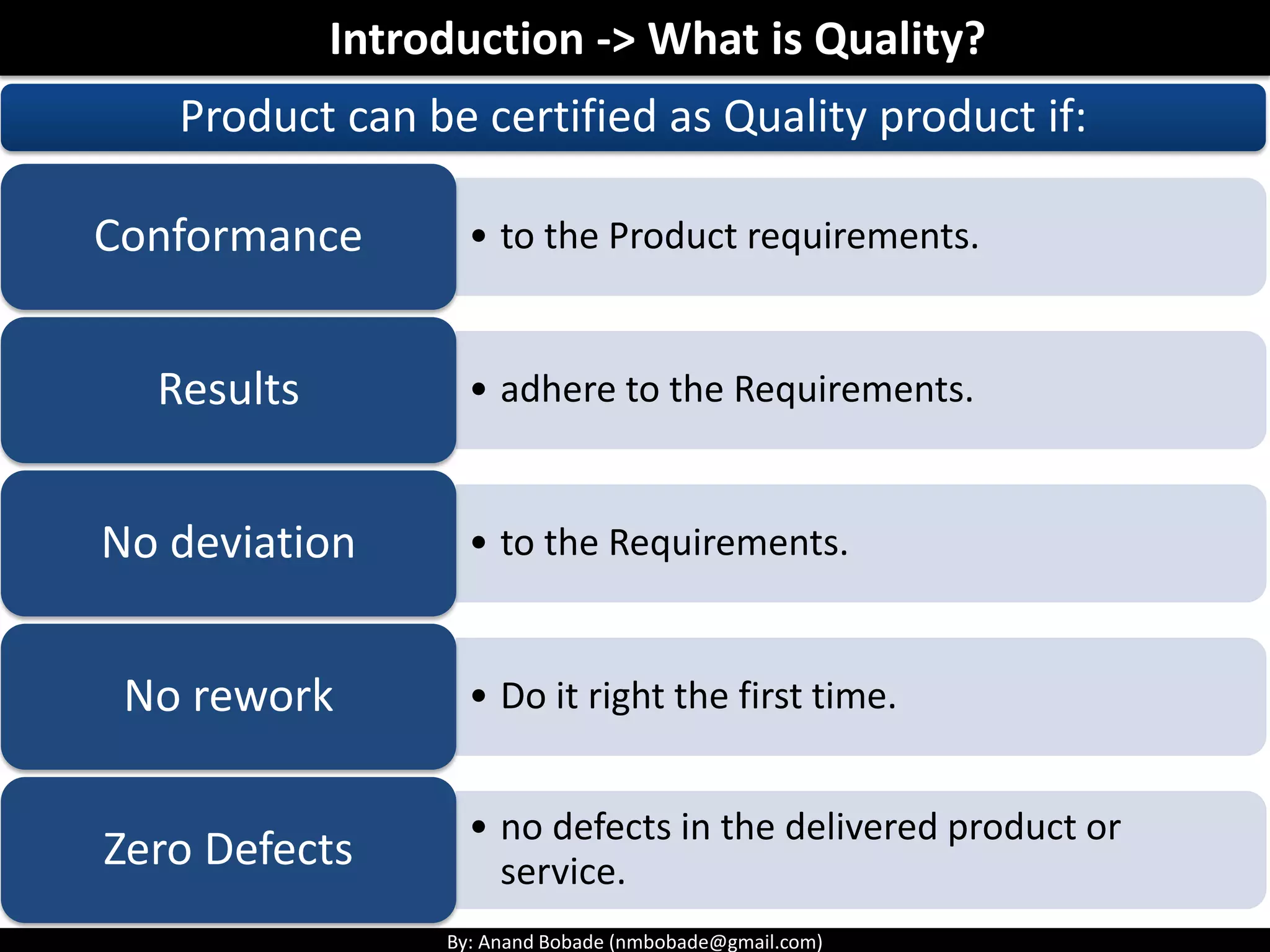
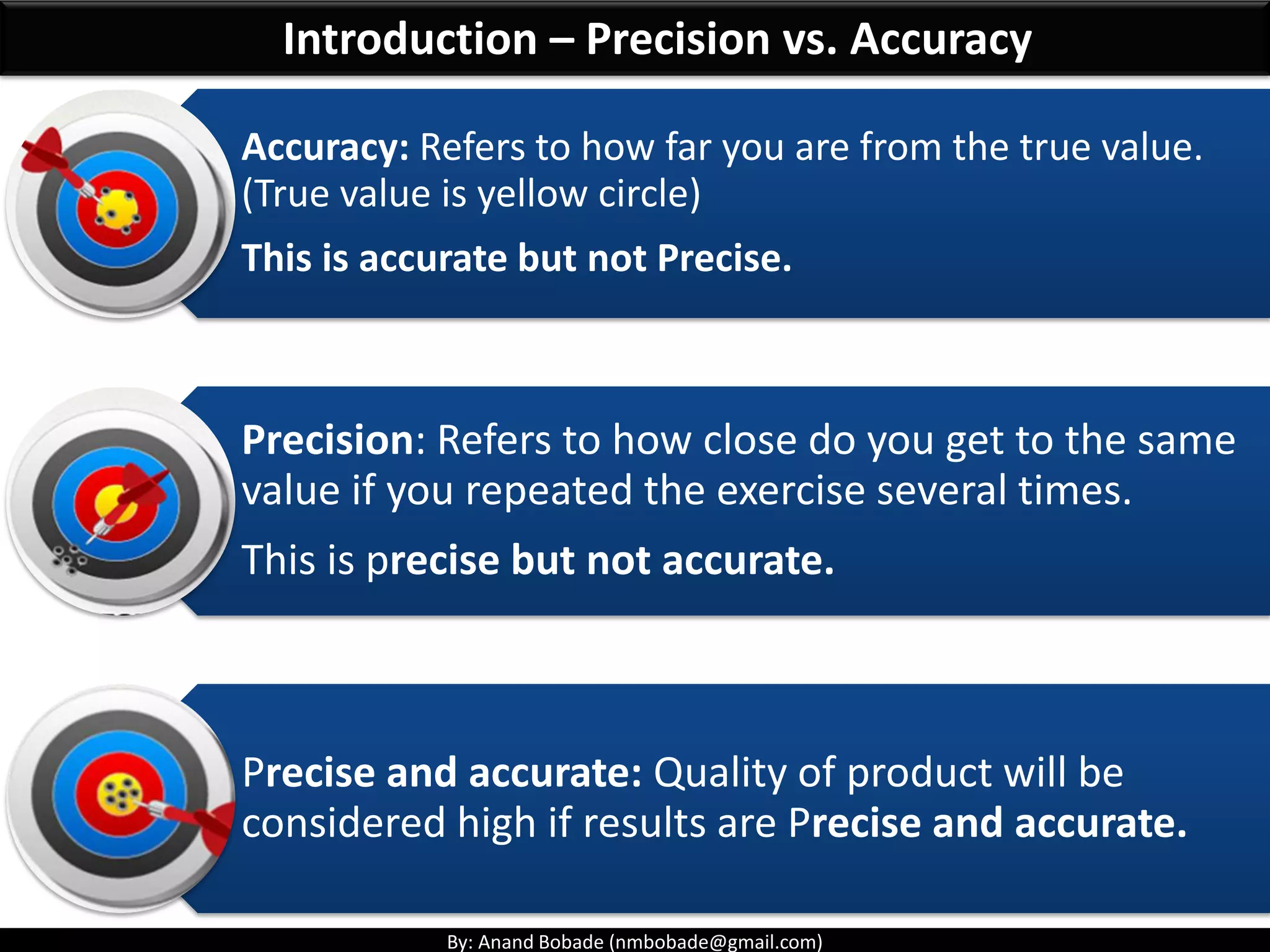
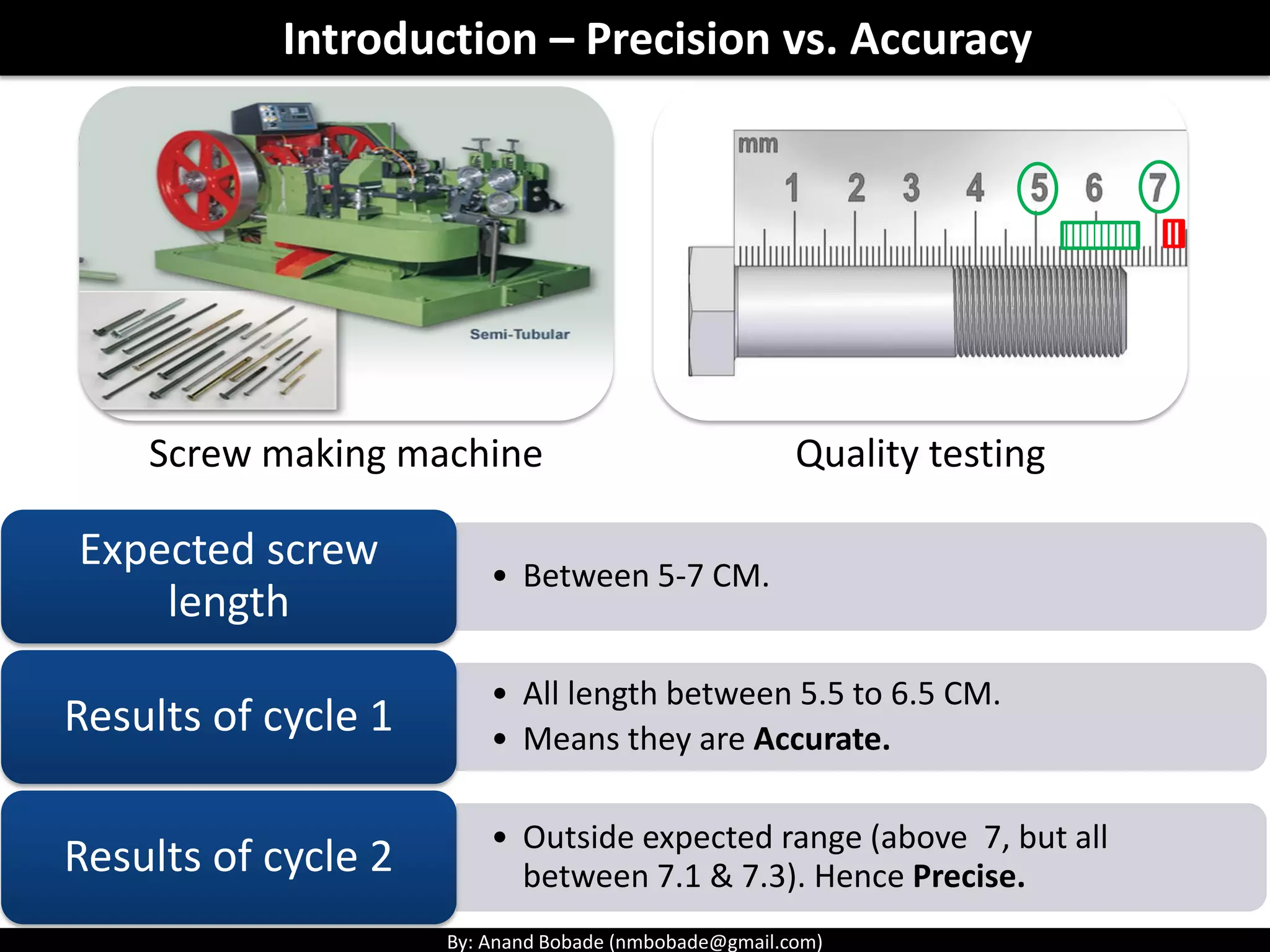
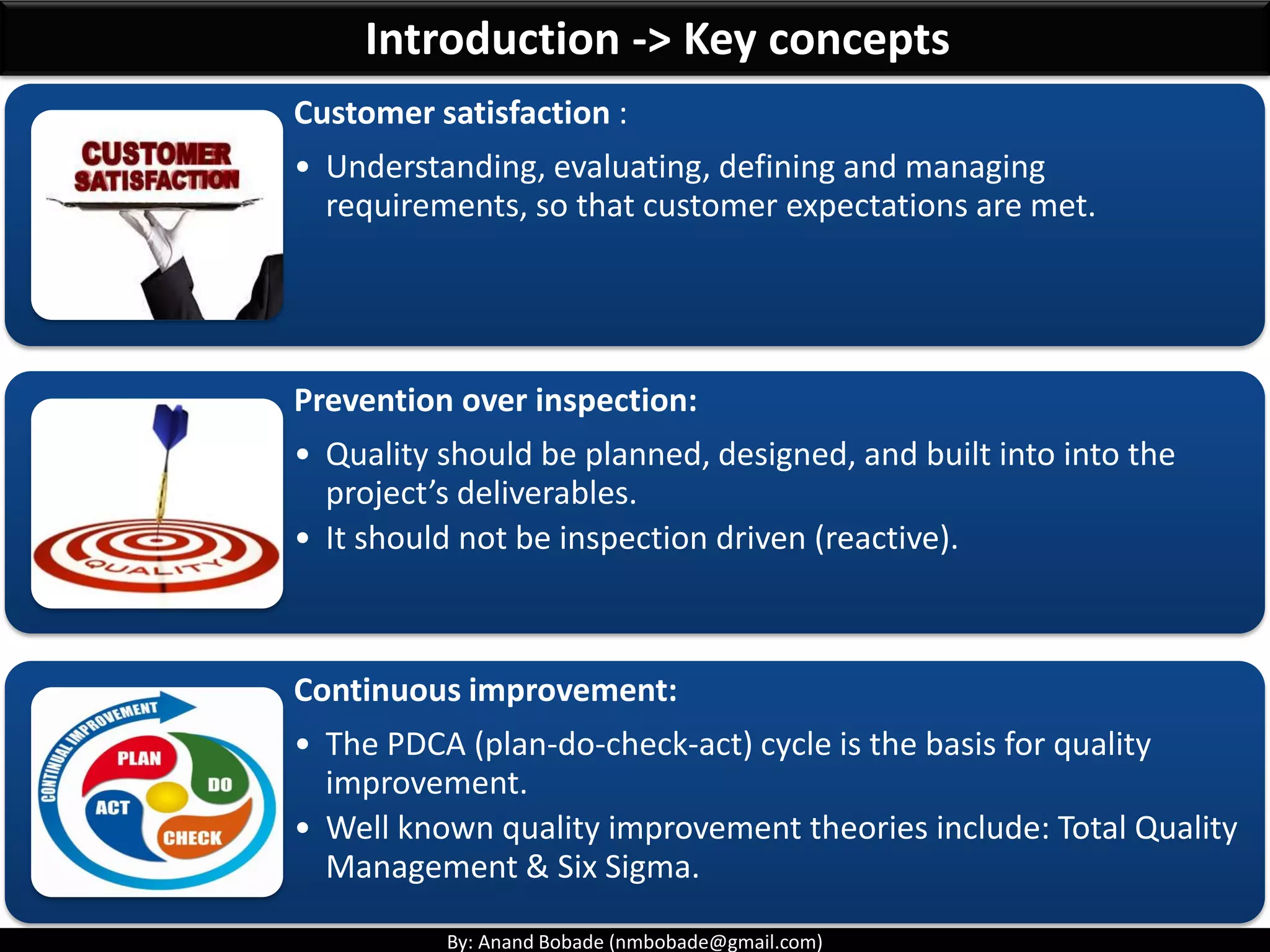
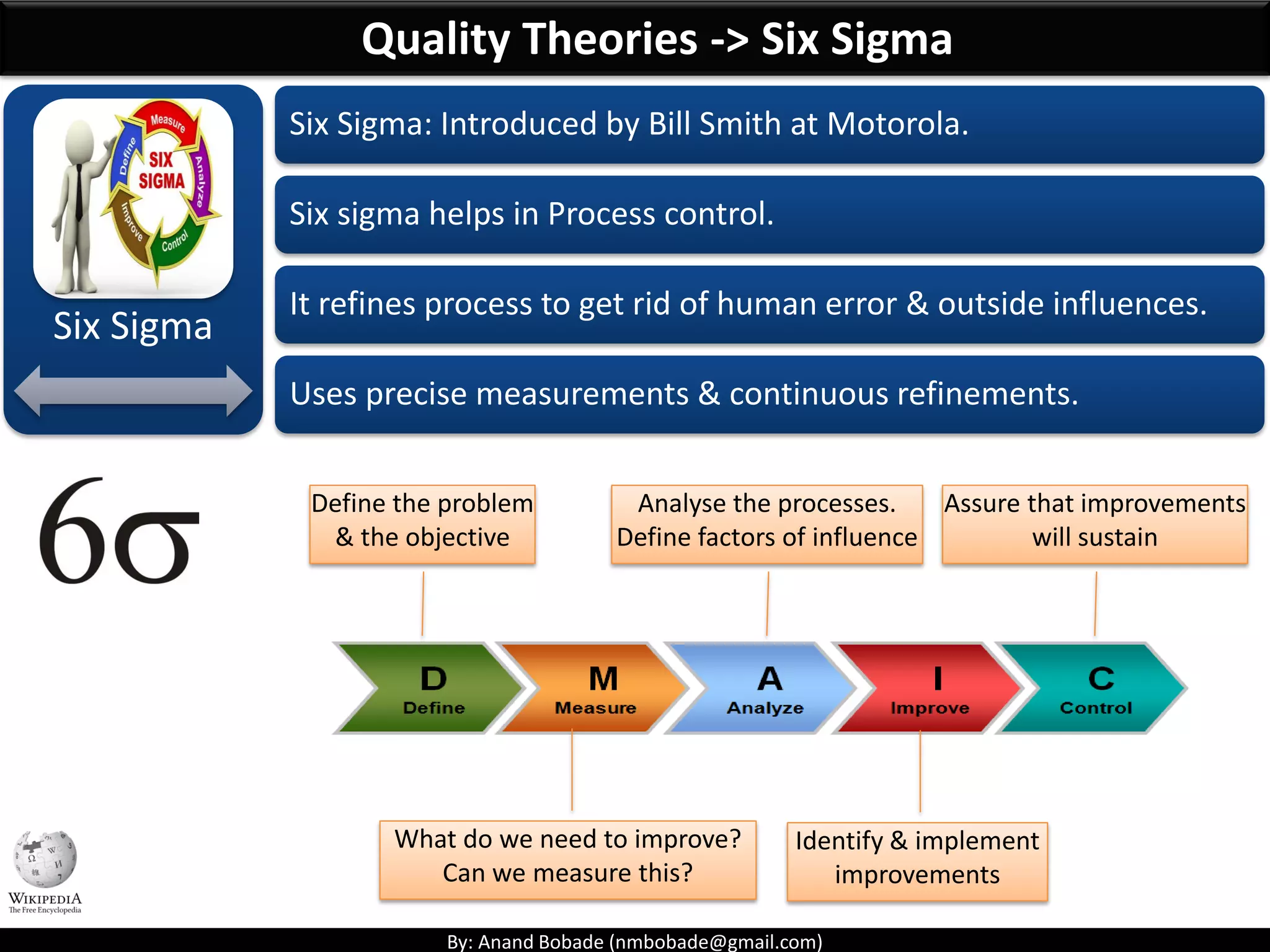
