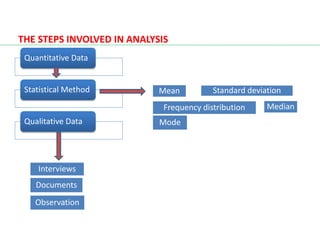
This document discusses interpretation and analysis of data in research. It defines interpretation as drawing inferences from collected facts after analysis to find broader meaning. Interpretation considers relationships within data and relates findings to other research. Effective interpretation requires considering all relevant factors and avoiding false generalizations. Data analysis organizes and models data to discover useful information for decision making. It distinguishes between quantitative data analyzed statistically and qualitative data analyzed through interviews, documents, and observation. Both interpretation and analysis are important for extracting meaningful insights from data.