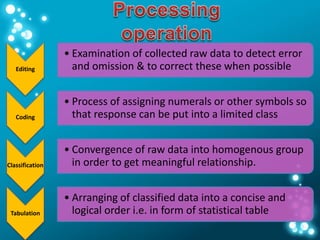
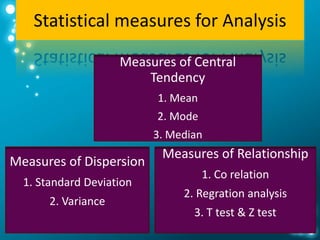
This document provides an overview of key components of results and discussion sections in a research paper. The results section presents findings from the study in tables, figures and narrative text using past tense. The discussion section interprets the results in the context of previous research and explains how the results answer the research question. Graphics such as photographs, drawings and graphs can be used to effectively present numerical data. The purpose of the results and discussion is to answer the questions "what are the findings?" and "what are the implications of the findings?".