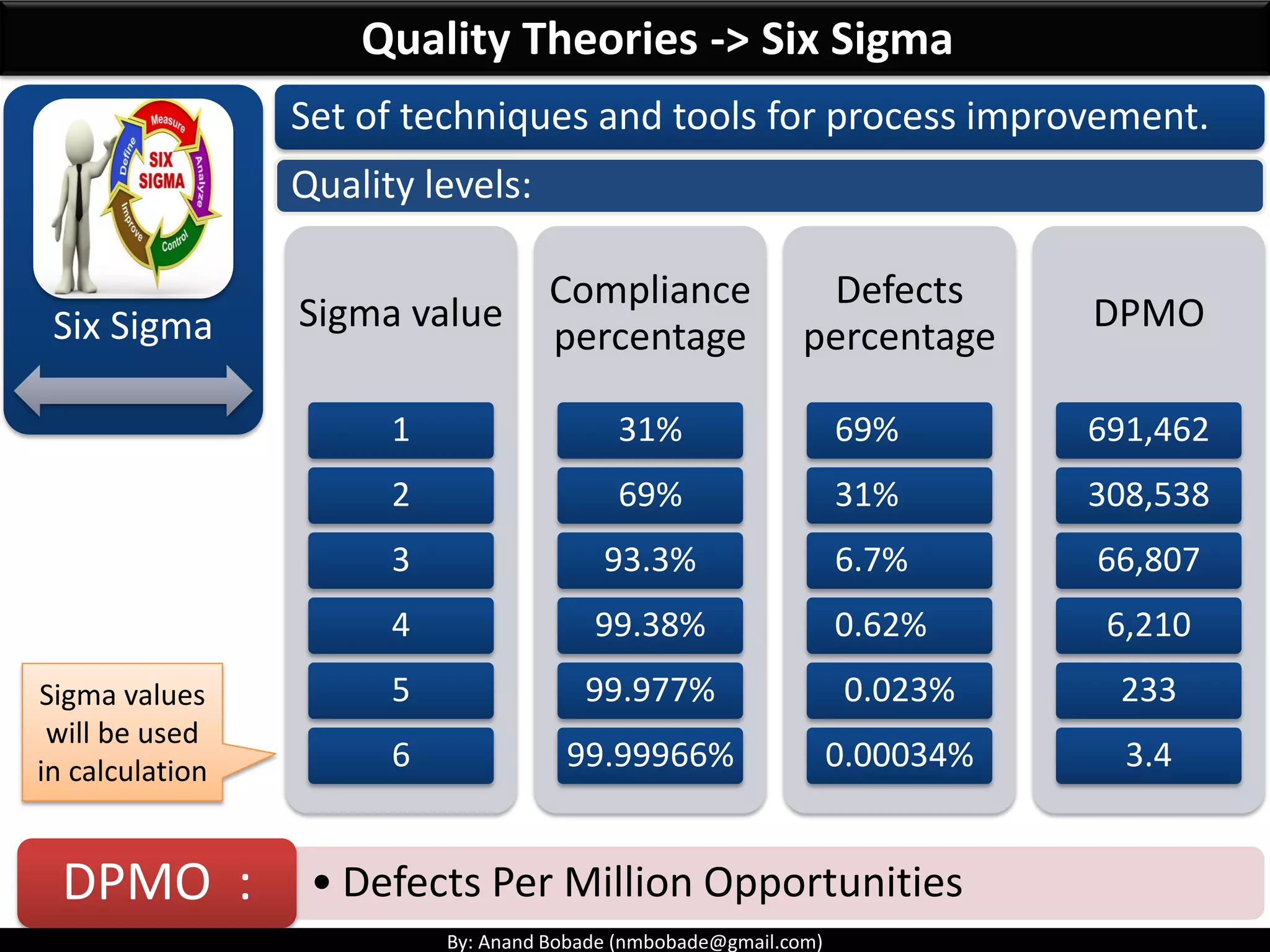
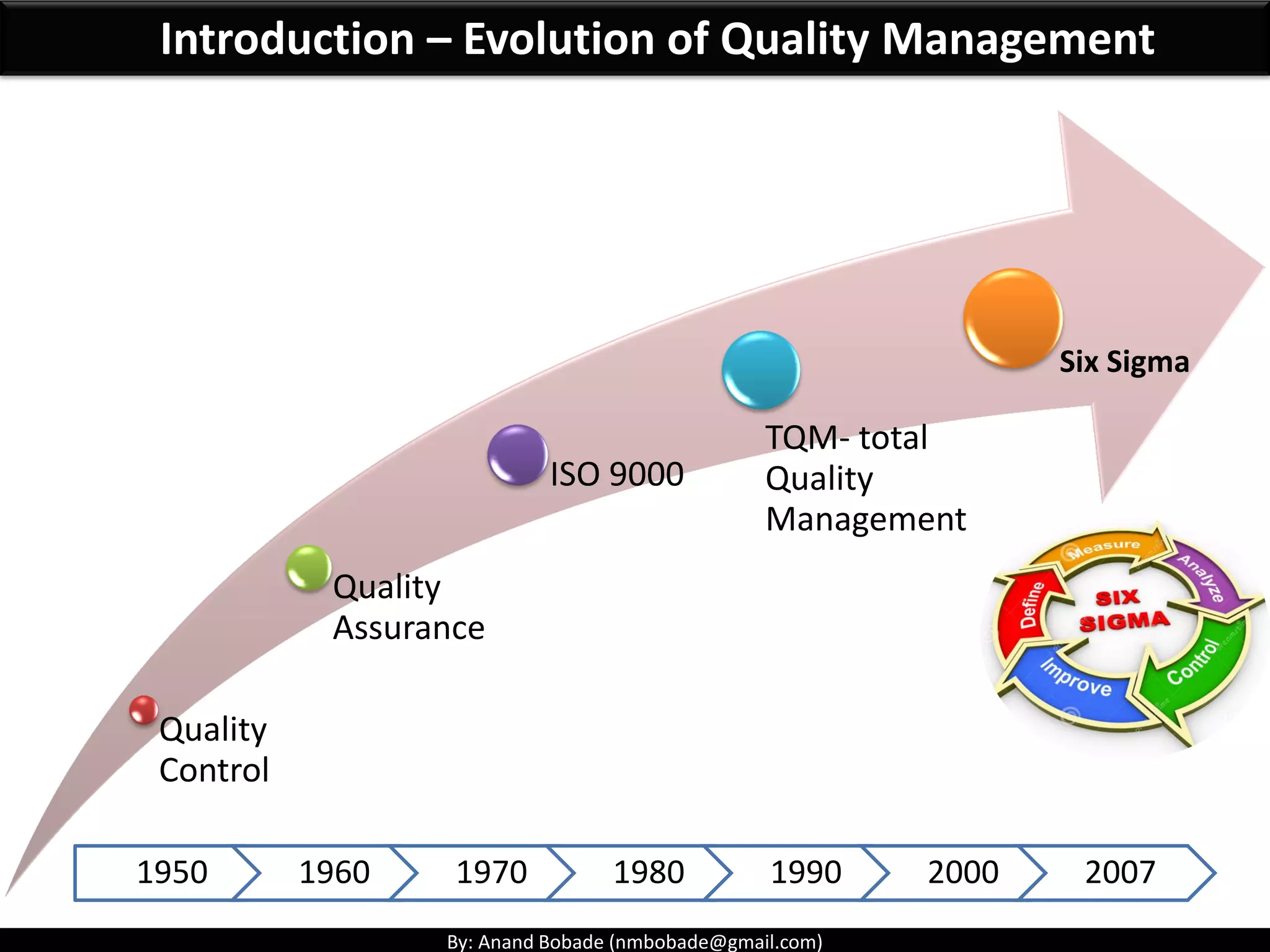
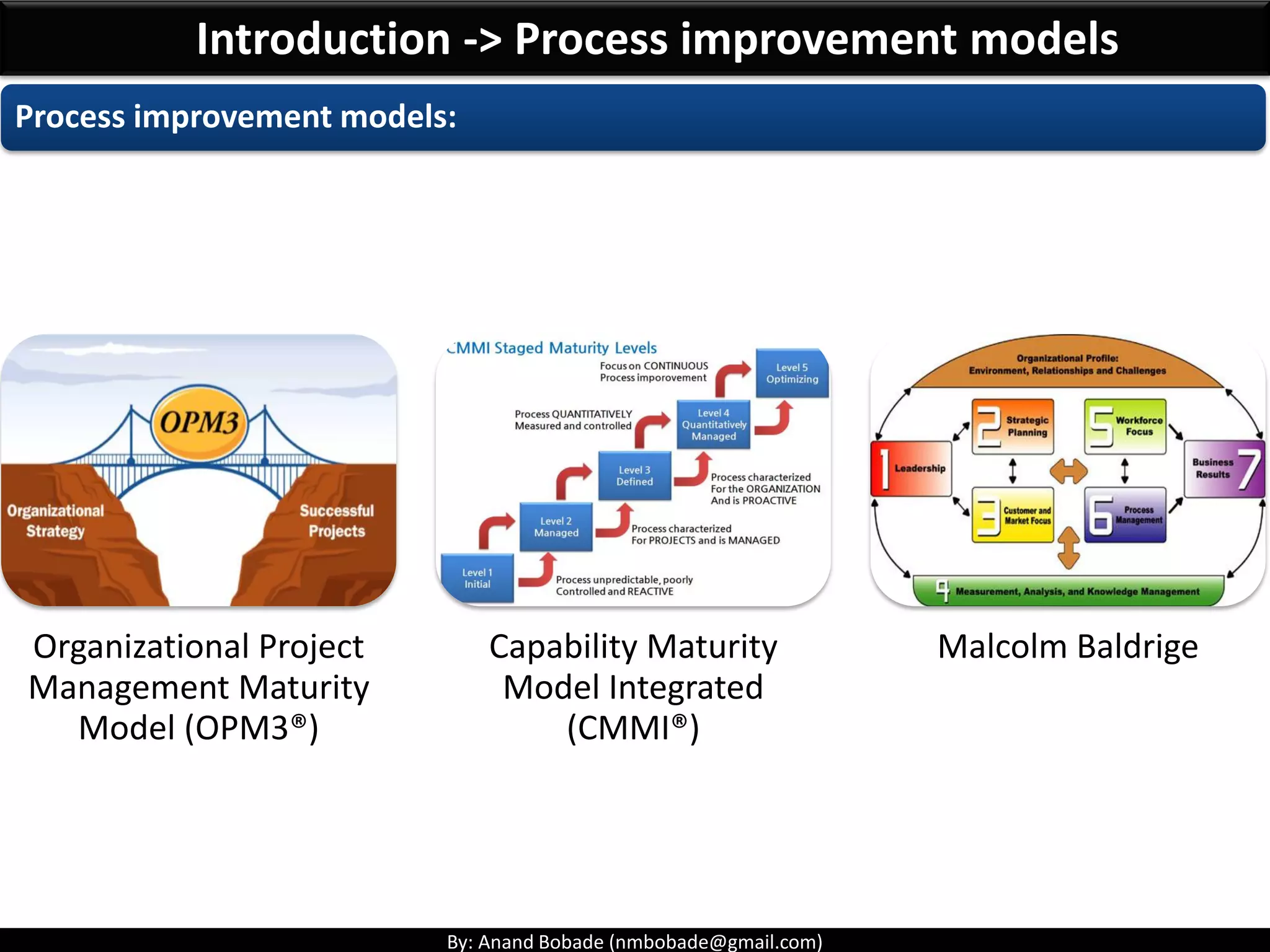
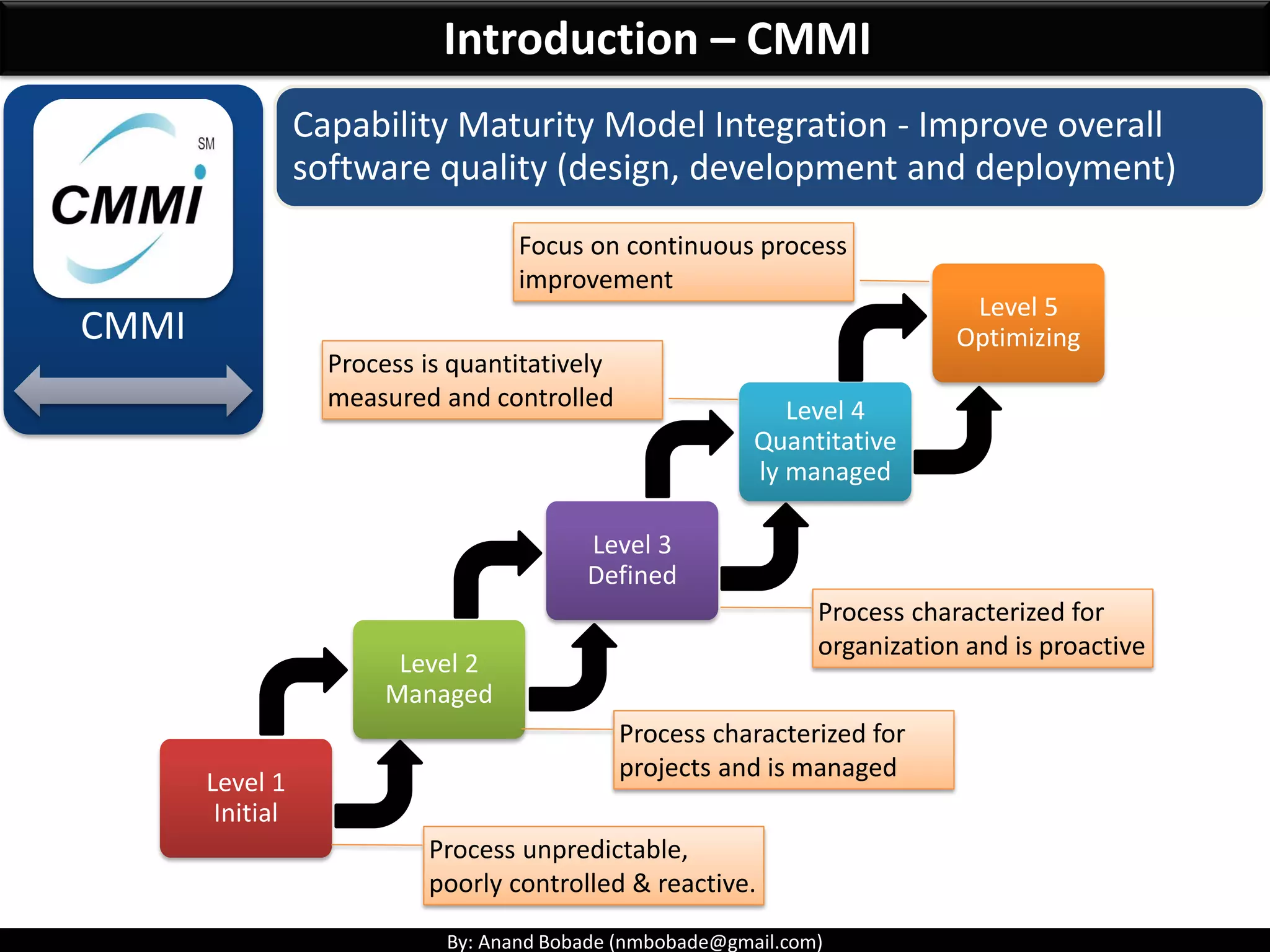
