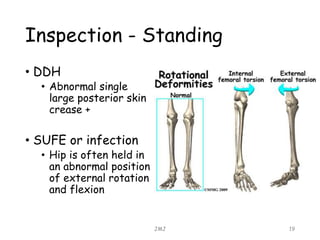
This document provides guidance on evaluating a child presenting with a limp. It discusses various possible differential diagnoses to consider, including septic arthritis, developmental dysplasia of the hip, Perthes disease, slipped femoral epiphysis, and more. Key aspects of history to obtain include age, presence of pain, associated symptoms, and past medical/family history. The examination should evaluate gait, limb length, range of motion, and tenderness. Initial investigations may include blood tests, x-rays of the hip and/or knee, ultrasound if effusion is suspected, and bone scan or MRI if further imaging is needed. The goal is to identify serious conditions like infections while considering more benign possibilities.