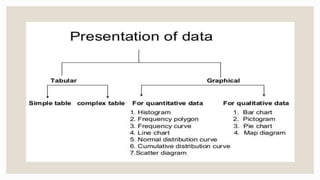
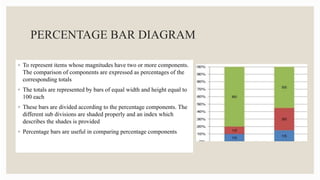
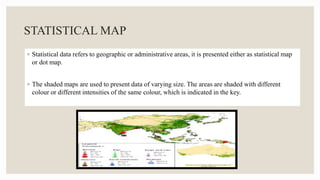
This document discusses various methods for presenting data, including text, tables, and graphs. It provides classifications of data types and outlines principles and criteria for selecting presentation methods. Text can convey brief quantitative information and interpretation, while tables and graphs are best for larger datasets. Tables arrange data in rows and columns for comparison and have strengths in precision. Graphs simplify complex information through visual patterns and are effective for exploring relationships. Selection of a presentation method depends on factors like the size, scope, and time constraints of a study.