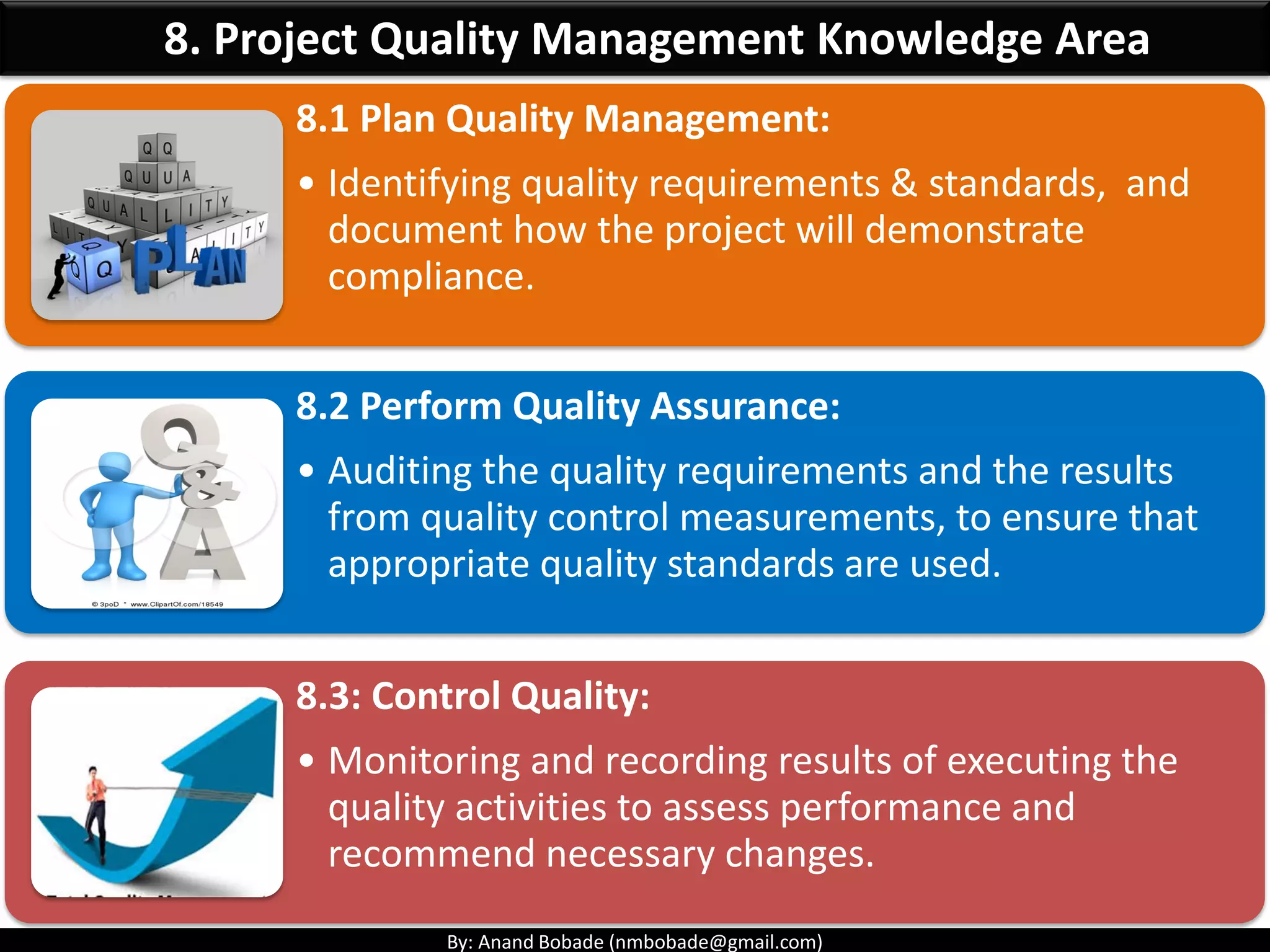
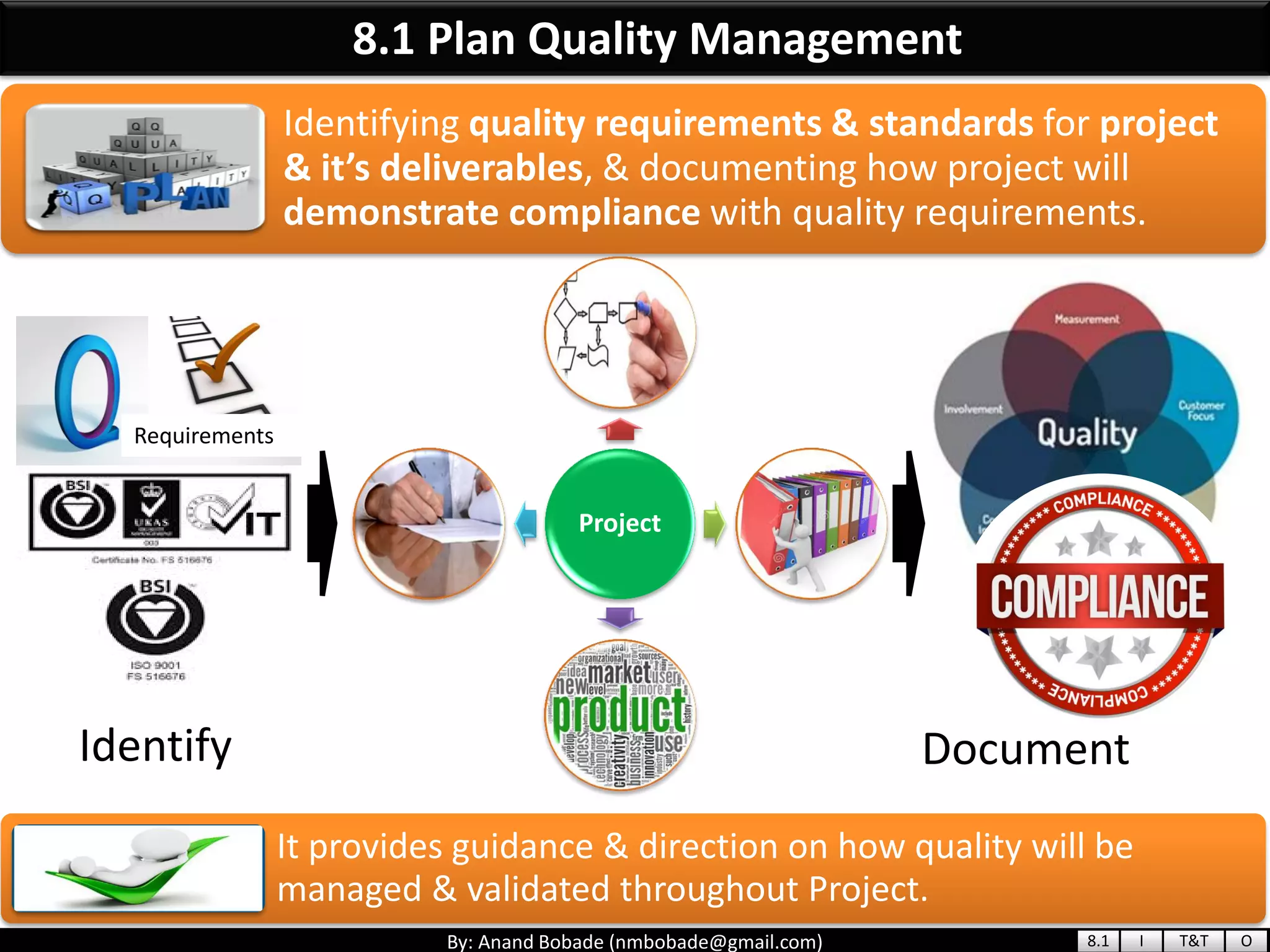
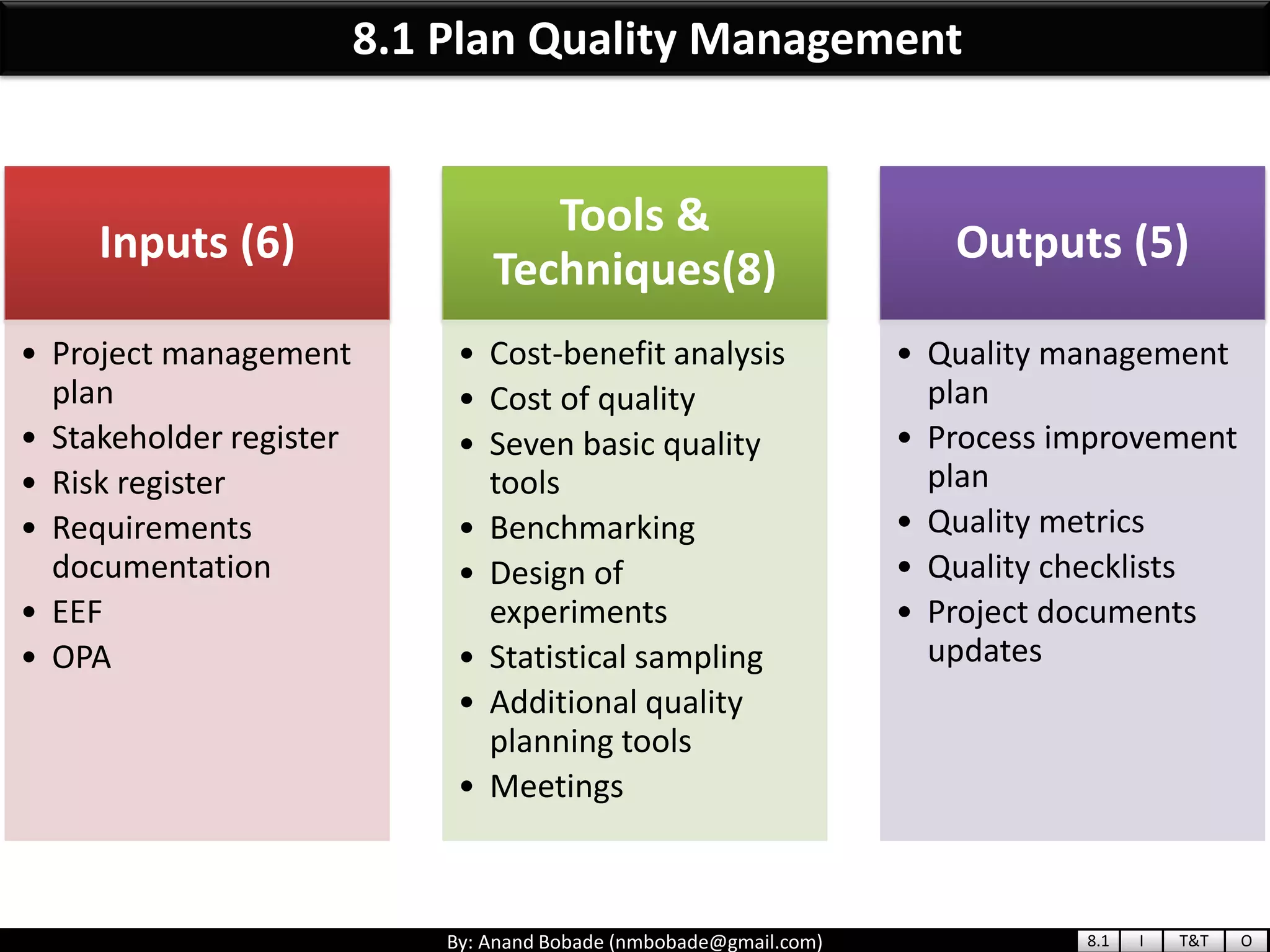
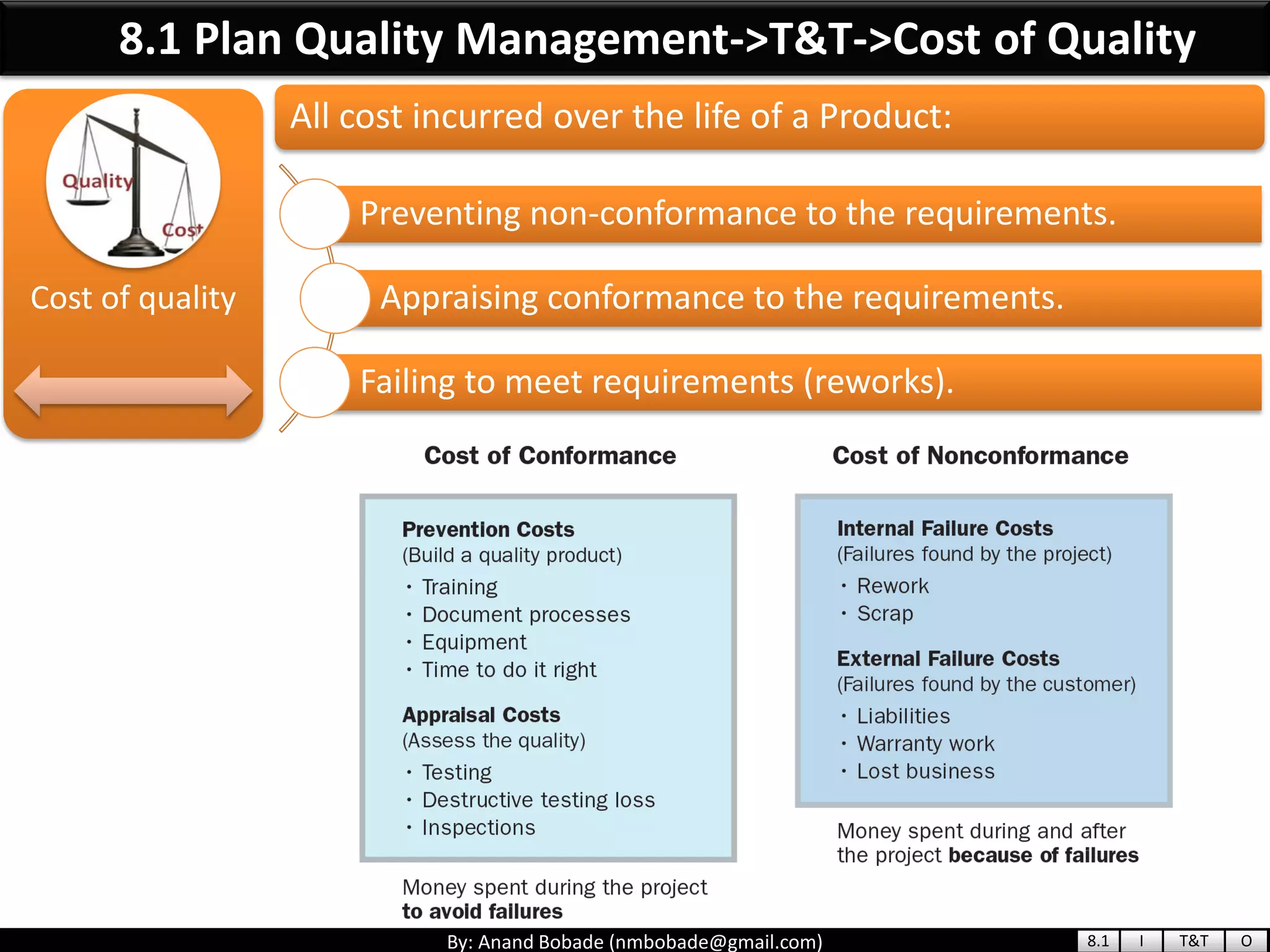
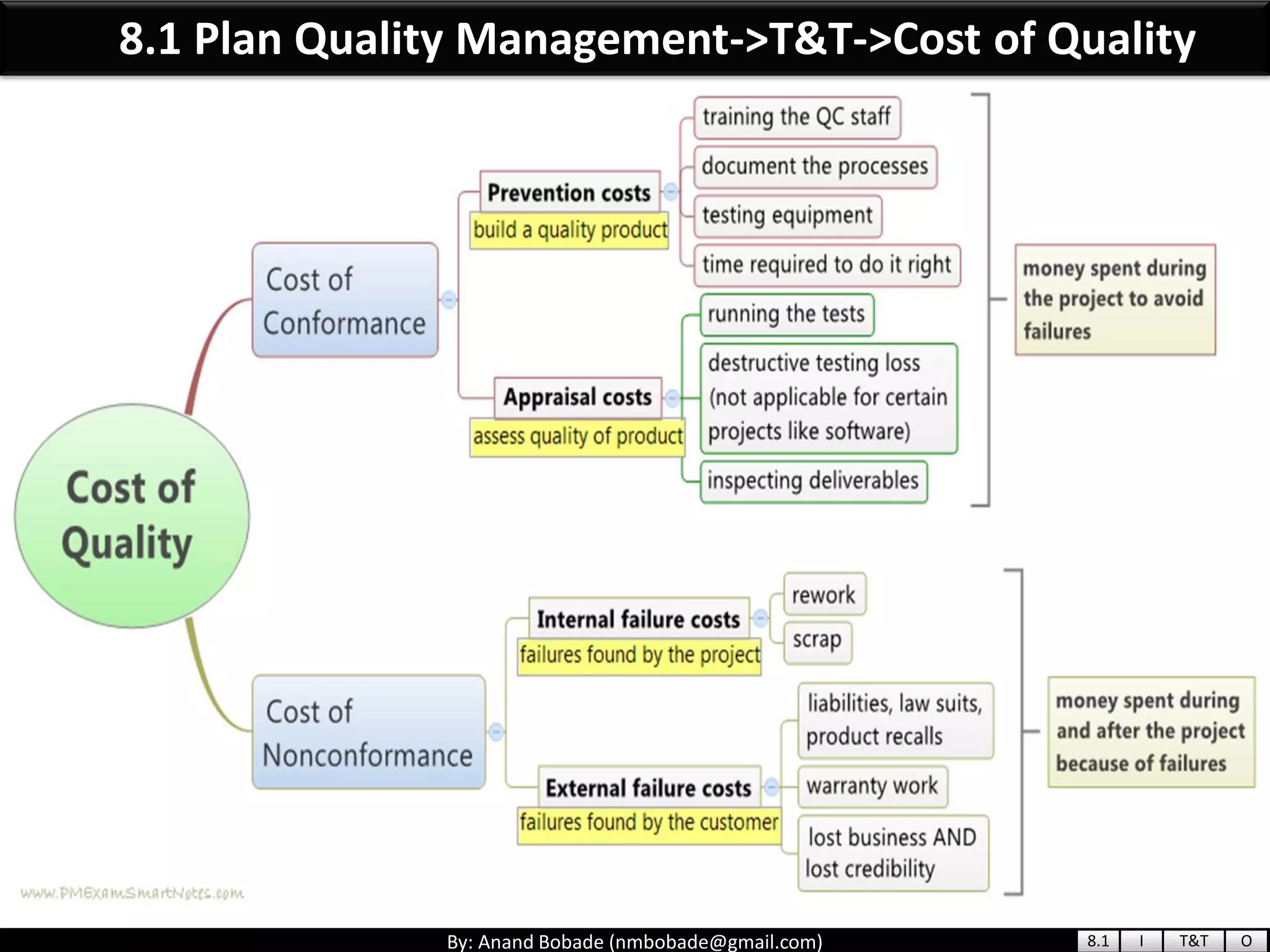
