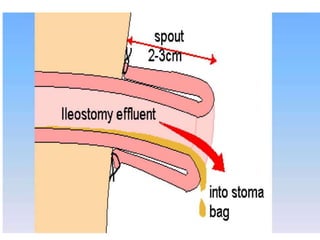
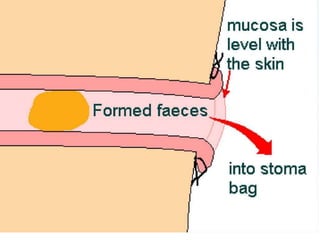
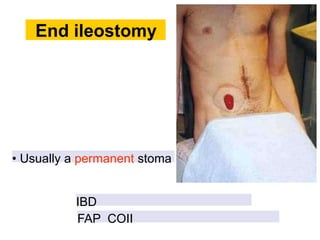
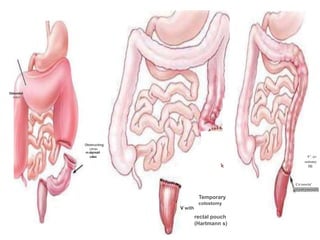
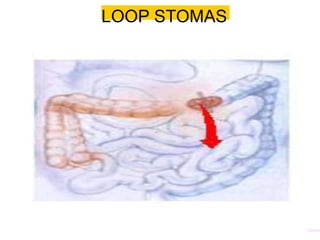
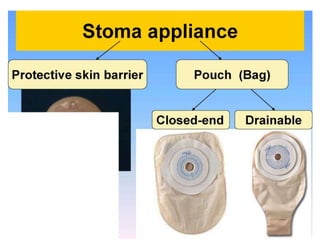
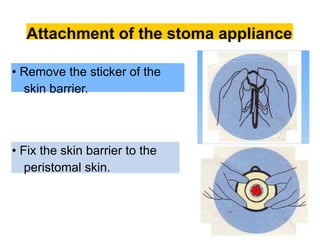
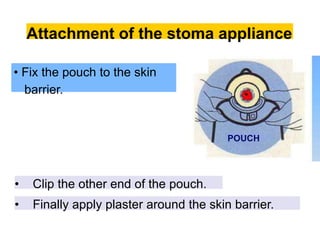
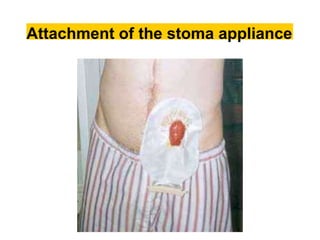
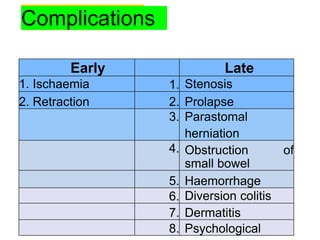
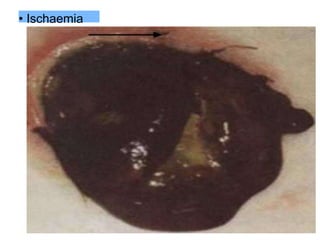
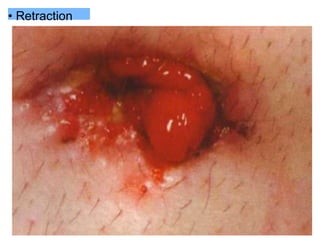
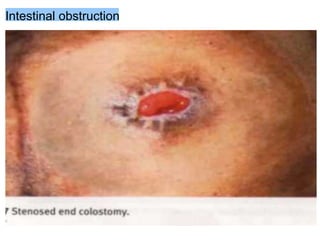
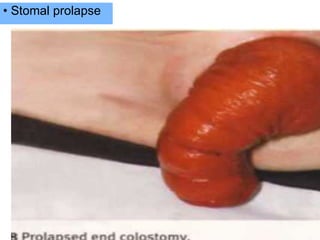
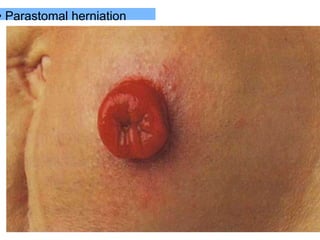
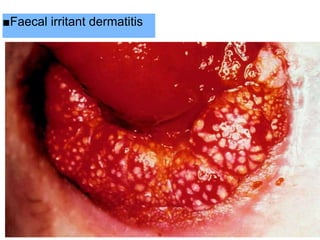
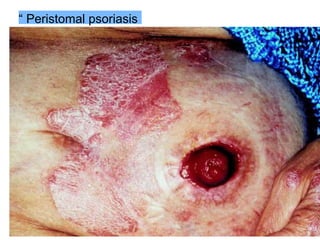
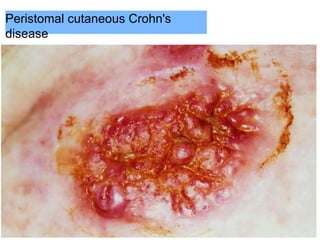
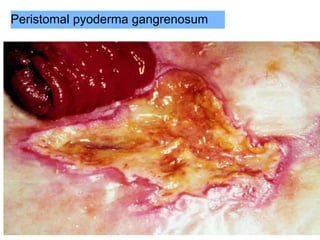
This document provides information on different types of intestinal stomas including definitions, principles of formation, and details on specific stomas like ileostomy and colostomy. It discusses how stomas are formed, attached, common complications, and dietary advice for stoma patients. Loop stomas are described as the most common type and are usually temporary to divert the fecal stream for procedures like anastomosis or fistula repairs. End stomas can be permanent outcomes of surgeries like colectomies or used temporarily in emergency settings. Proper stoma care and appliance attachment is covered along with managing common issues.