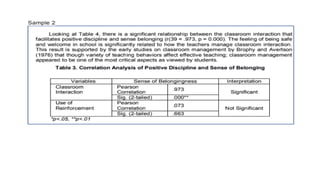
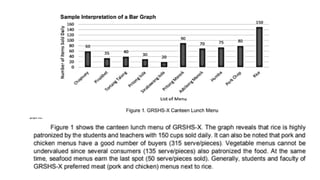
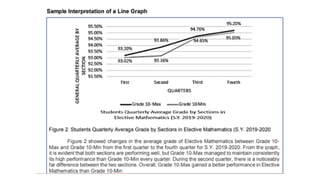
The document outlines essential techniques for data presentation and interpretation in research, emphasizing the importance of data organization, statistical testing, and effective presentation formats such as tables and graphs. It details processes like editing, coding, and tabulation for proper data handling and highlights methods for analyzing and interpreting results. Additionally, it stresses the significance of supporting findings with relevant literature and ensuring clarity and precision in communication.