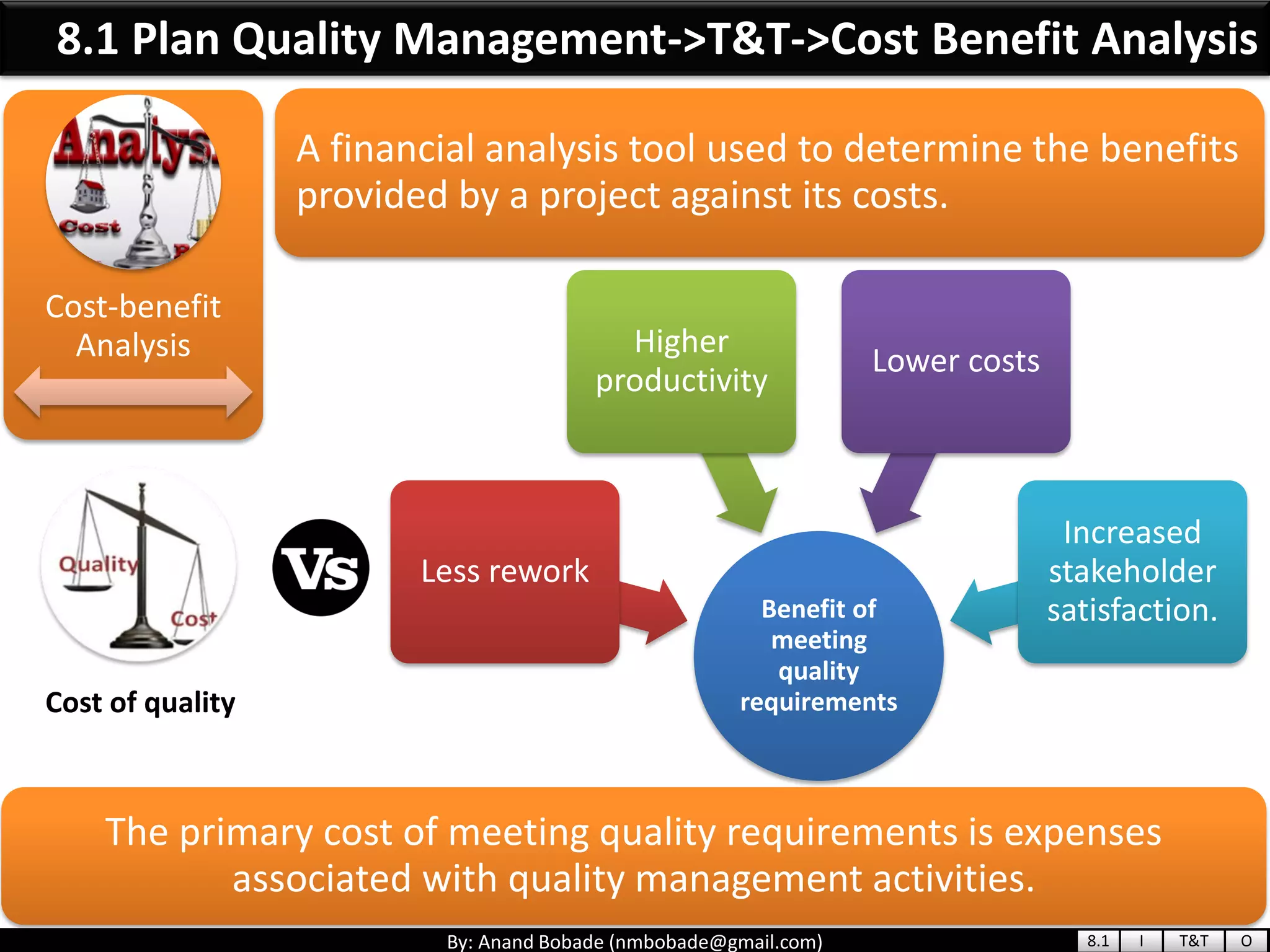
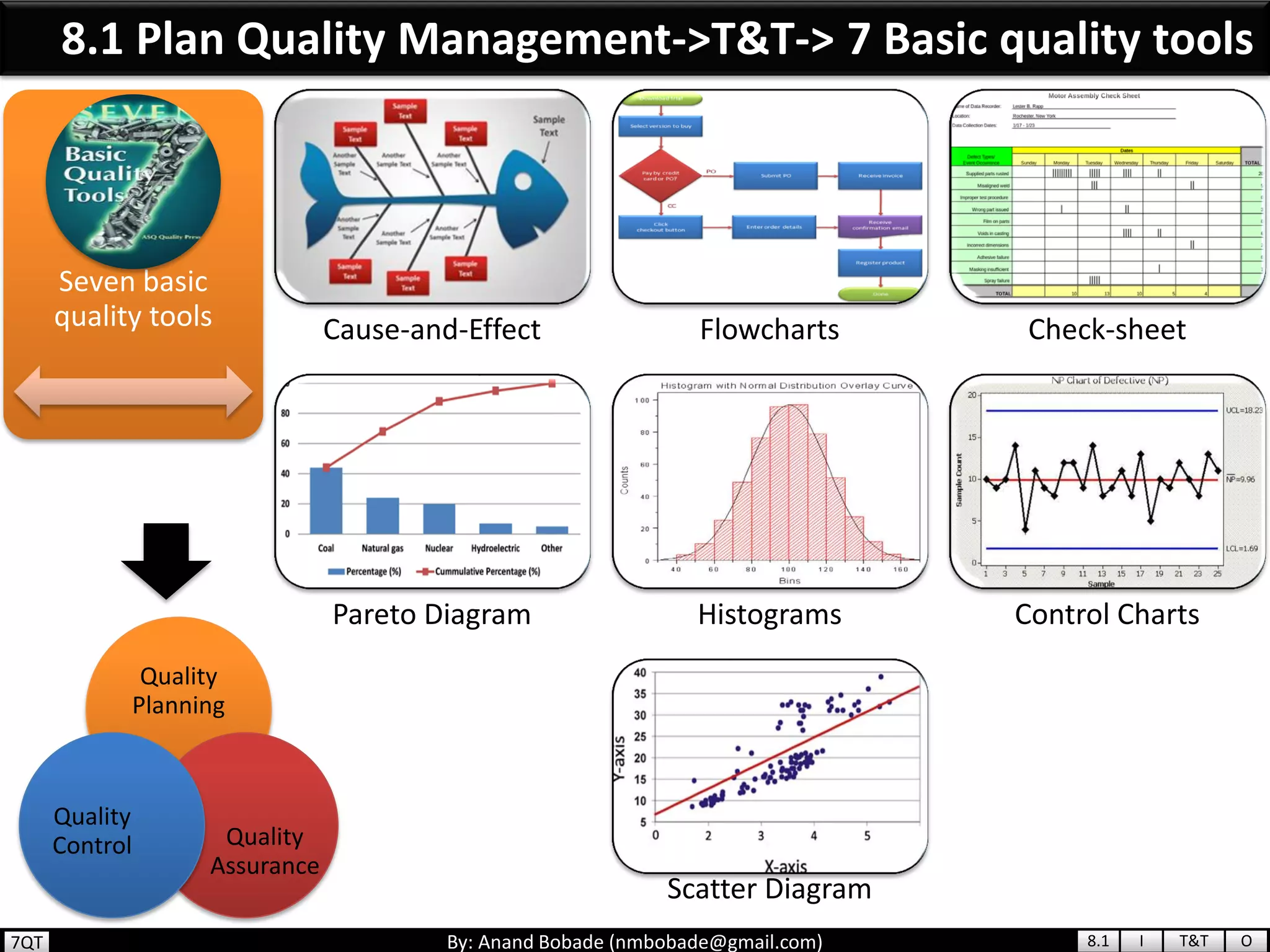
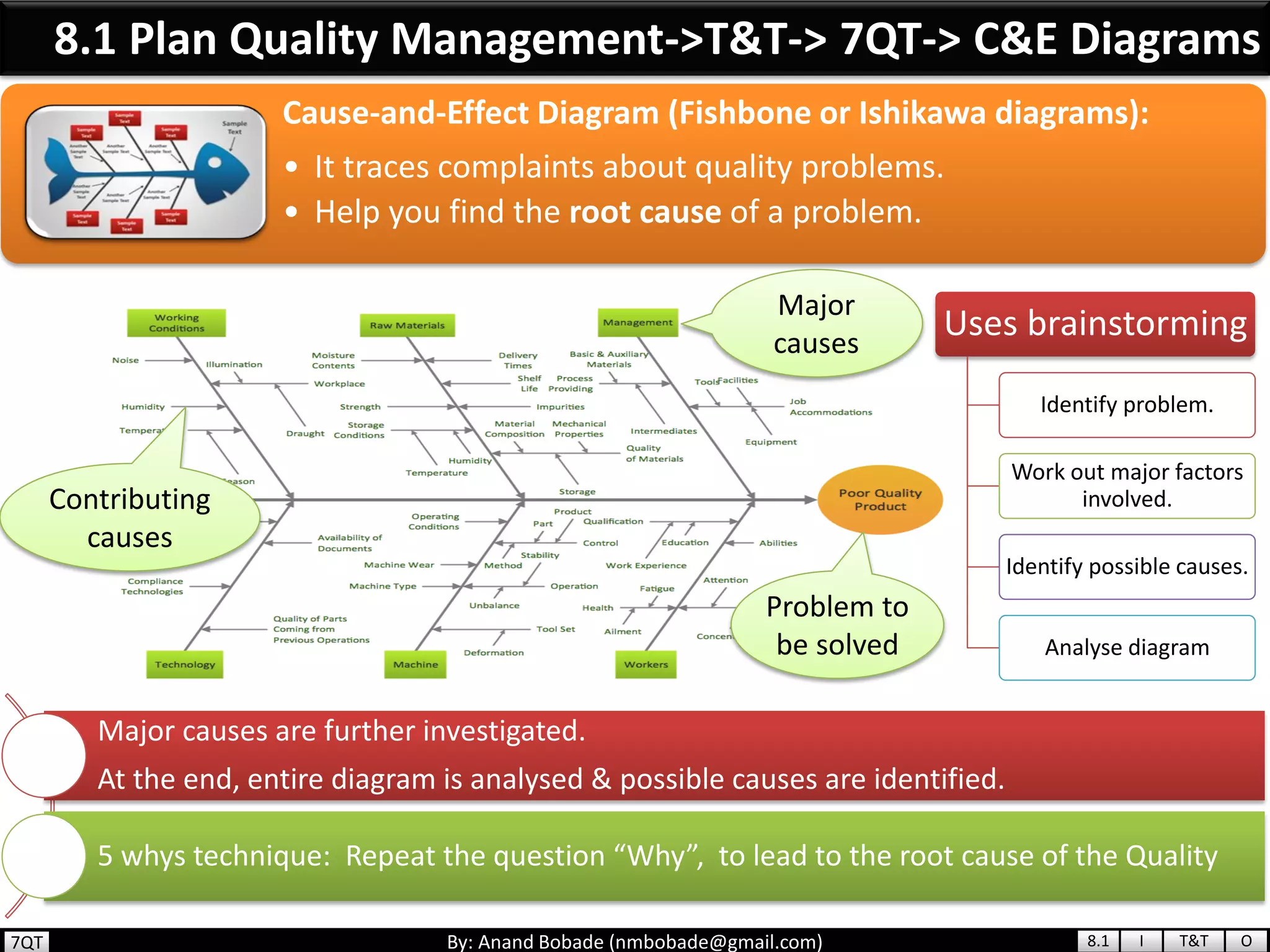
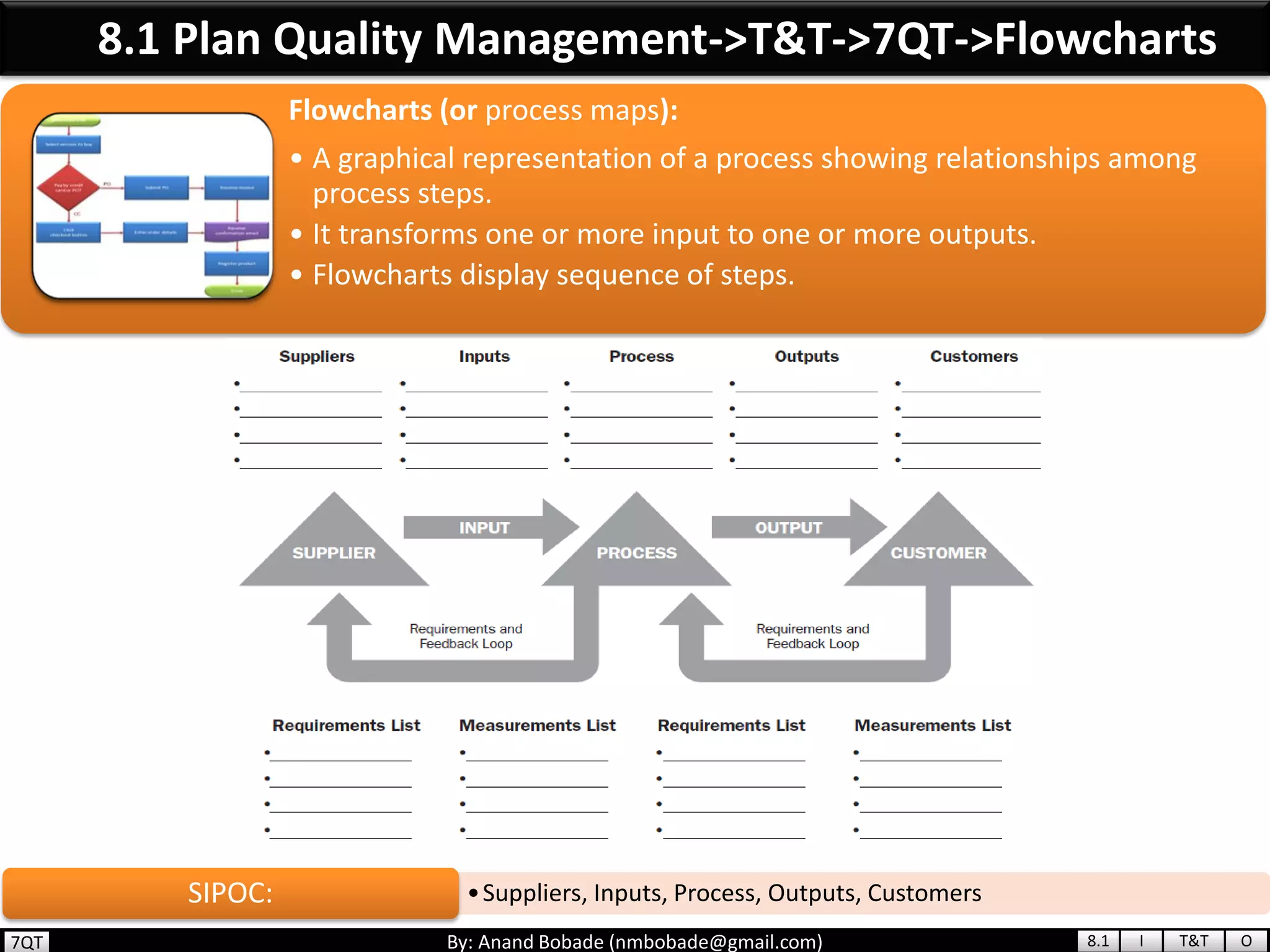
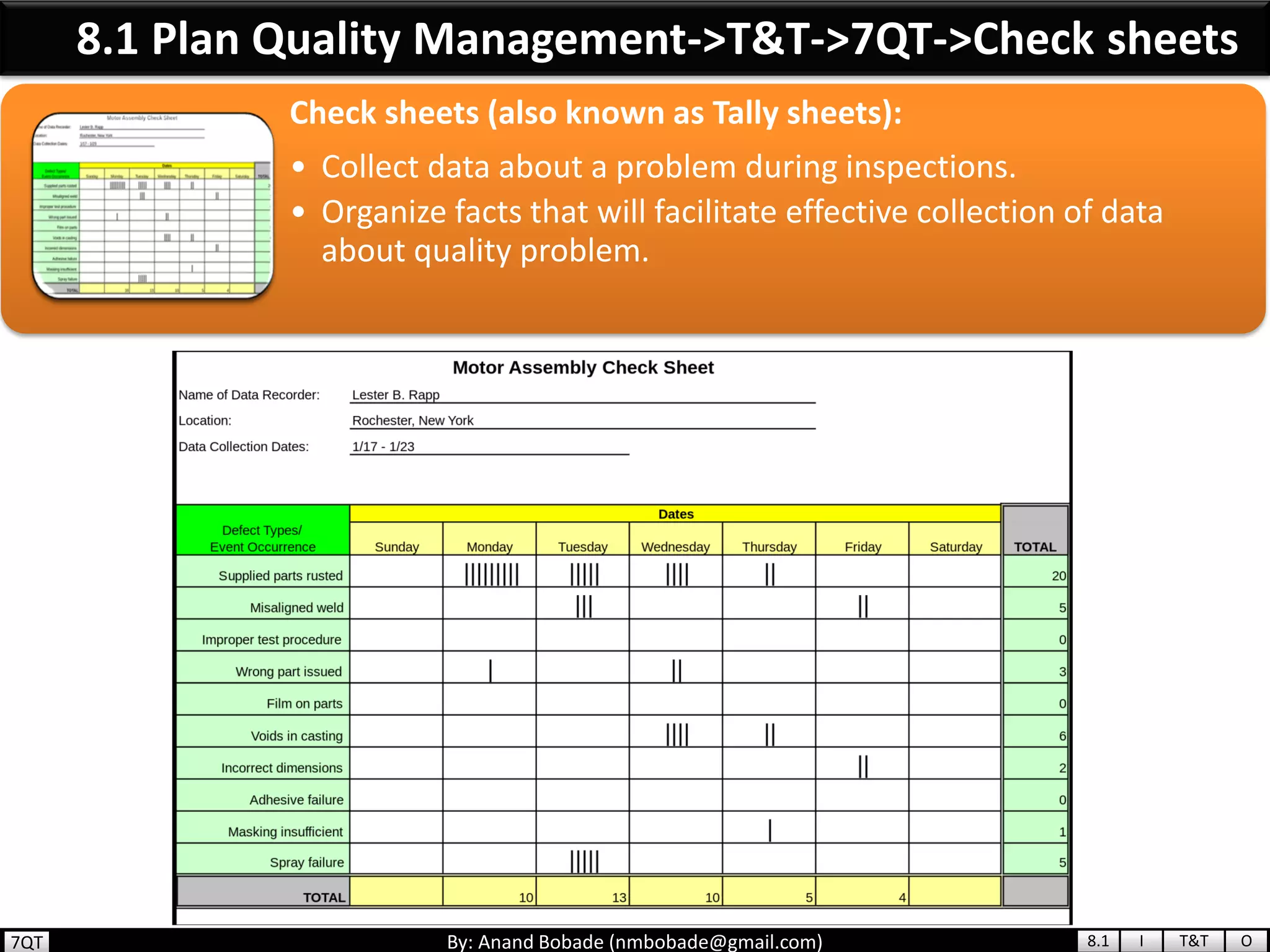
