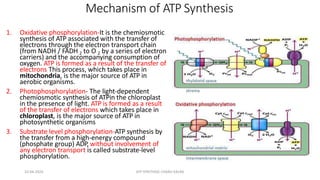
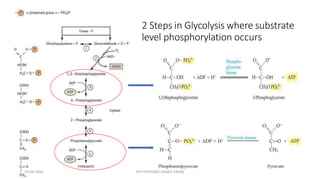
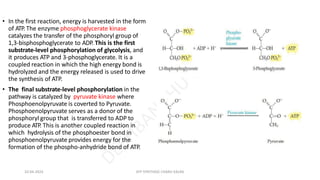
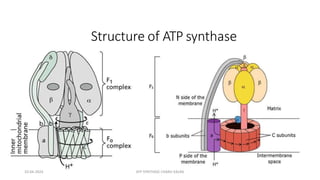
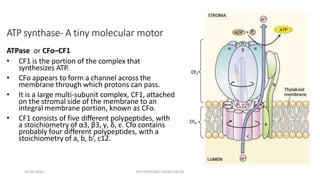
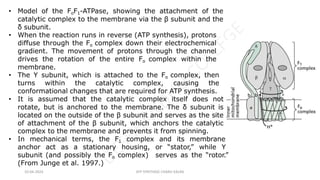
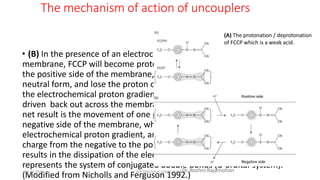
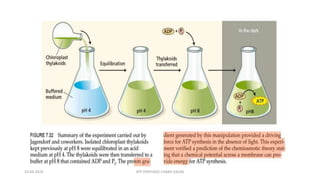
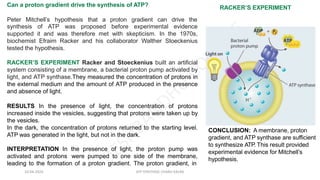
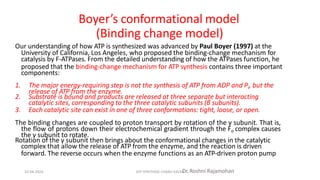
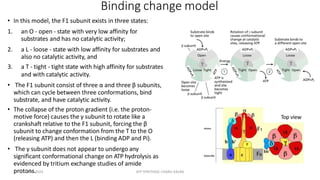
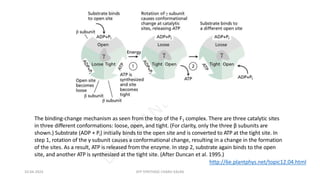
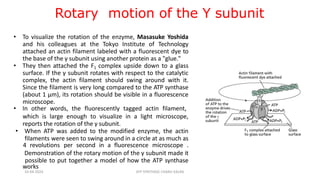
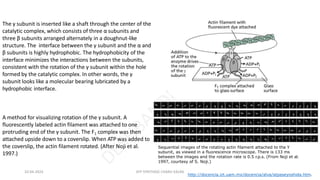
The document discusses three mechanisms of ATP synthesis: substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation, and photophosphorylation. It describes ATP synthase, the enzyme complex responsible for synthesizing ATP during oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation. ATP synthase consists of two parts, CF1 which protrudes into the mitochondrial matrix and synthesizes ATP, and CFo which forms a channel in the membrane through which protons pass. Uncouplers disrupt phosphorylation by allowing protons to pass through the membrane via the uncoupler rather than the ATP synthase, dissipating the proton gradient without generating ATP.