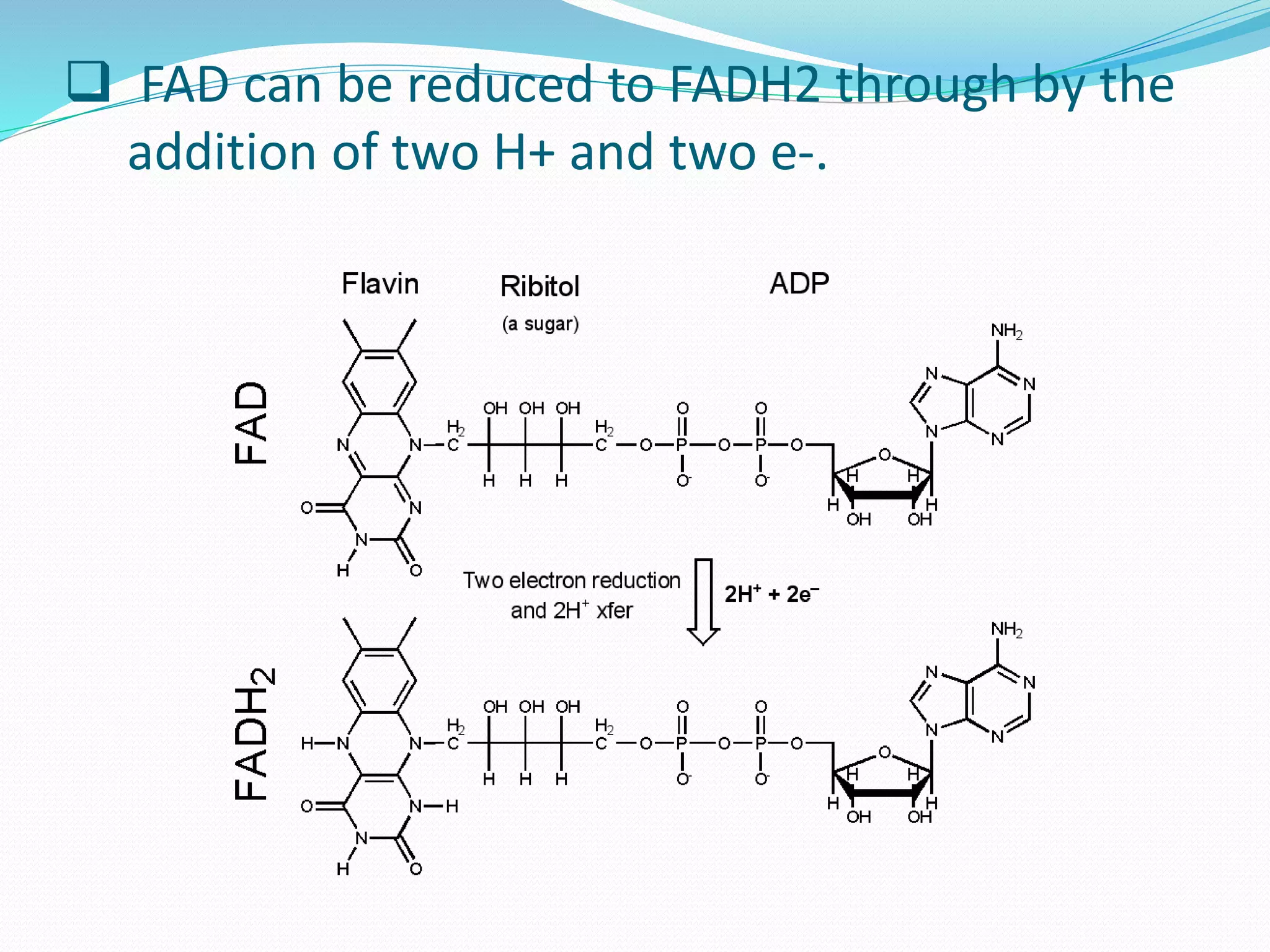
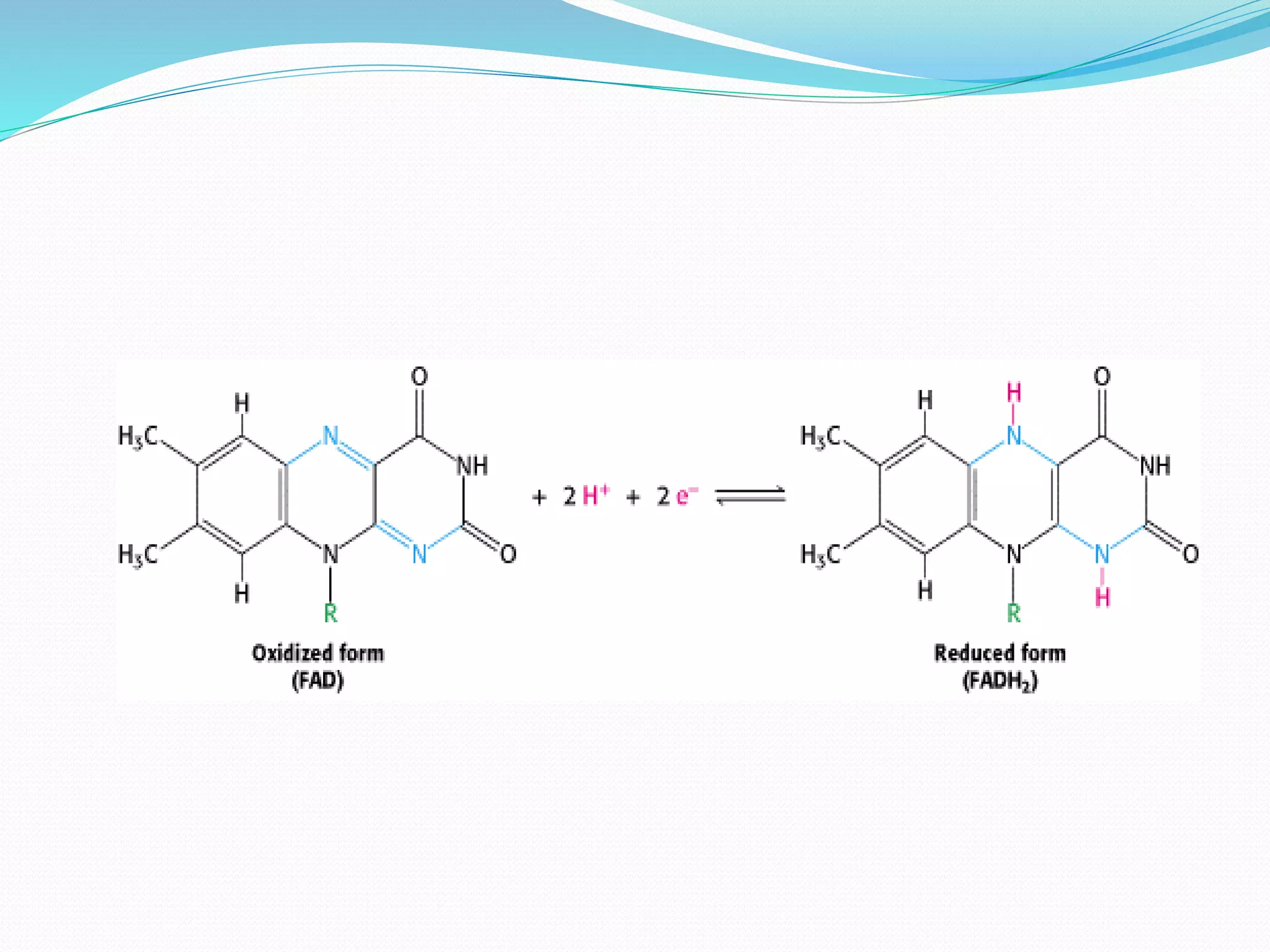
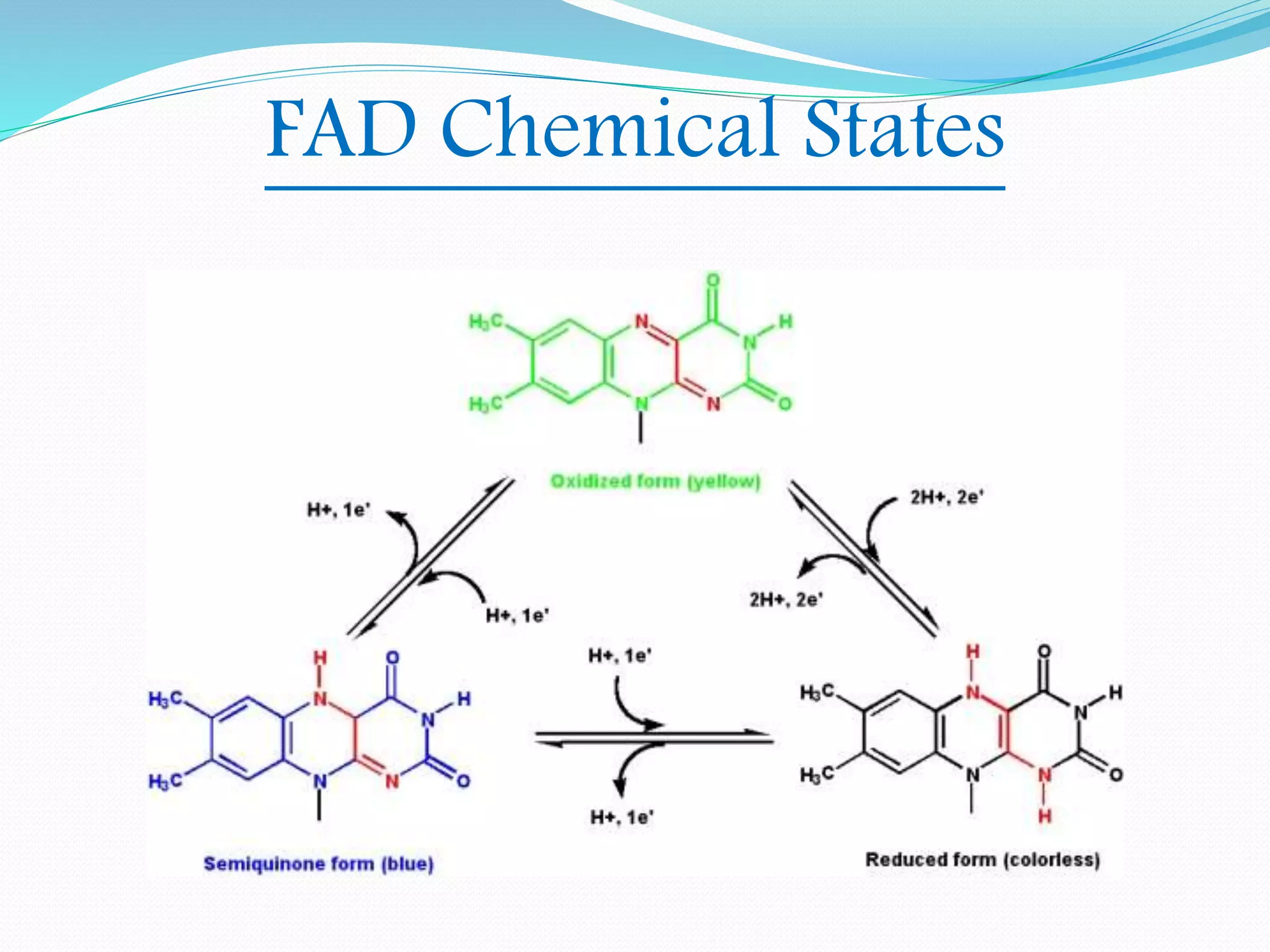
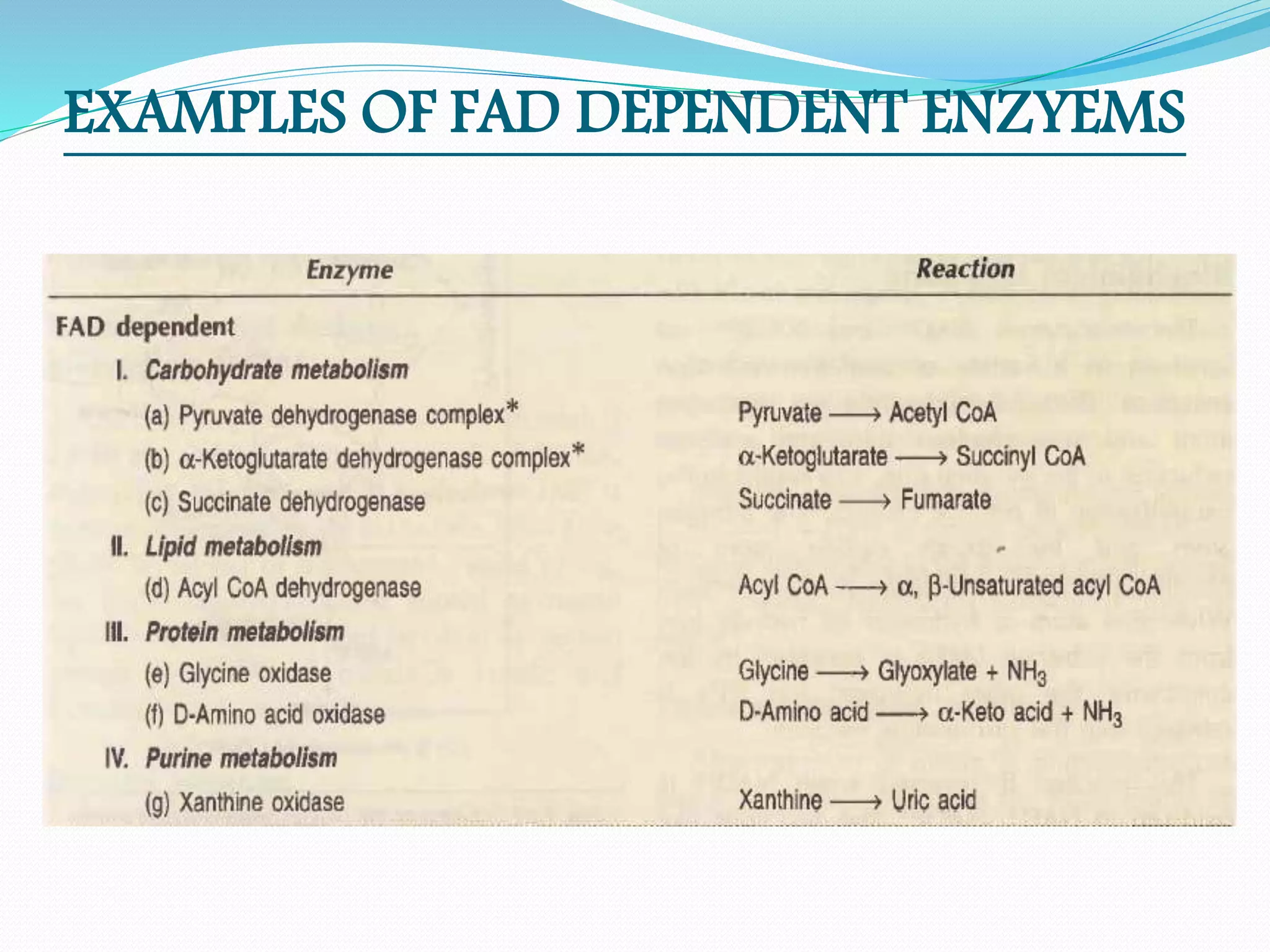
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a coenzyme derived from riboflavin (vitamin B2) that plays a critical role in oxidation and reduction reactions, existing in three redox states: oxidized, half-reduced, and fully reduced. FAD is biosynthesized from riboflavin through two key enzymatic steps and functions as a crucial cofactor in various metabolic pathways, including ATP production and amino acid catabolism. Humans must obtain riboflavin through diet, as they can no longer synthesize it, unlike certain bacteria, fungi, and plants.