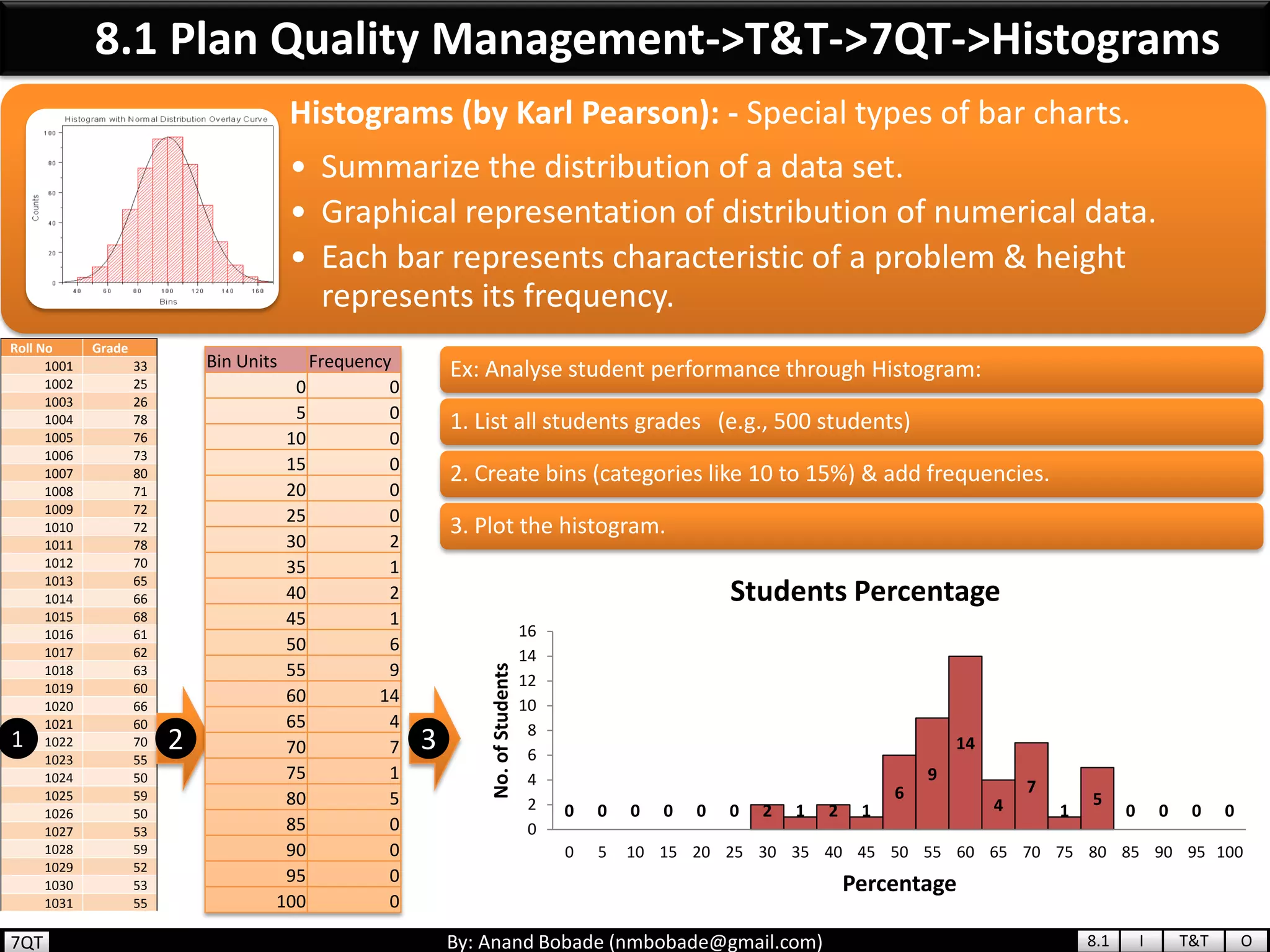
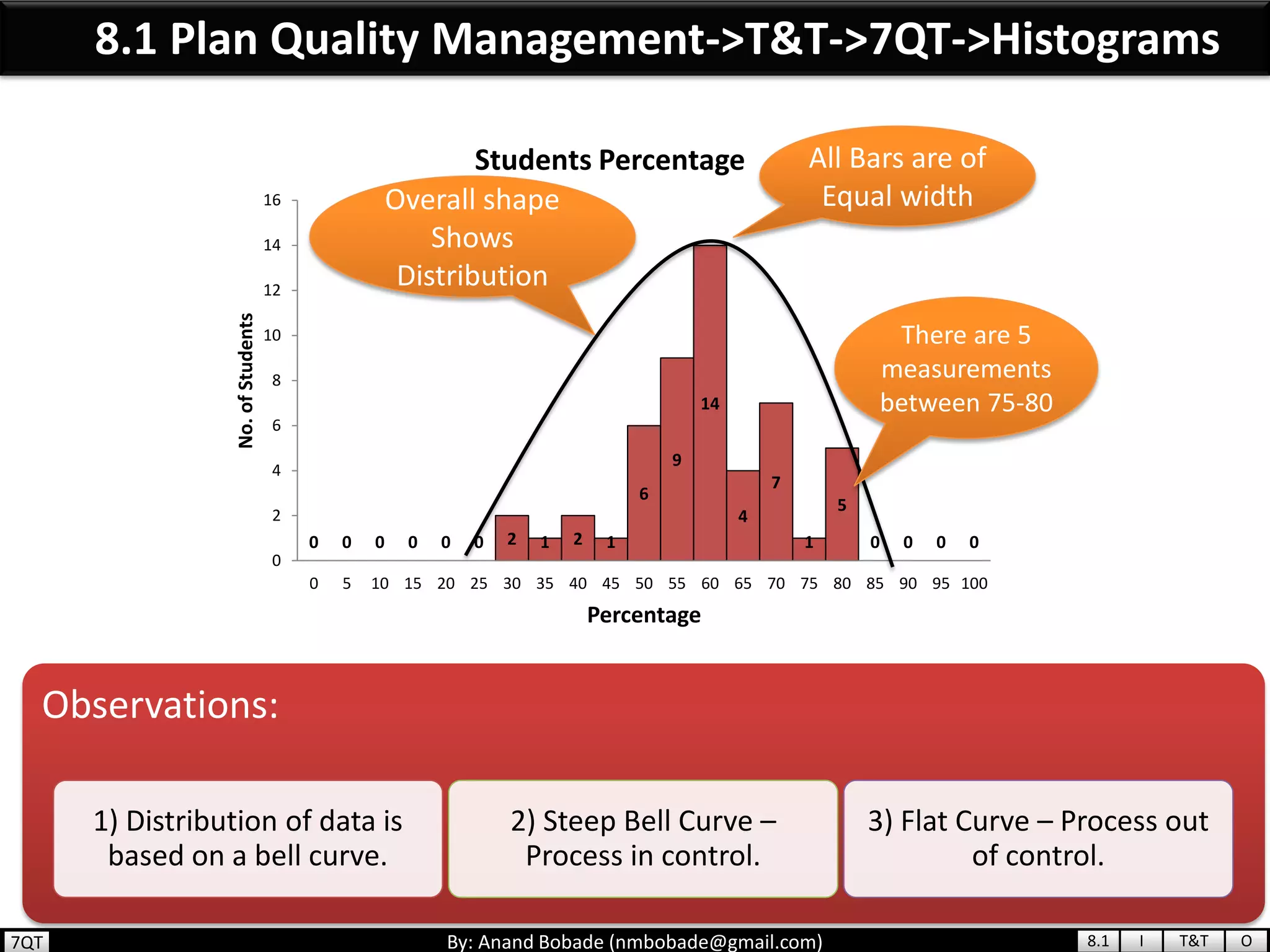
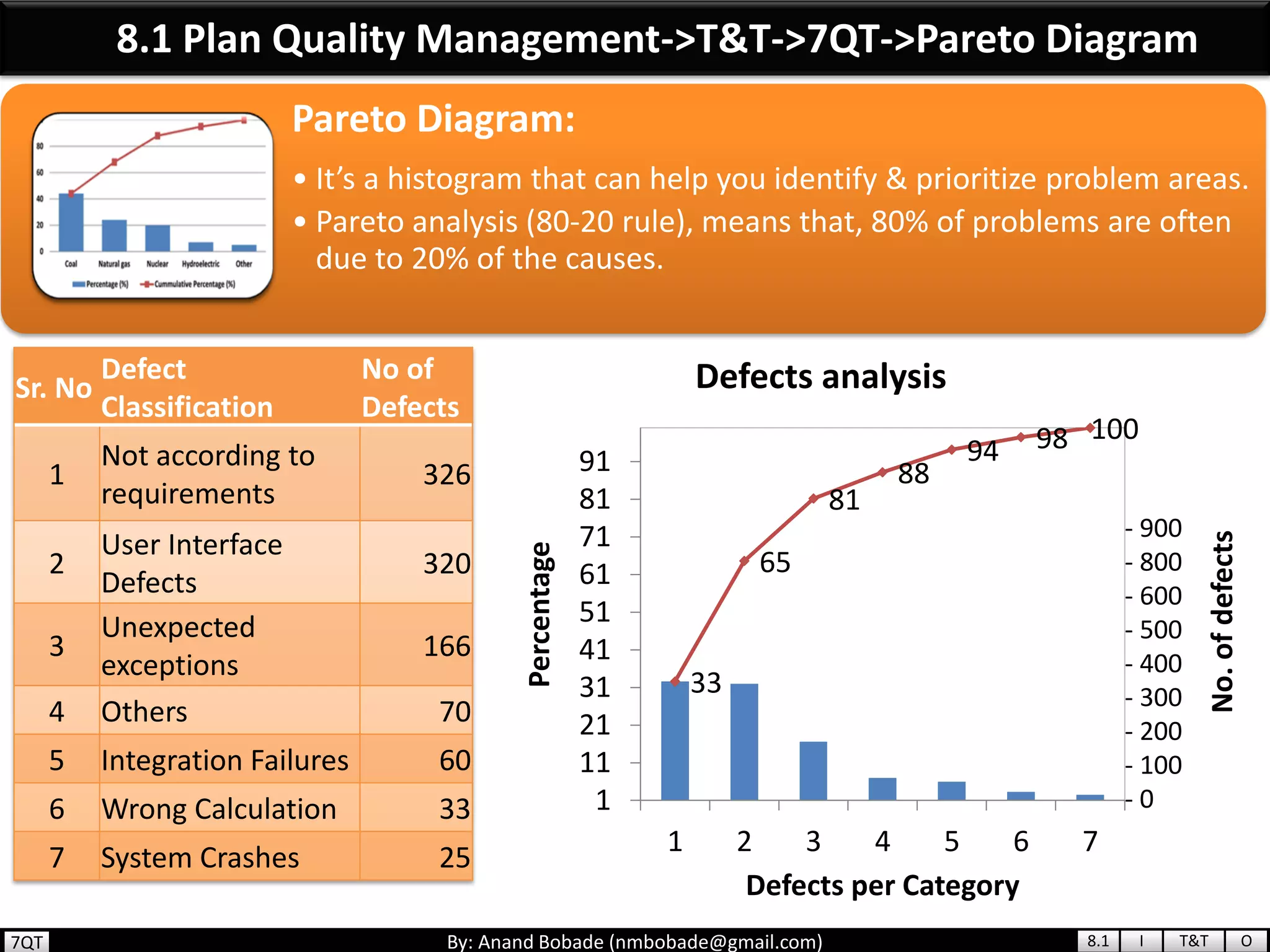
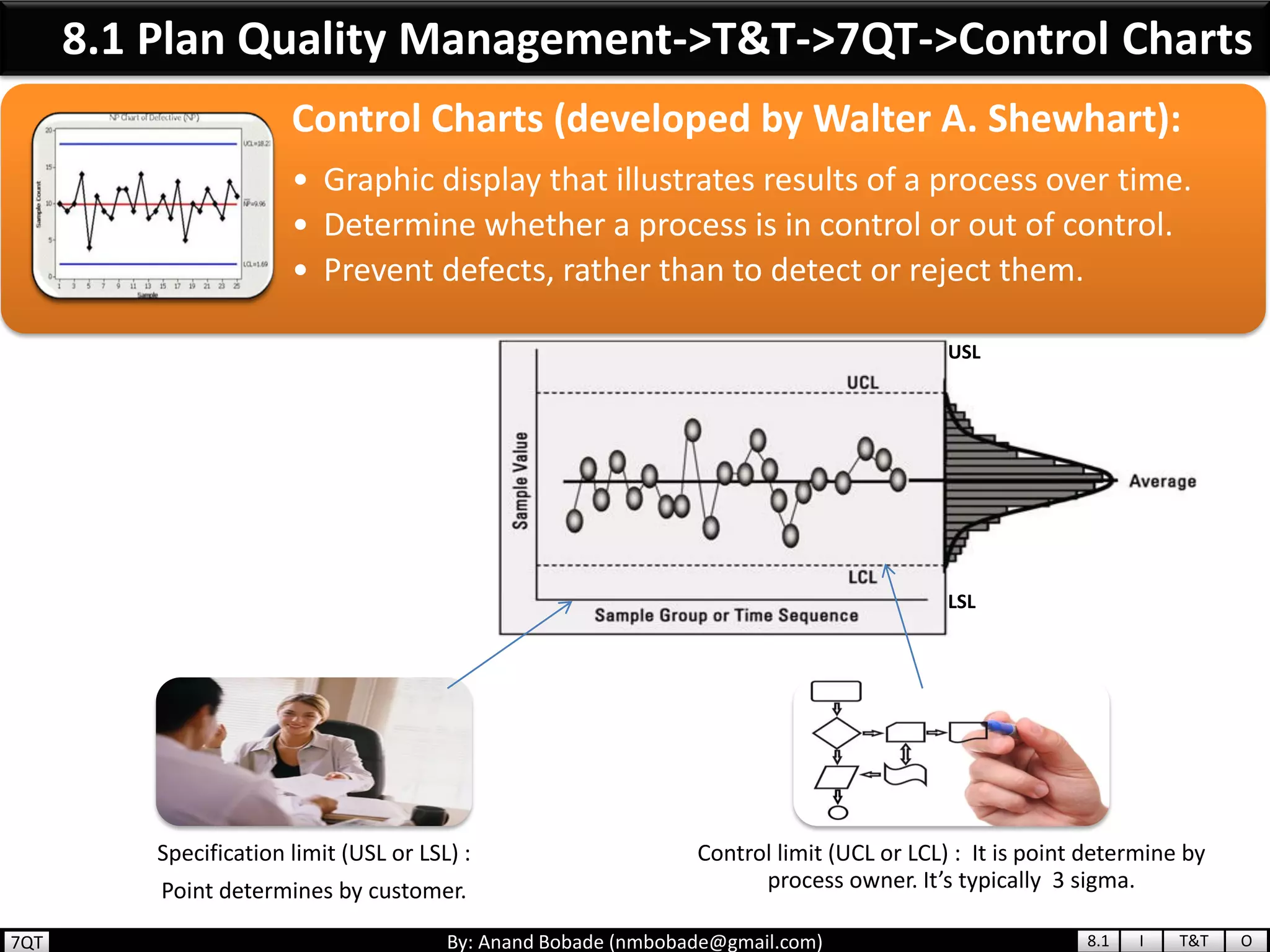
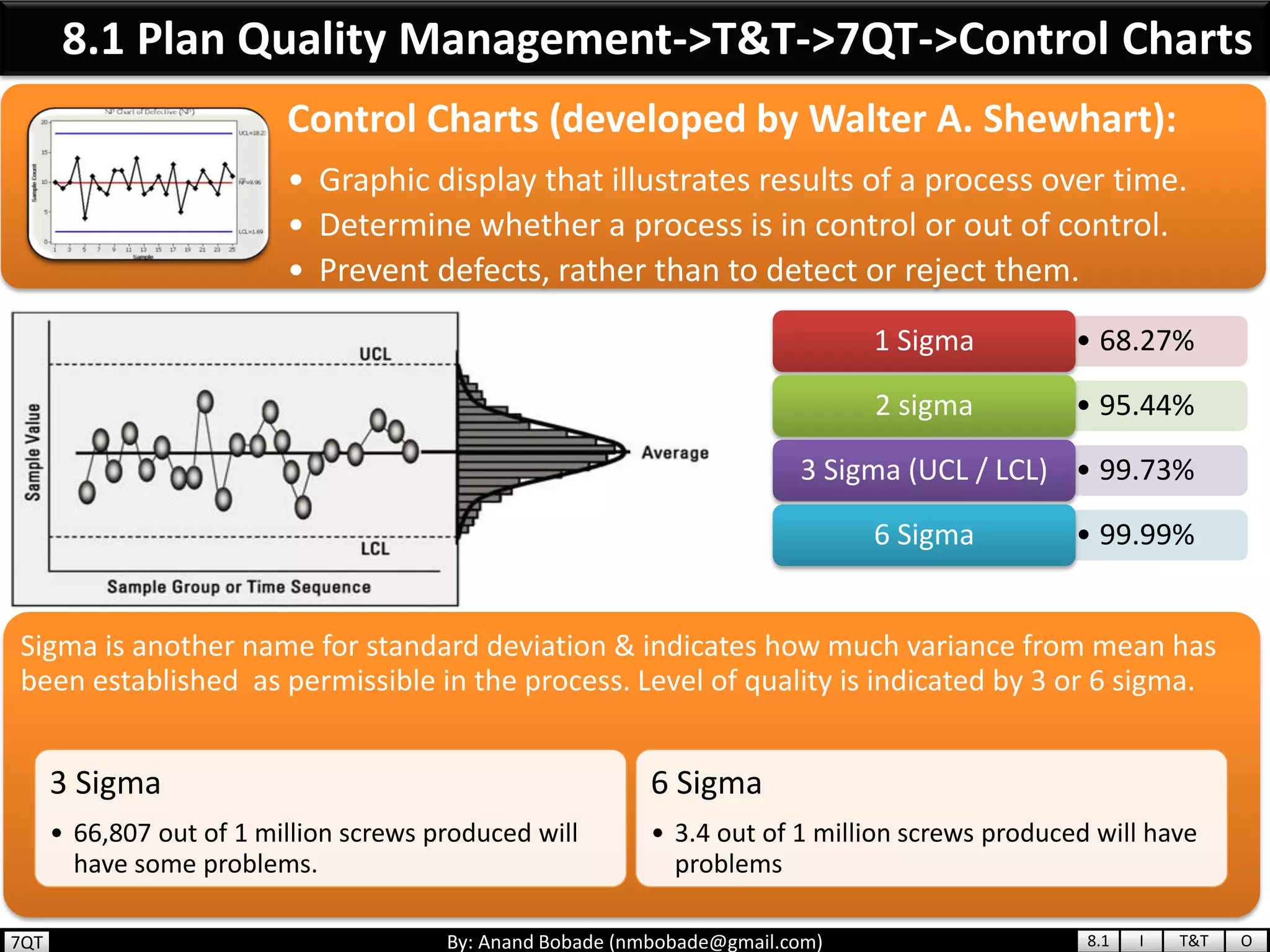
