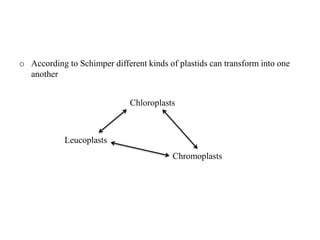
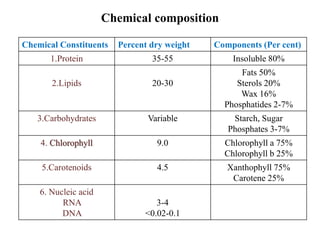
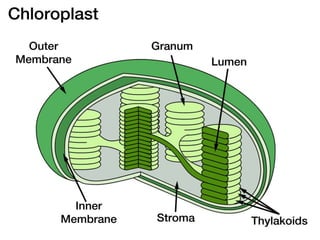
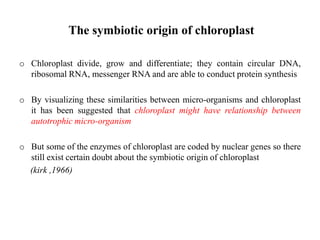
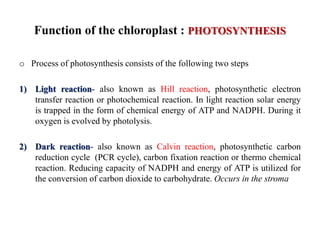
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and algae that conduct photosynthesis. They have their own DNA and can synthesize some of their own proteins, making them semi-autonomous. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and carotenoids which capture light energy. Their internal structure includes an envelope, stroma, and thylakoids where the light reactions take place. It is believed that chloroplasts originated through endosymbiosis between cyanobacteria and eukaryotic cells. The two main stages of photosynthesis are the light reactions on the thylakoid membranes which produce ATP and NADPH, and the dark reactions in the stroma that use these products to fix carbon into sugars.