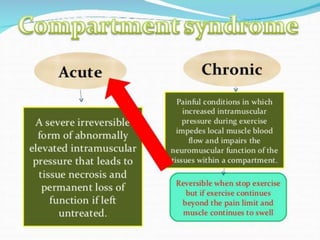
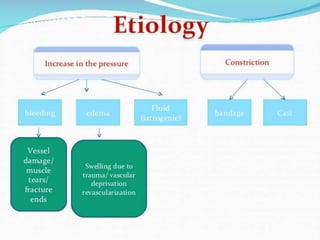
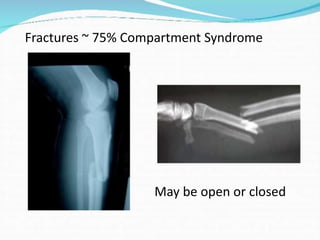
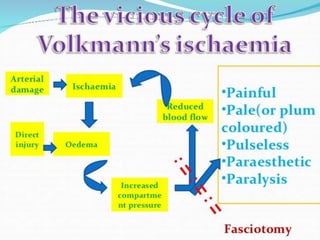
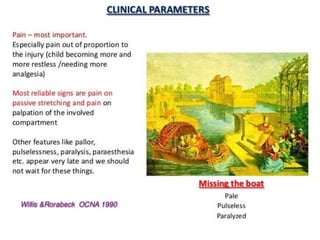
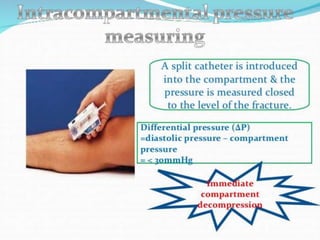
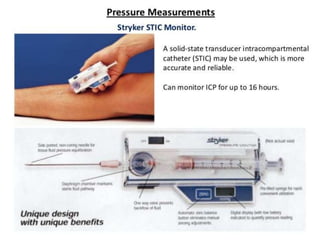
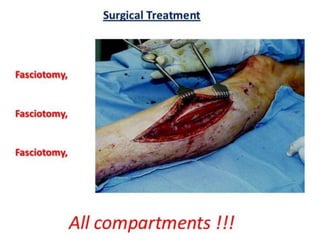
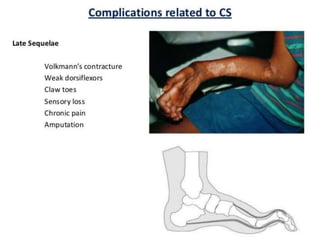
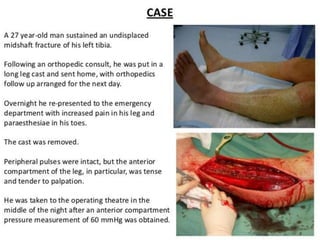
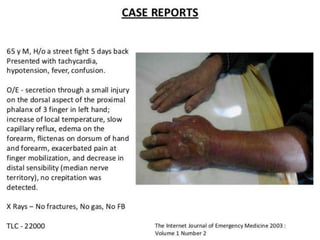
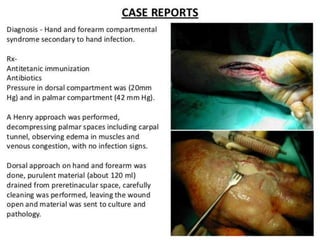
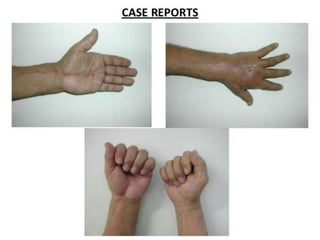
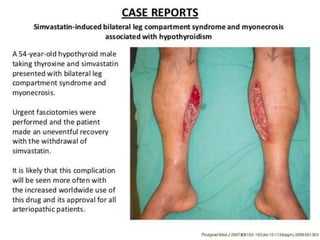
This document discusses compartment syndrome, which can occur in 75% of fractures and requires timely treatment to prevent serious complications. Compartment syndrome is a true orthopedic emergency where increased pressure in an anatomical space can reduce blood flow leading to tissue death. Measurement of compartment pressures is important and adequate analgesia, IV fluids, and urine output monitoring are needed. Fasciotomy surgery within 6 hours leads to almost complete recovery but delays over 12 hours significantly reduce limb function with risks of gangrene, contractures, and renal failure from rhabdomyolysis.












![References
• Marx JA, Hockberger R, Walls RM. Rosen’s Emergency
Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice, 7th edition
(2009) Mosby, Inc. [mdconsult.com]
• Newton EJ, Love J. Acute complications of extremity
trauma. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2007
Aug;25(3):751-61, iv. PMID: 17826216.
• Perron AD, Brady WJ, Keats TE. Orthopedic pitfalls in
the ED: acute compartment syndrome. Am J Emerg
Med. 2001 Sep;19(5):413-6. PMID: 11555801.
• Simon RR, Sherman SC, Koenigsknecht SJ. Emergency
Orthopedics — The Extremities (5th edition), McGrawHill, 2007.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compartmentsyndrome-131023223248-phpapp01/85/Compartment-Syndrome-32-320.jpg)