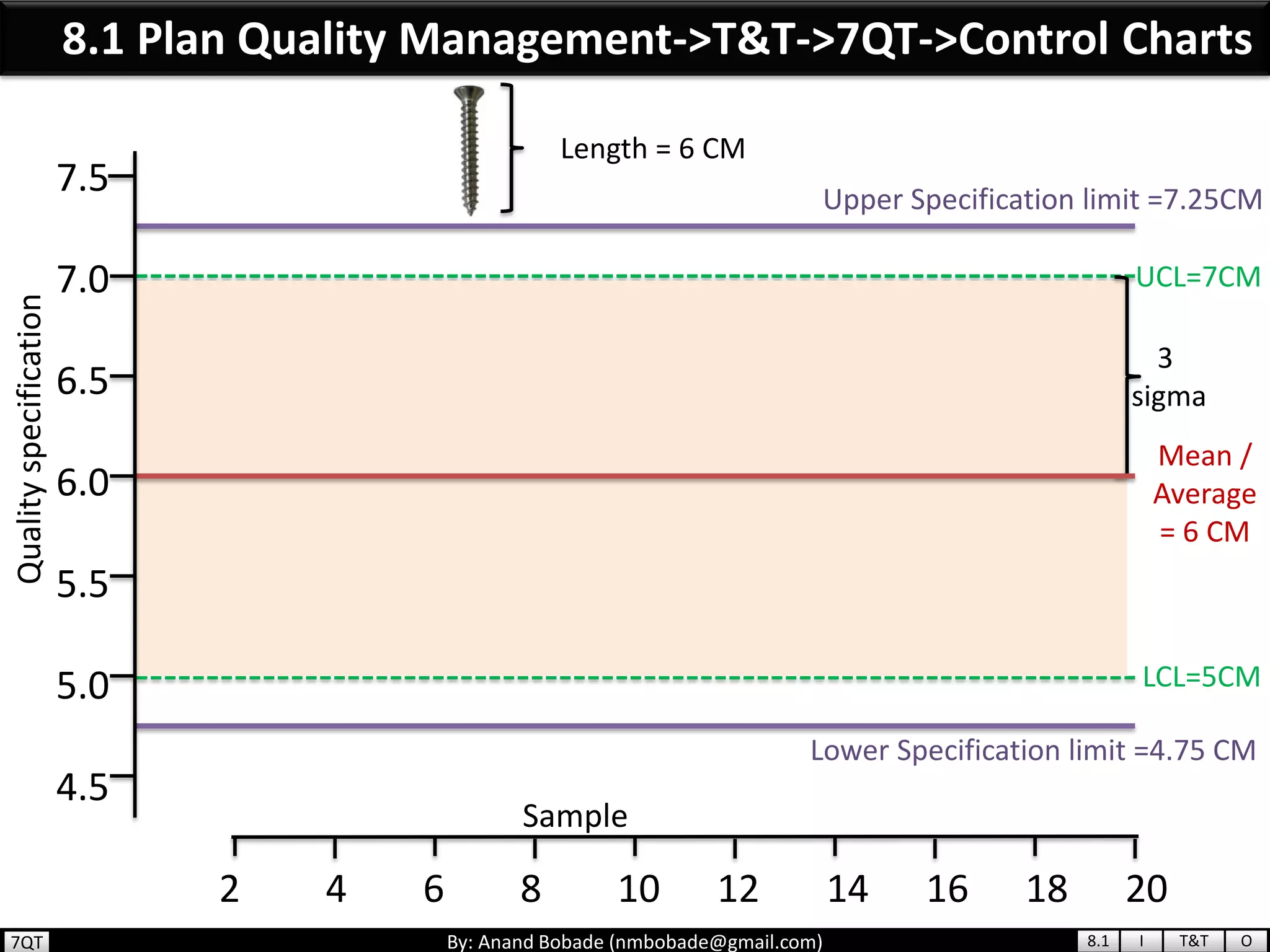
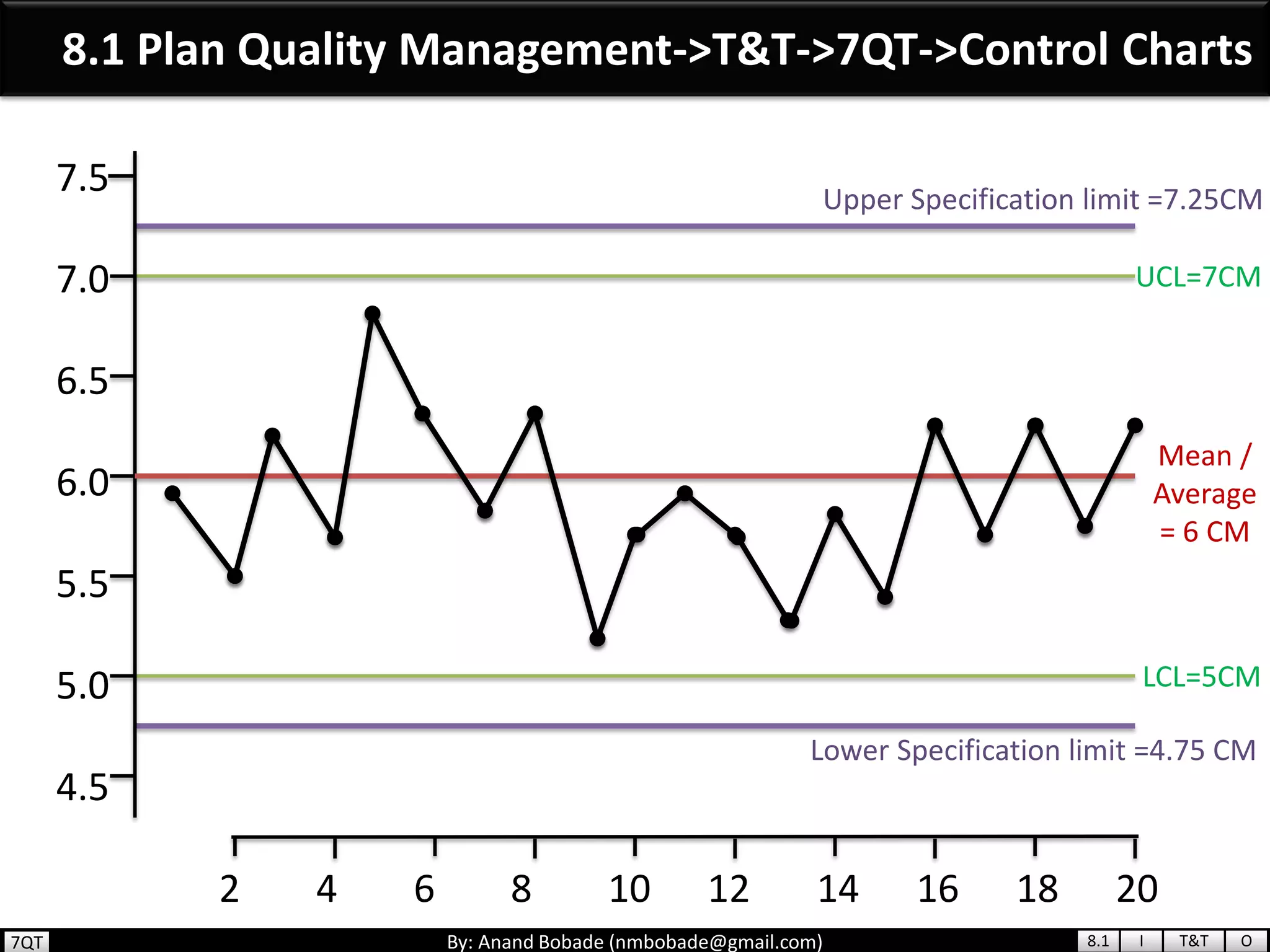
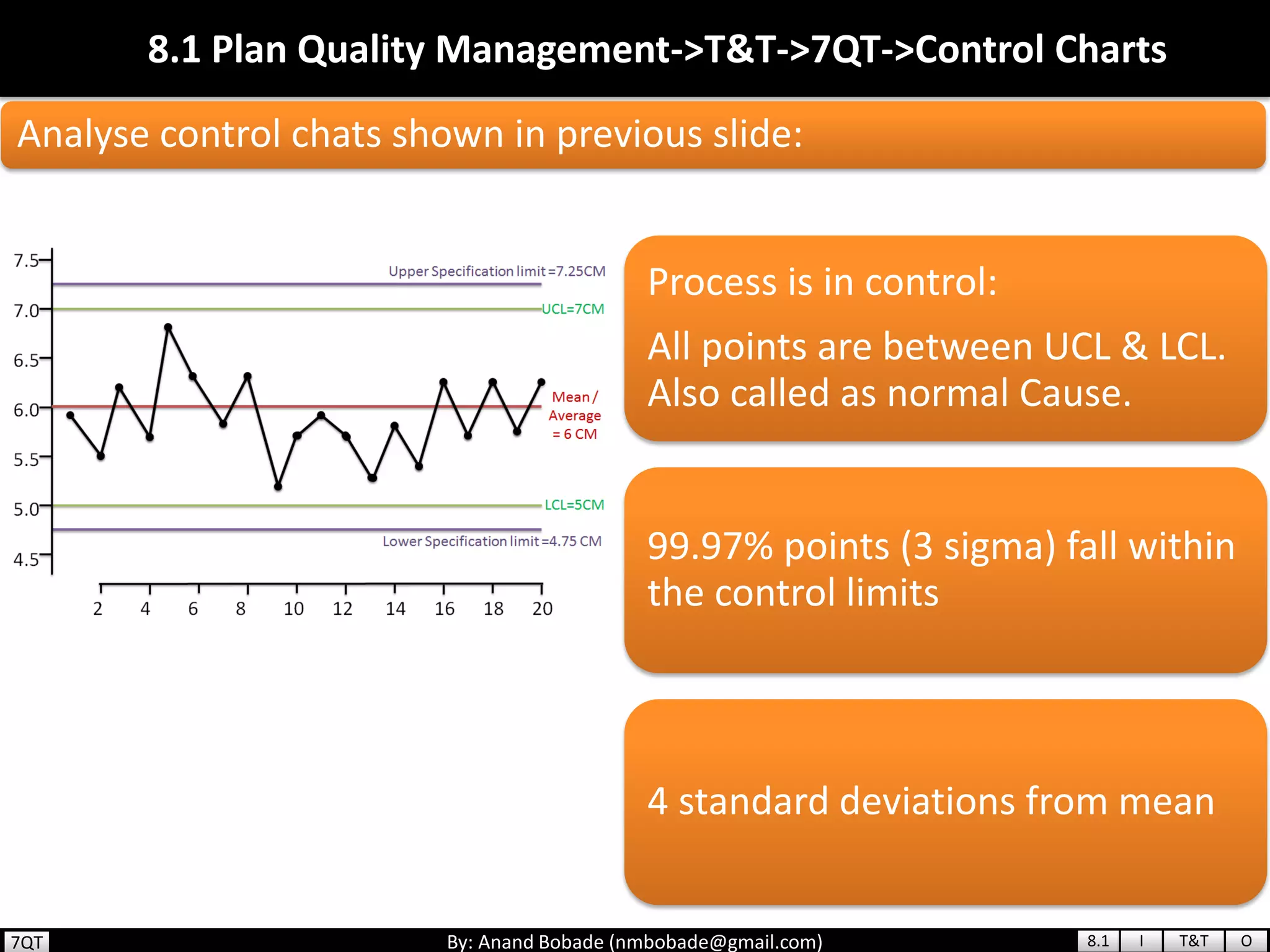
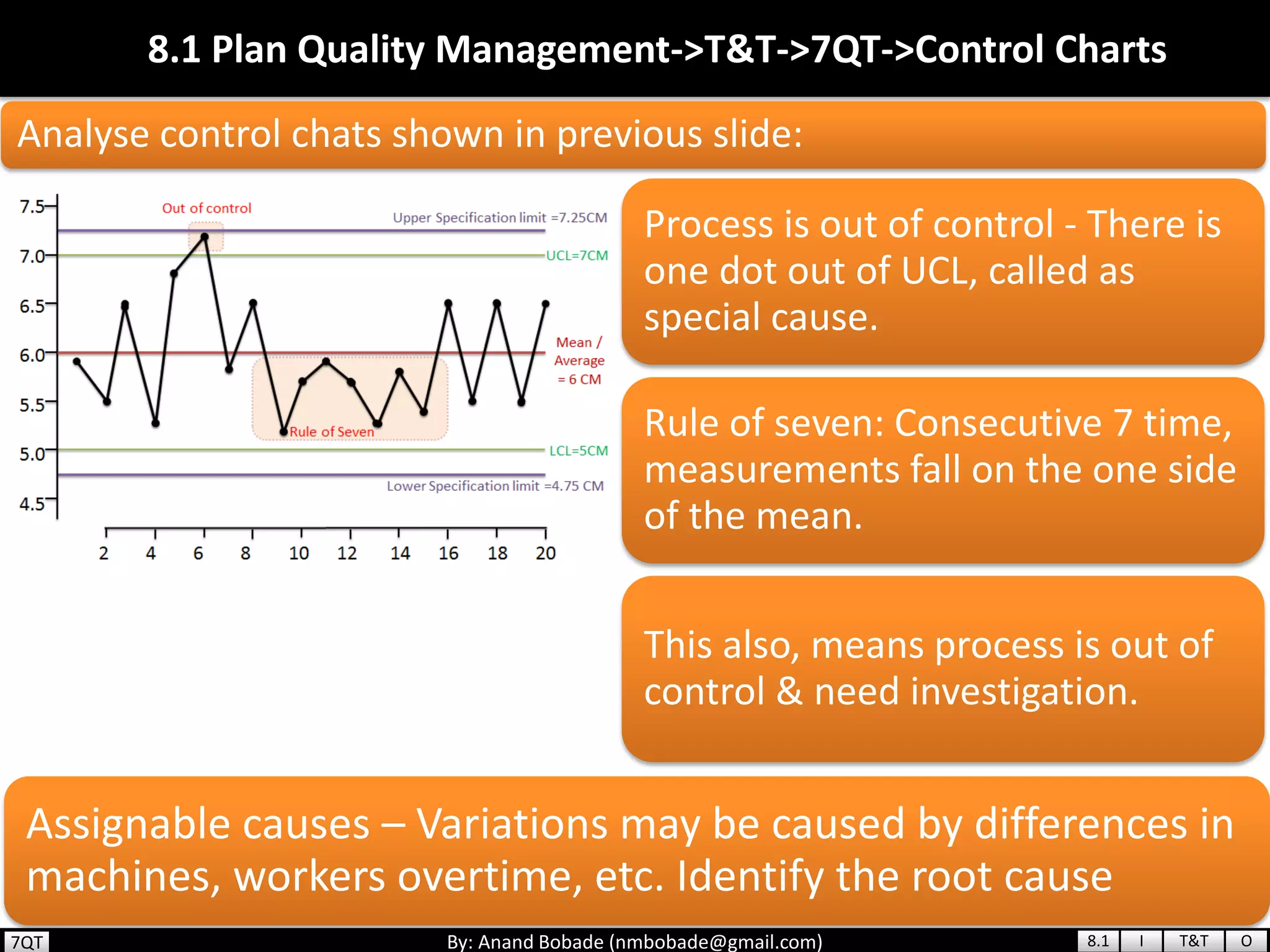
