Embed presentation
Downloaded 427 times







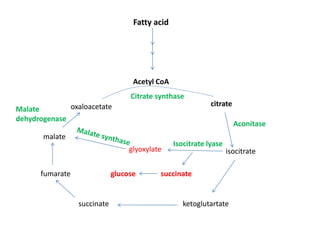
The glyoxylate cycle is a metabolic pathway in plants and microorganisms that converts fats into carbohydrates, as animals cannot synthesize carbohydrates from fats. This cycle occurs in glyoxysomes, where acetyl CoA from fatty acid oxidation combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then transformed through a series of reactions that ultimately produce glucose. It serves as an anabolic variant of the citric acid cycle, allowing organisms to convert two-carbon fragments into four-carbon compounds.







