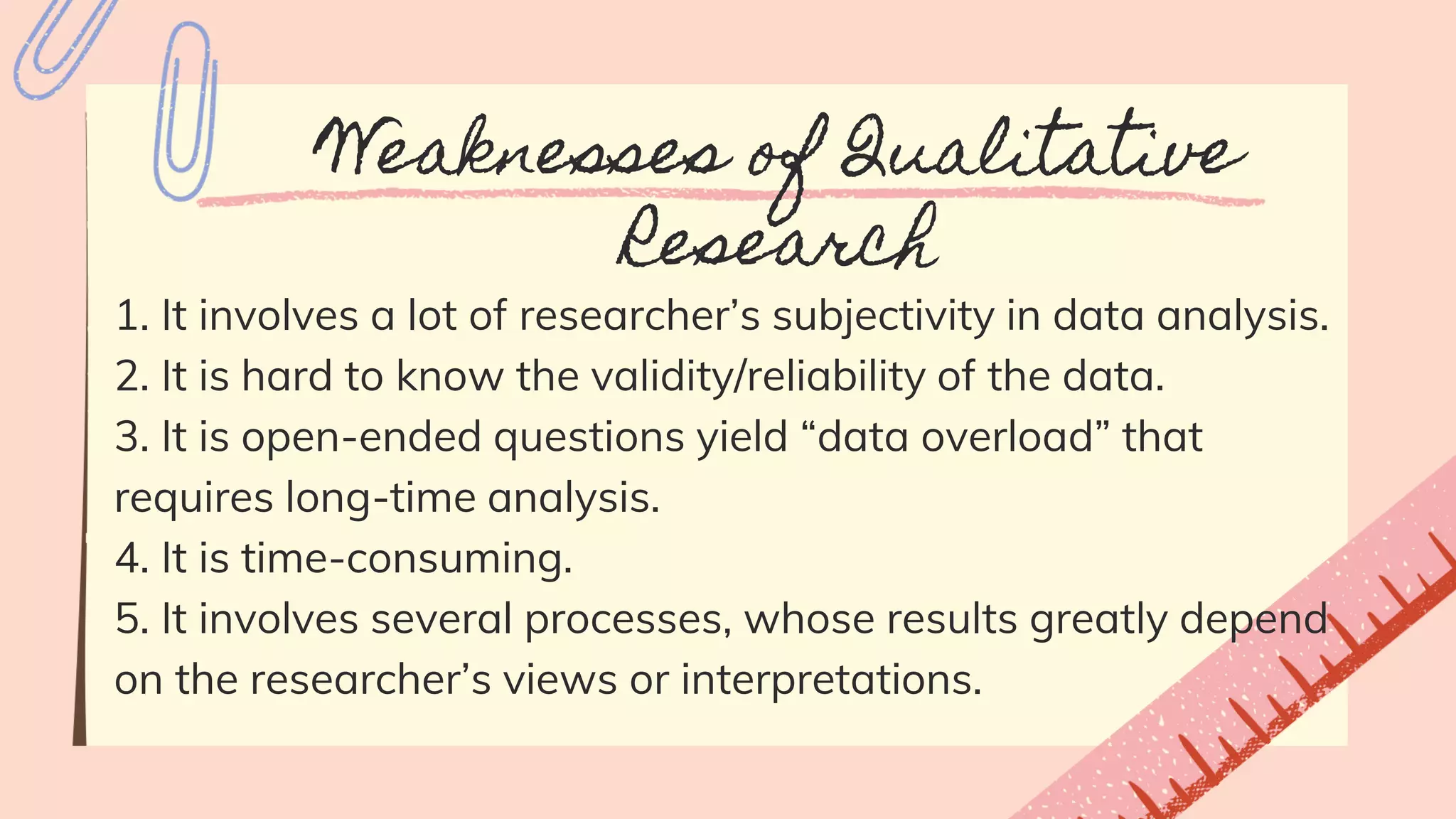
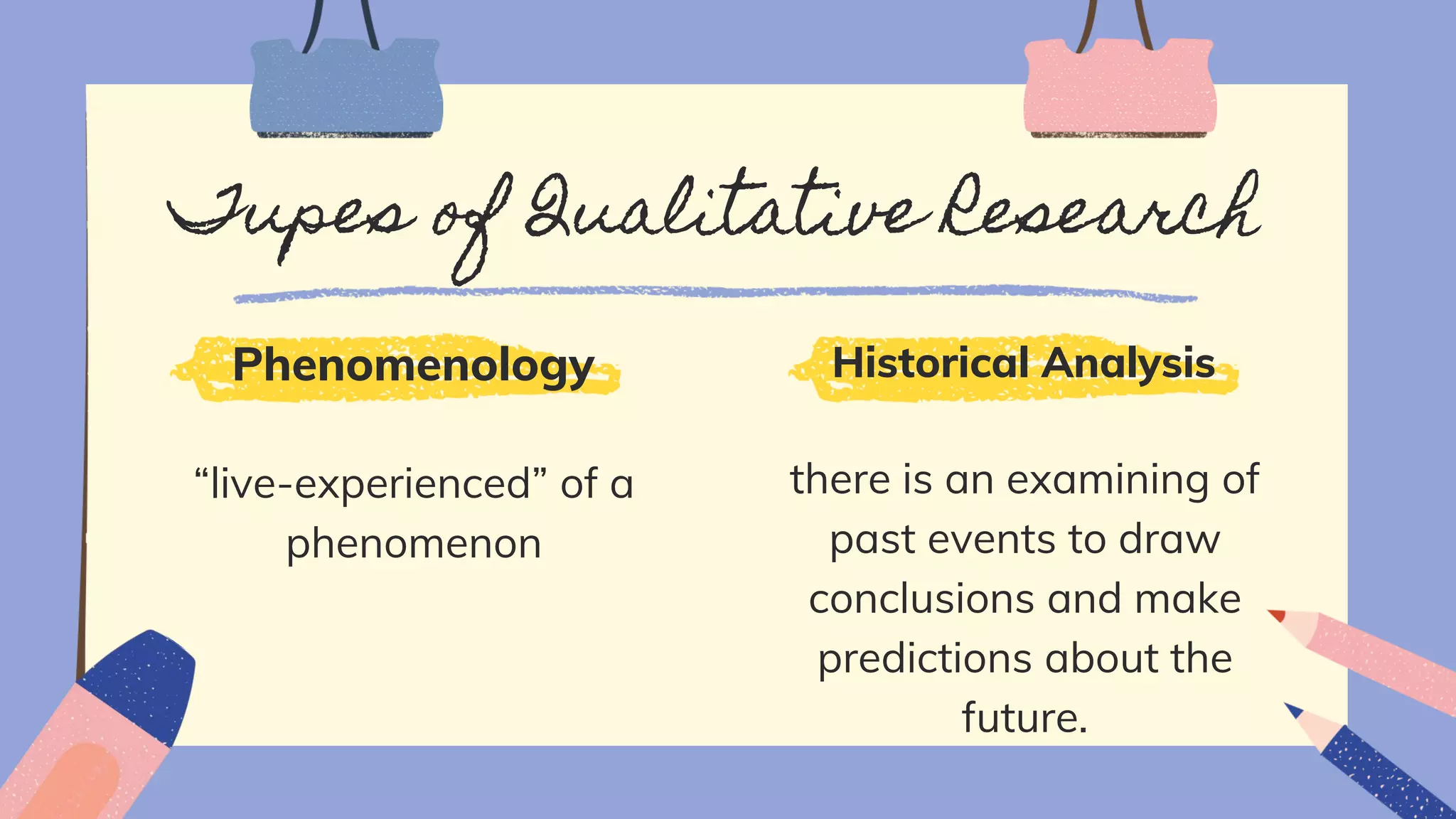
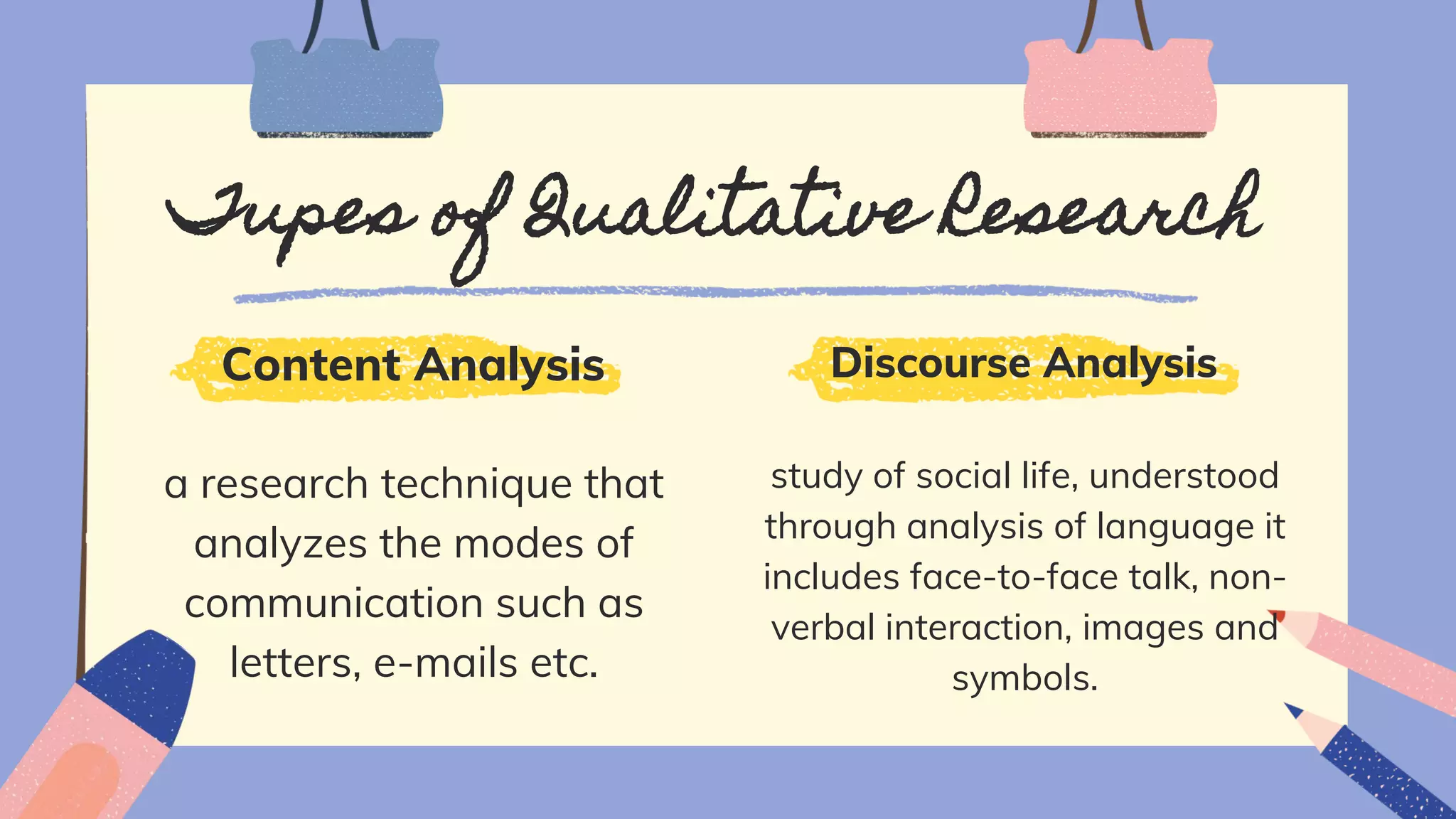
The document discusses qualitative research, defining its purpose, characteristics, strengths, weaknesses, and various types. It highlights the researcher's role and the qualitative approach's ability to provide a comprehensive understanding of human behavior in natural settings. Additionally, it outlines the challenges and limitations inherent in qualitative methodology.















![Activity Time!
Activity is in Google Classroom
References:
Pastor, m (2020) Practical Research 1 – Grade 11
Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 1– Module 2: Qualitative Research and
its important to daily life, First Edition
Abdullah, S.N. (2018) .Practical Research 1: Qualitative Research for SHS
[PowerPoint slides].Retrieved from
http://www.academia.edu./ppt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prthevalueofqualitativeresearch-201106085816/75/THE-VALUE-OF-QUALITATIVE-RESEARCH-19-2048.jpg)
