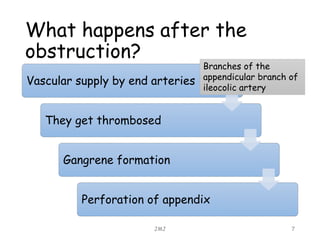
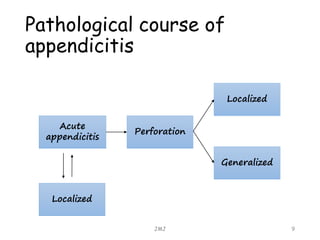
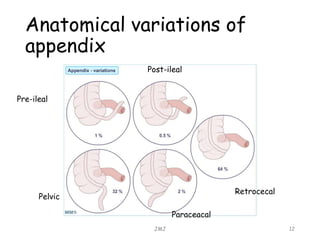
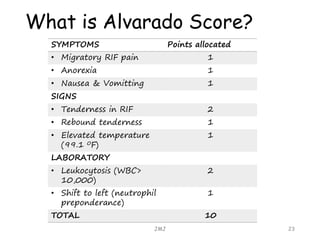
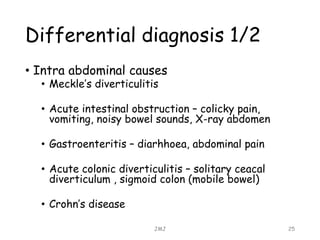
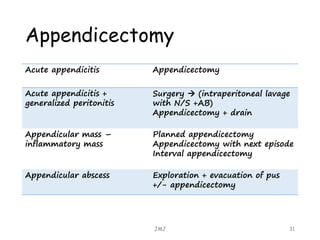
Acute appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix that is commonly caused by obstruction. It occurs in about 10% of the population between ages 10-20 but can occur at any age. The obstruction leads to bacterial proliferation, invasion of the appendix wall, and damage from pressure necrosis. Initial pain is periumbilical but shifts to the right lower quadrant as the inflamed appendix touches the peritoneum. Signs include maximum tenderness, guarding, and rebound tenderness in the right iliac fossa. The Alvarado score is used to evaluate the likelihood of appendicitis. Treatment is antibiotic therapy and an appendectomy.