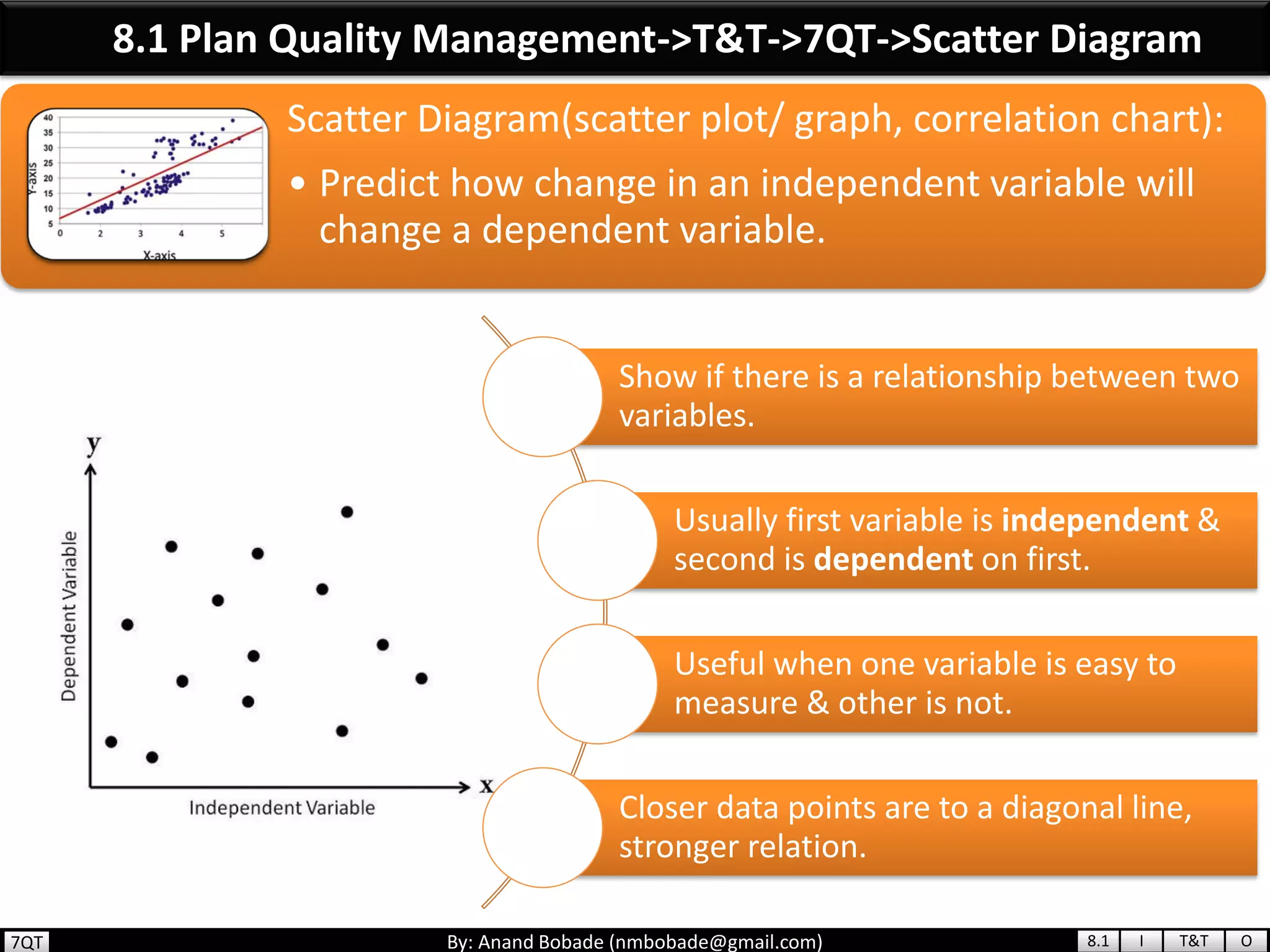
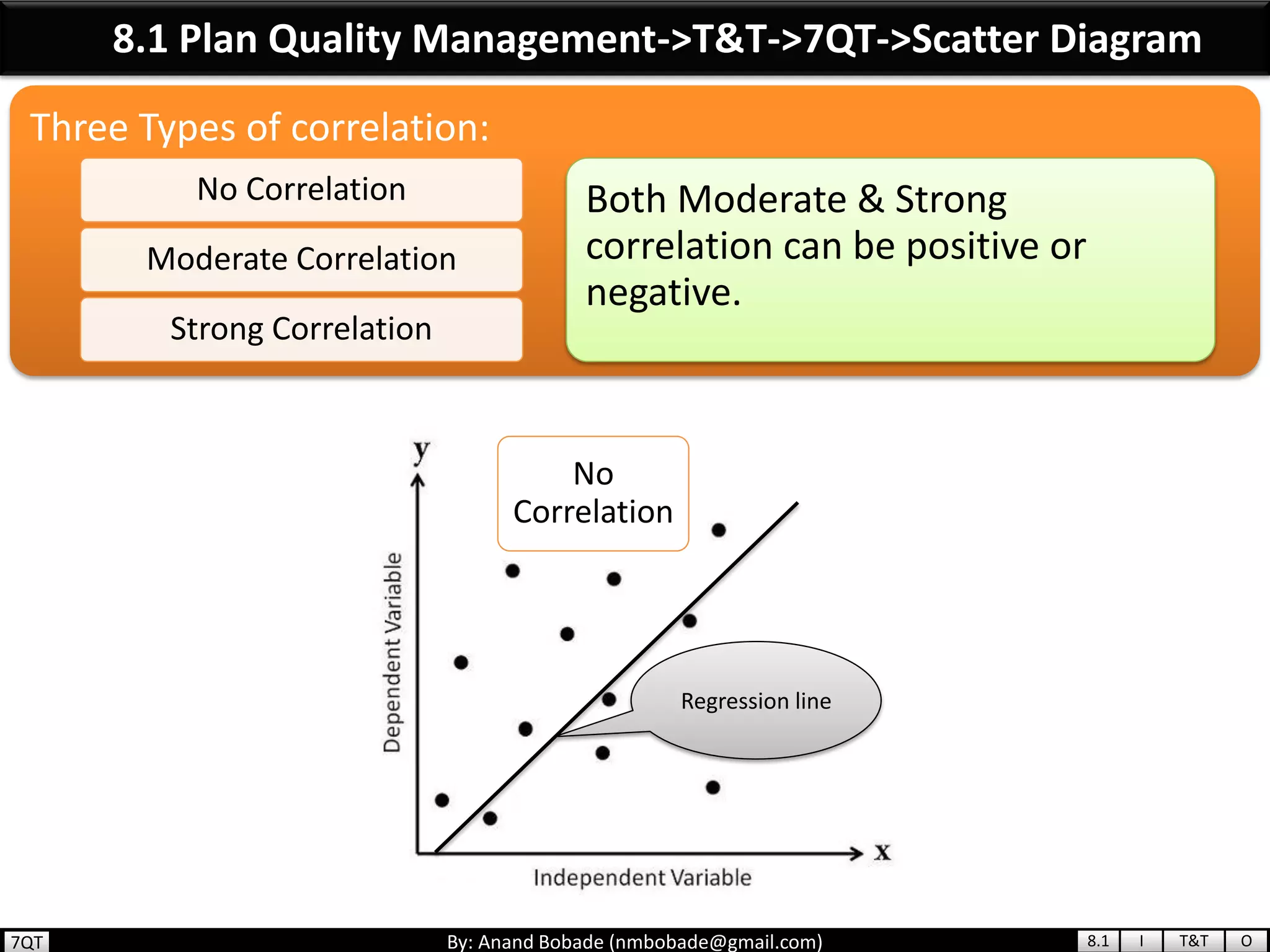
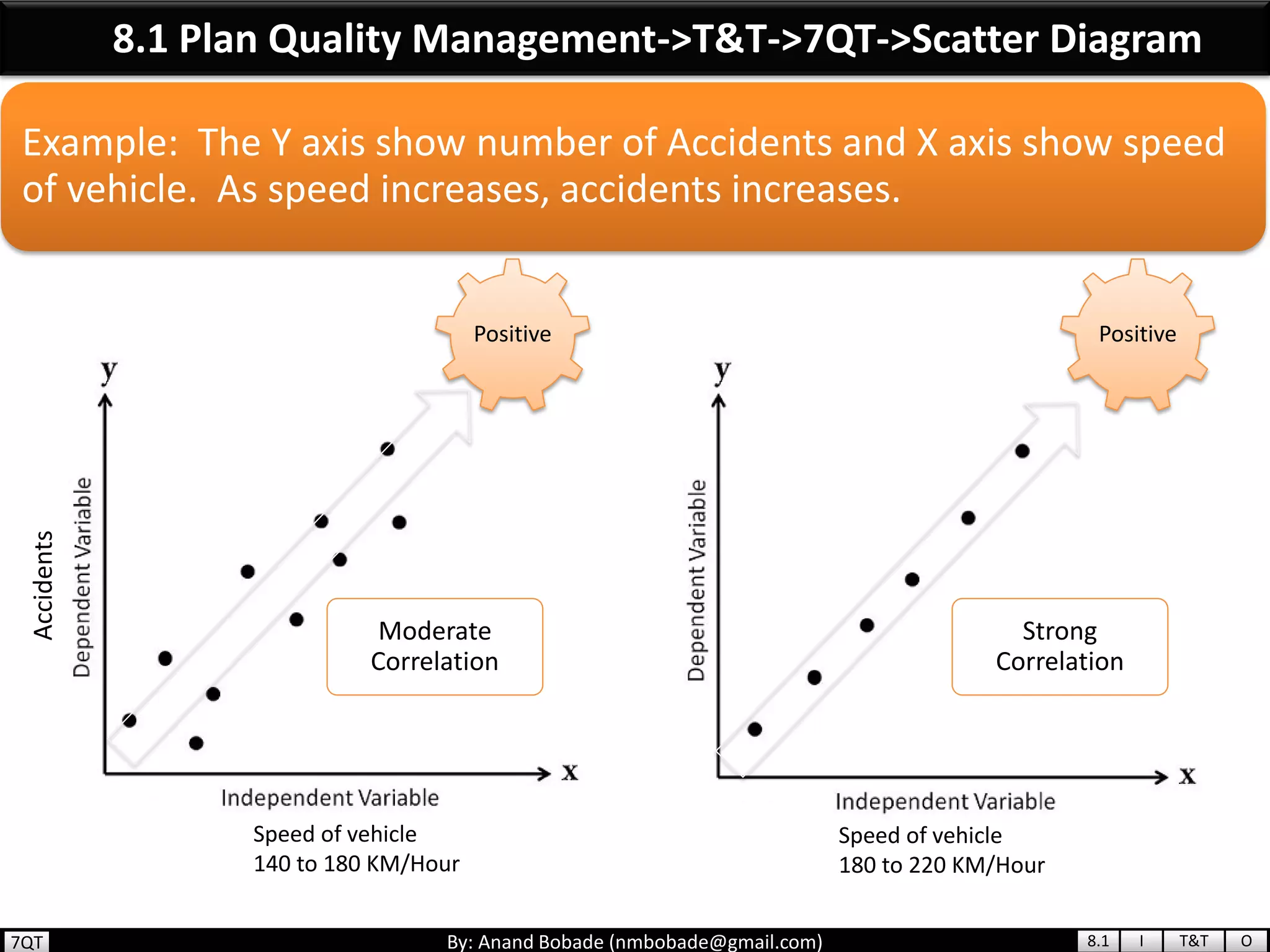
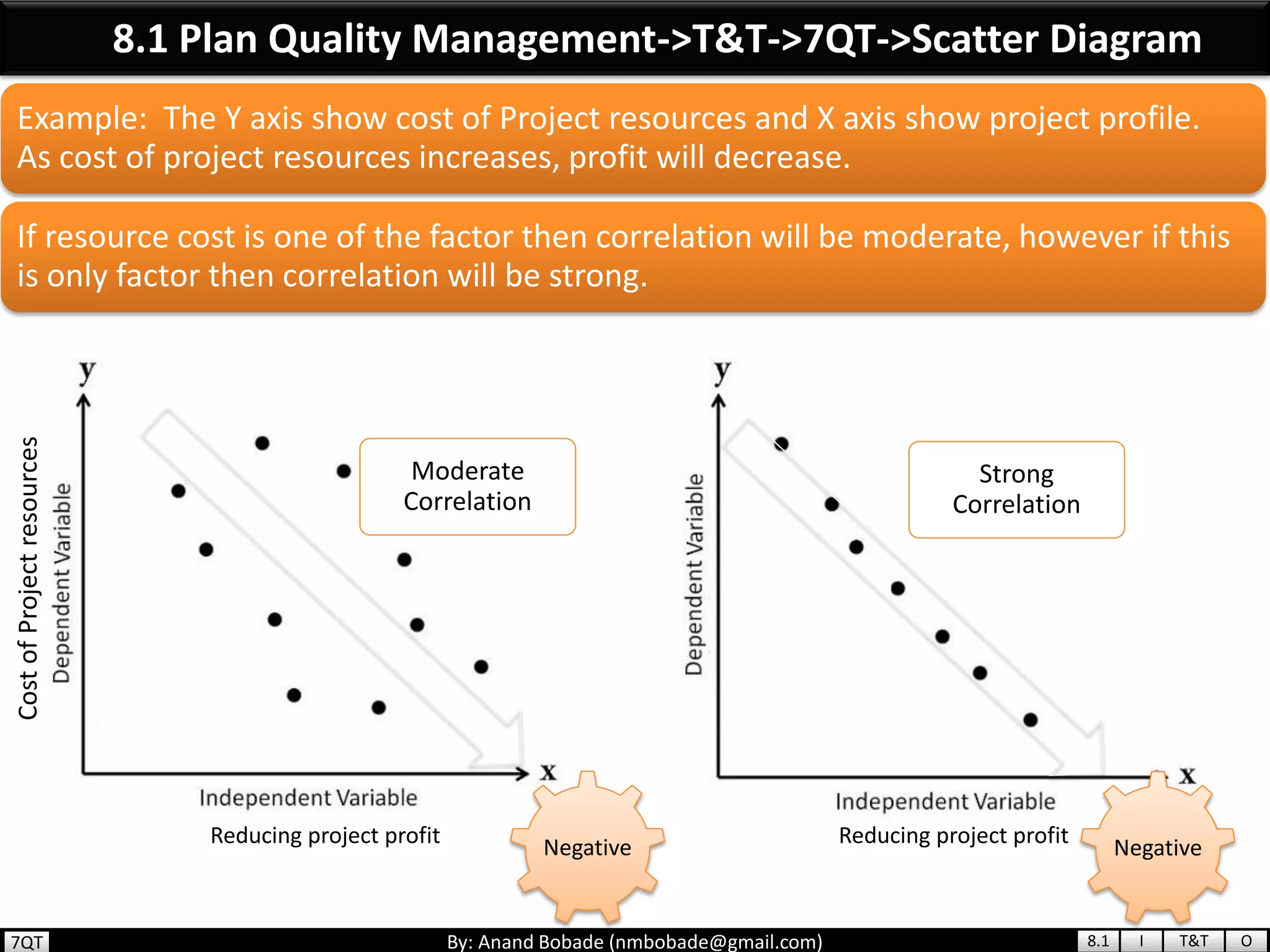
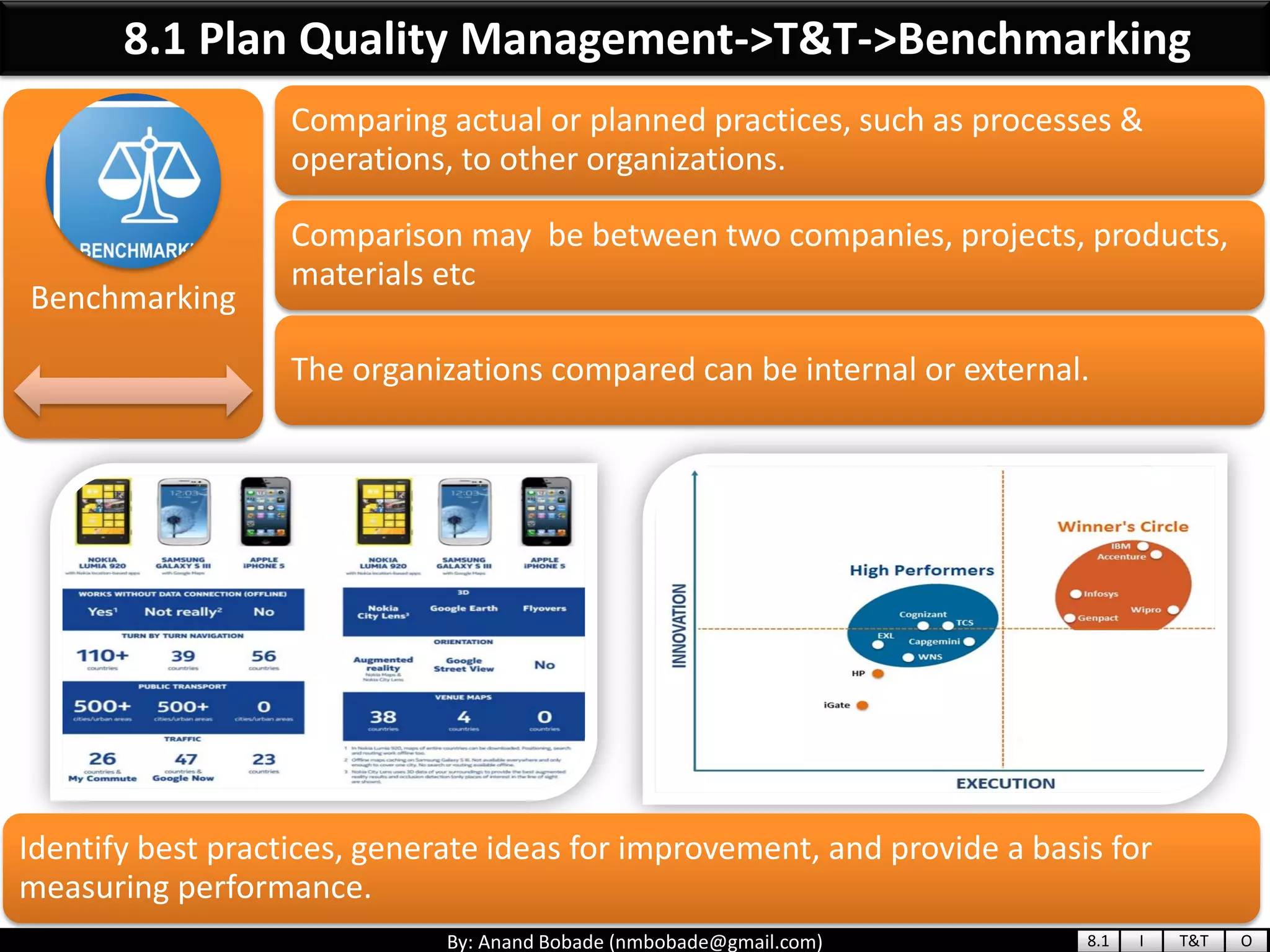
