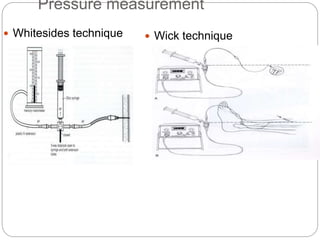
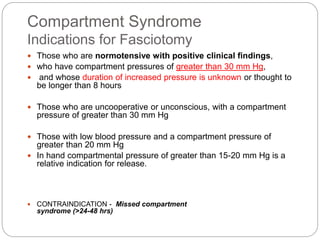
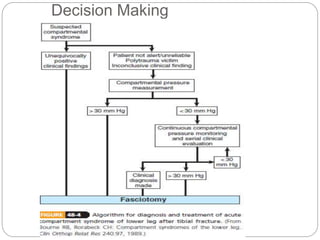
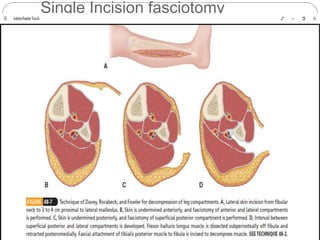
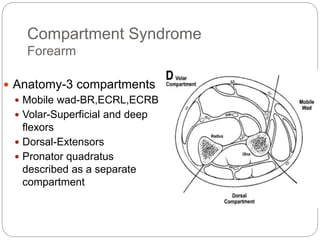
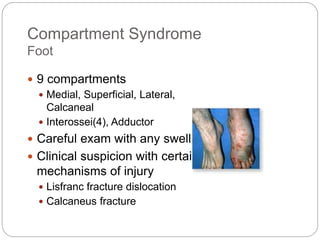
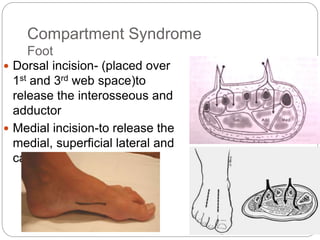
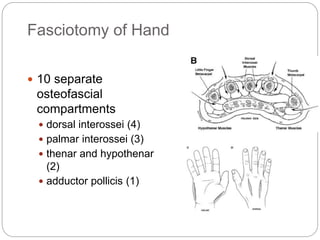
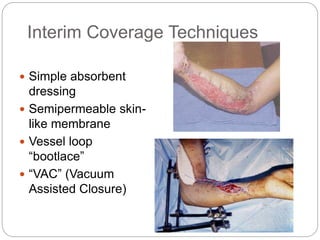
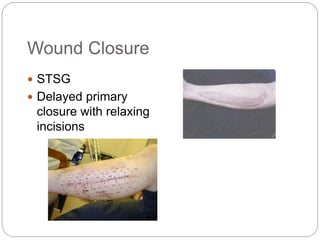
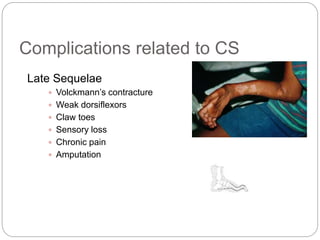
Compartment syndrome occurs when increased pressure within a closed muscle compartment compromises blood flow, and if left untreated, causes tissue damage. It is most commonly caused by fractures, but can result from other injuries. The diagnosis is based on pain out of proportion to the injury that is worsened with passive stretching of the muscles. Measurement of compartment pressure is the diagnostic standard, with fasciotomy (surgical release of fascial compartments) required if pressure is over 30 mmHg. Timely fasciotomy is crucial to prevent permanent nerve and muscle damage.