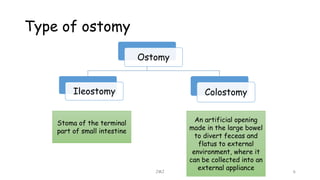
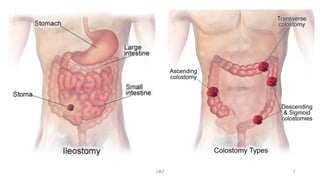
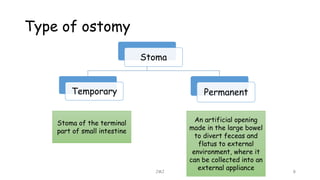
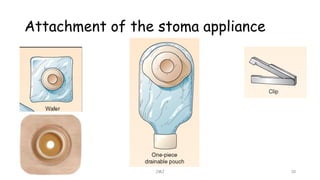
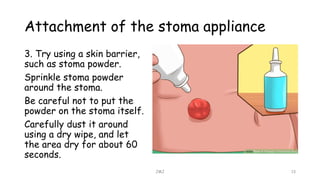
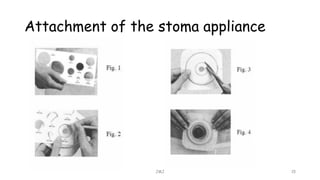
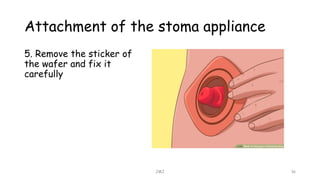
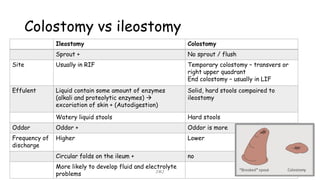
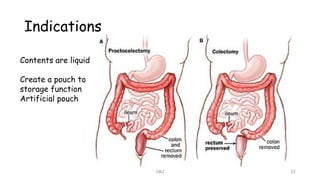
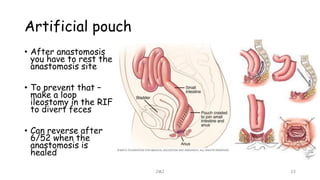
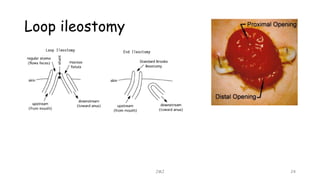
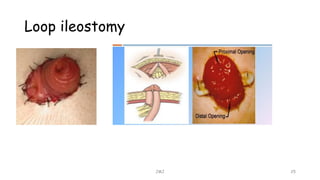
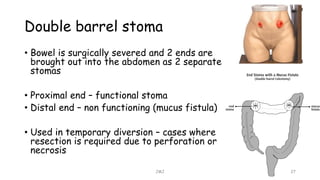
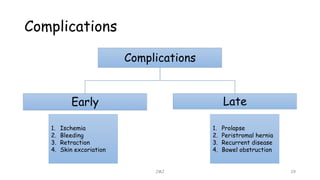
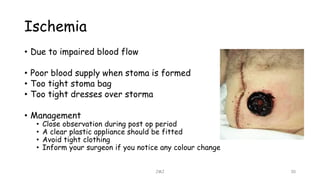
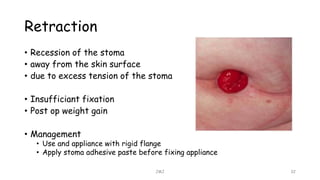
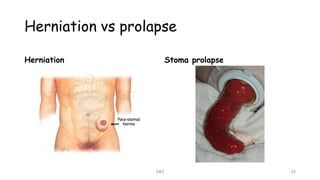
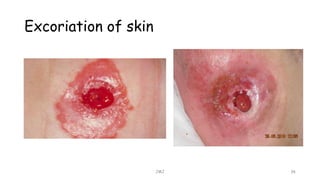
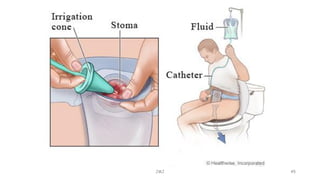
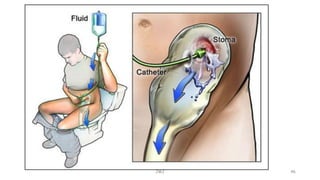
An ostomy is a surgically created opening in the intestine that allows for waste to exit the body into an external bag. There are two main types - an ileostomy, which is created from the small intestine, and a colostomy, which is created from the large intestine. An ostomy may be temporary or permanent and is usually required due to conditions like cancer, IBD, or injury. Attaching the external bag securely is important to prevent complications. Diet and lifestyle adjustments are also needed after an ostomy is created.