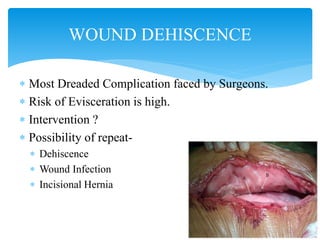
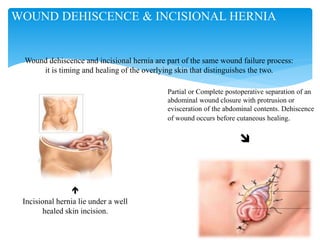
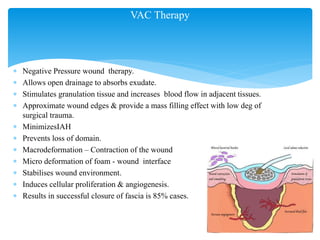
Wound dehiscence is a complication of surgery where the surgical incision ruptures or reopens. It can lead to evisceration of internal organs. Risk factors include obesity, diabetes, wound infection, and surgical factors like tension on the incision. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and drainage at the wound site. Treatment depends on the severity but may involve antibiotics, packing the wound, or re-suturing the incision. Negative pressure wound therapy can also be used to help close wounds at high risk of dehiscence. Preventing wound dehiscence requires proper surgical technique like layered closure with adequate suture length and tissue bites.