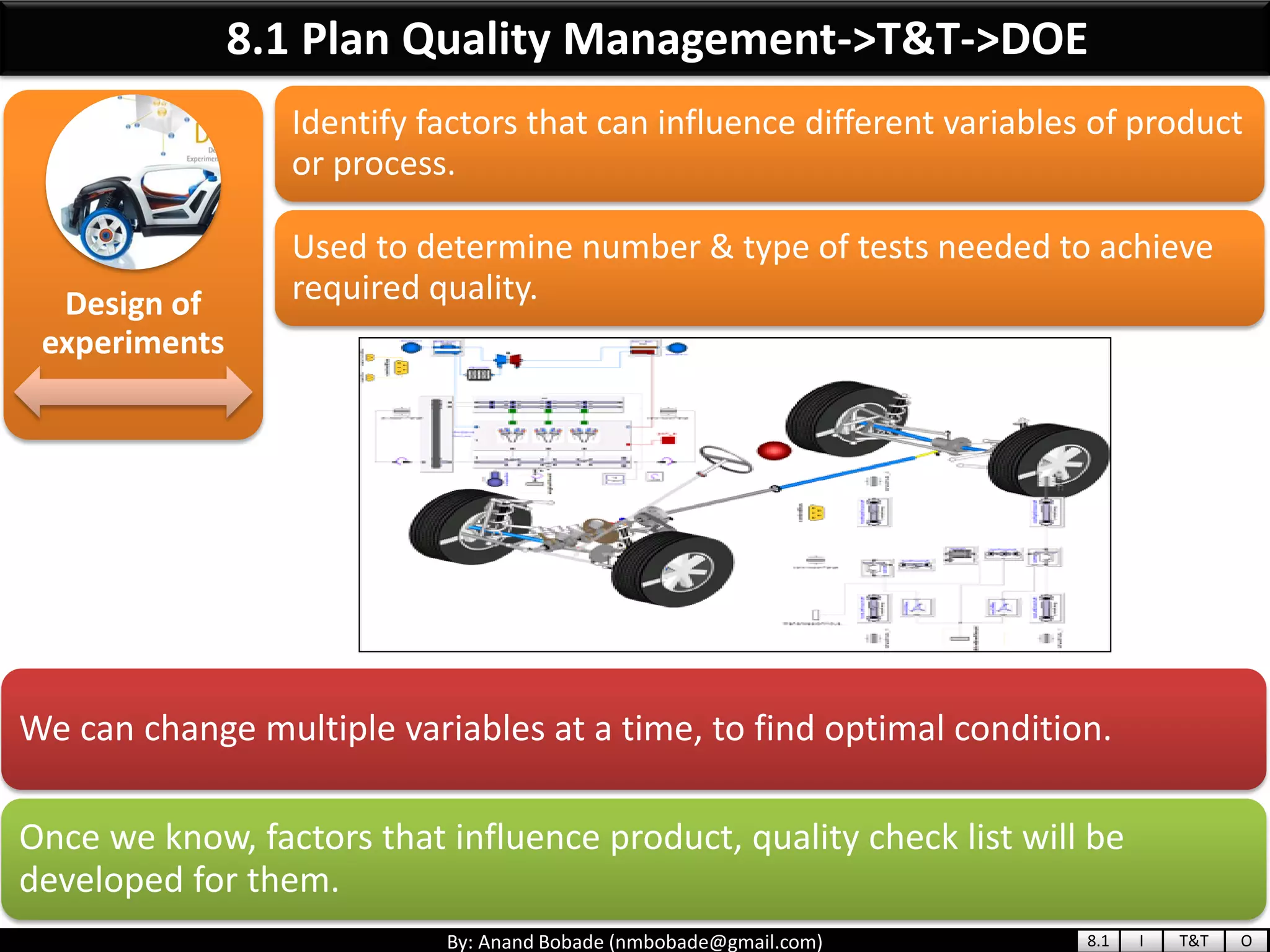
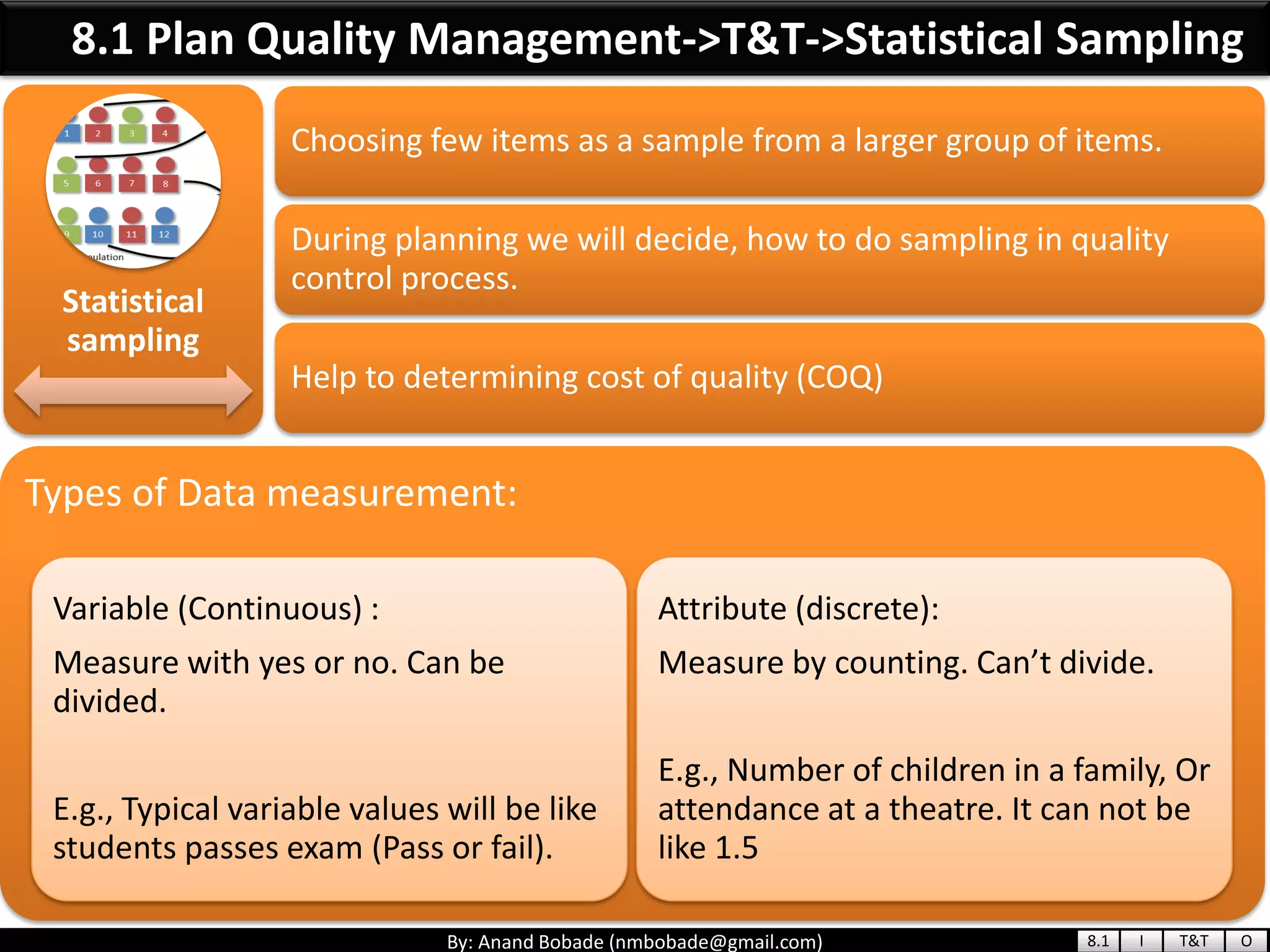
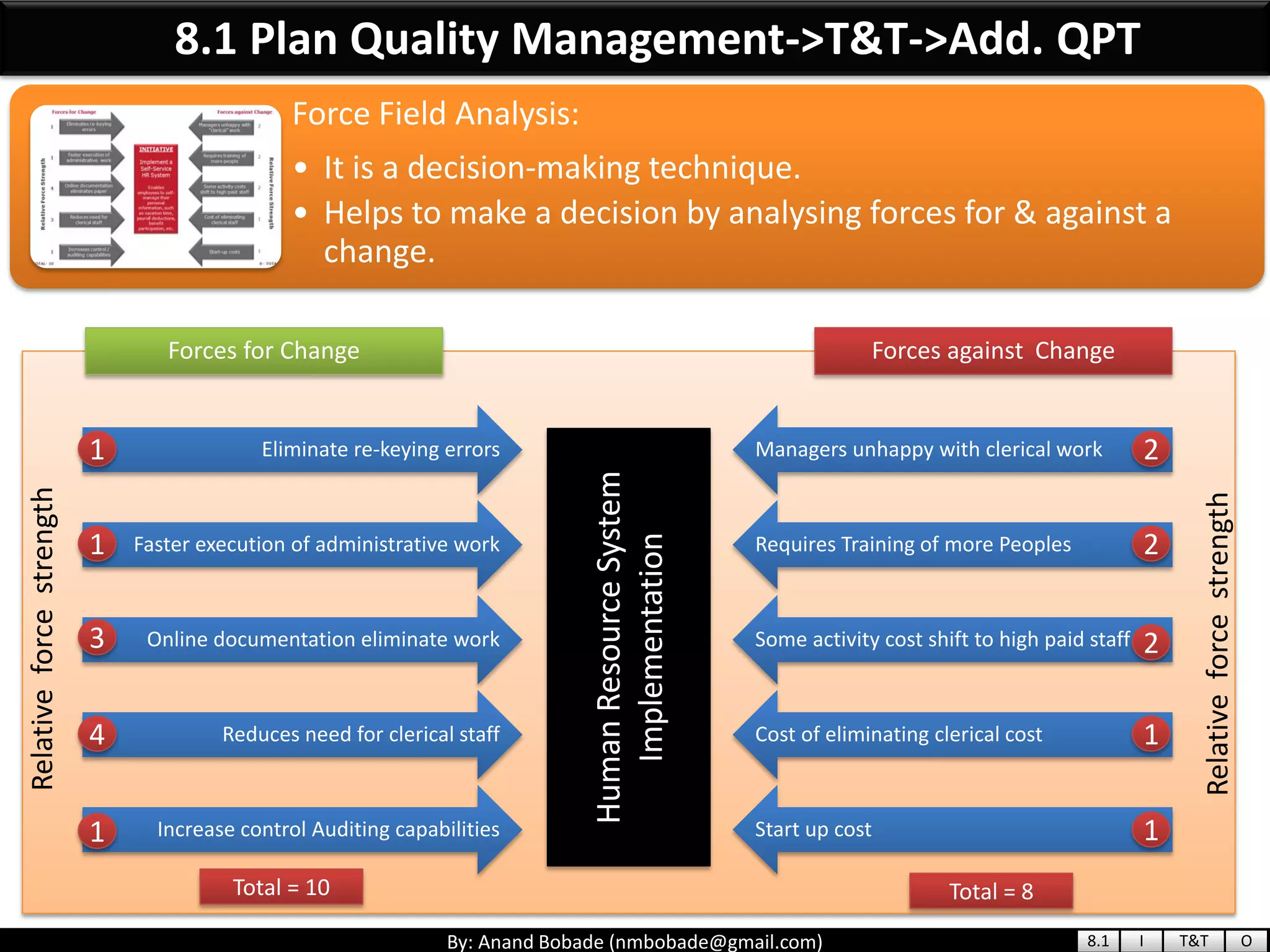
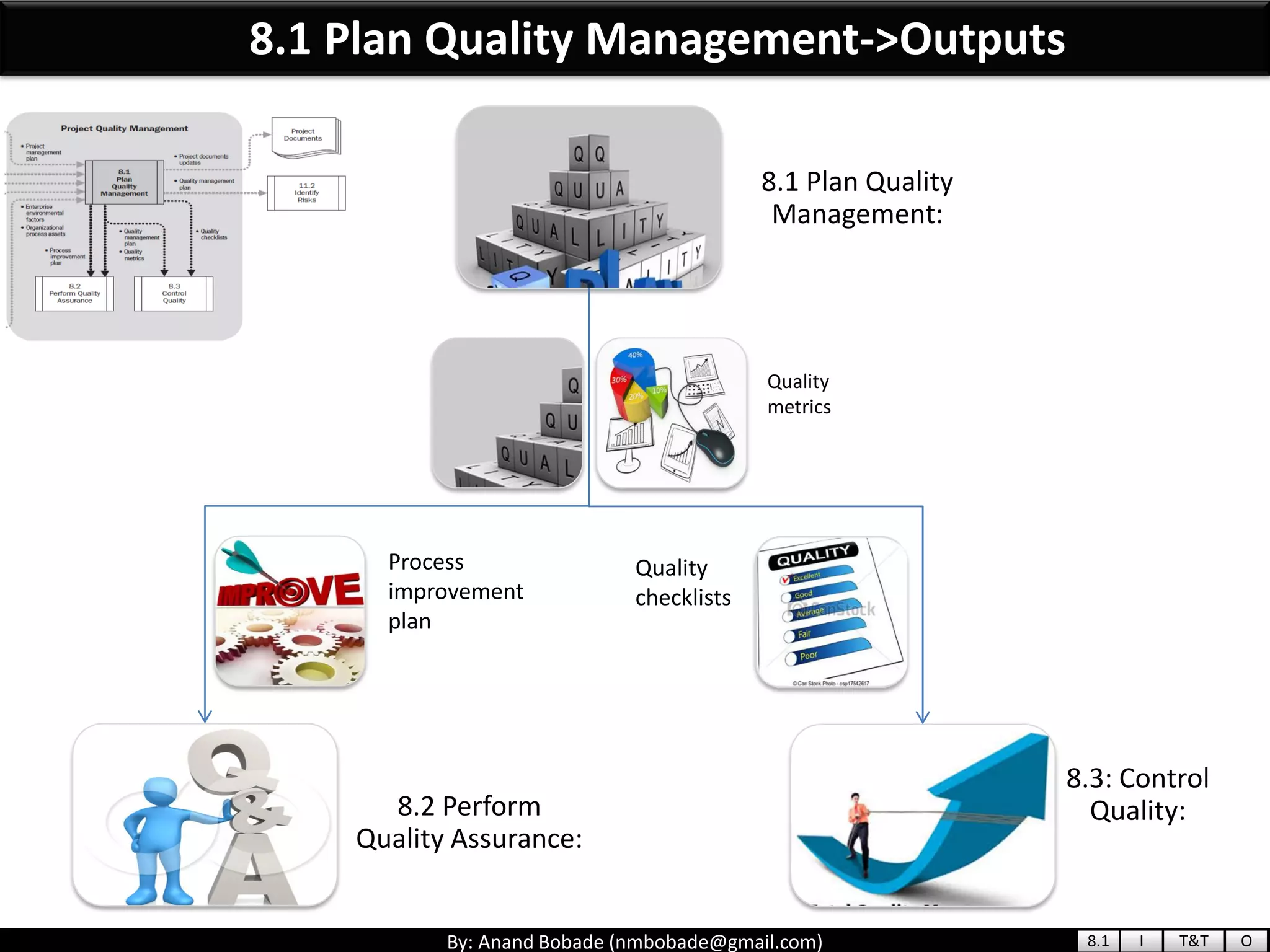
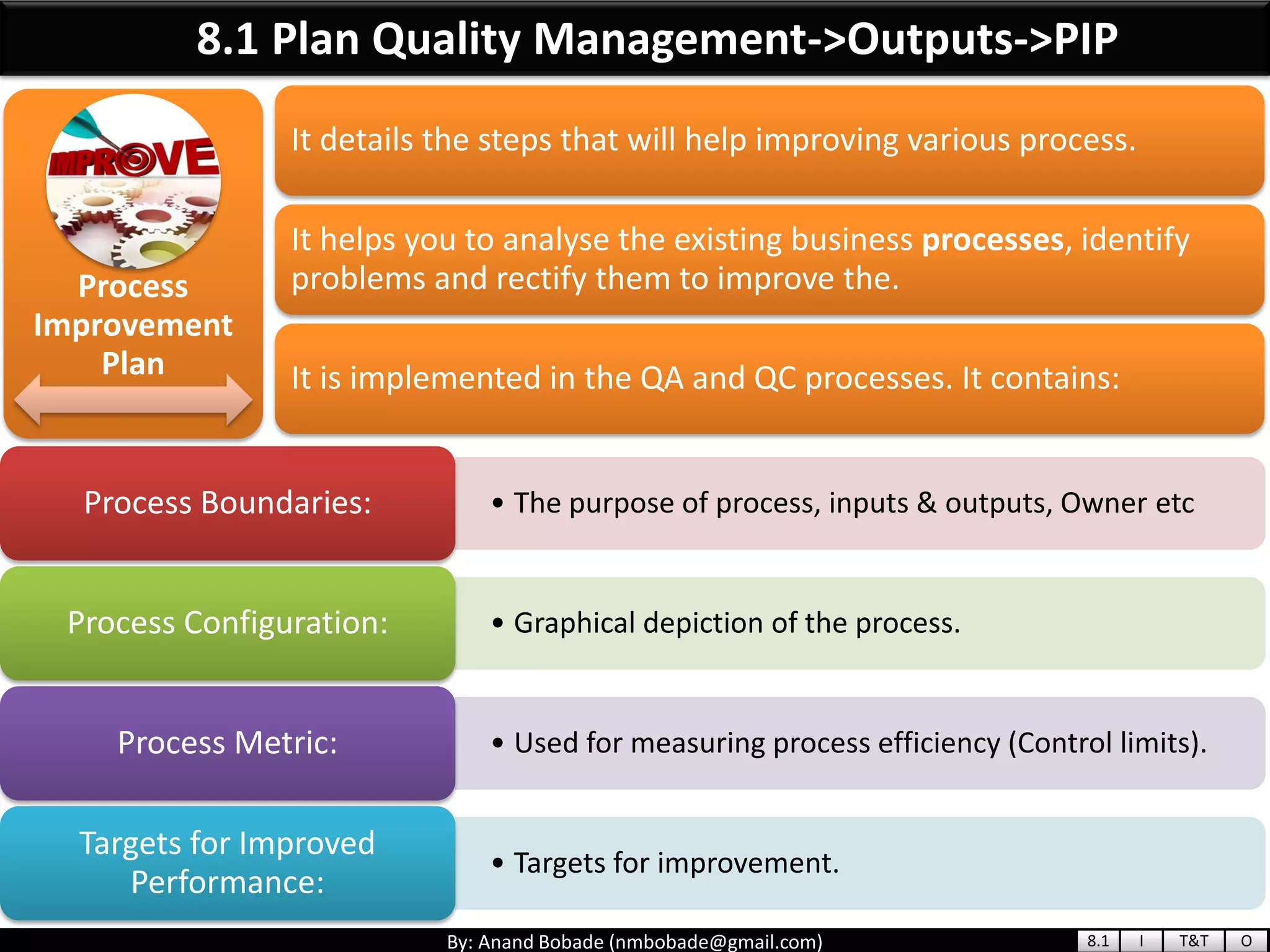
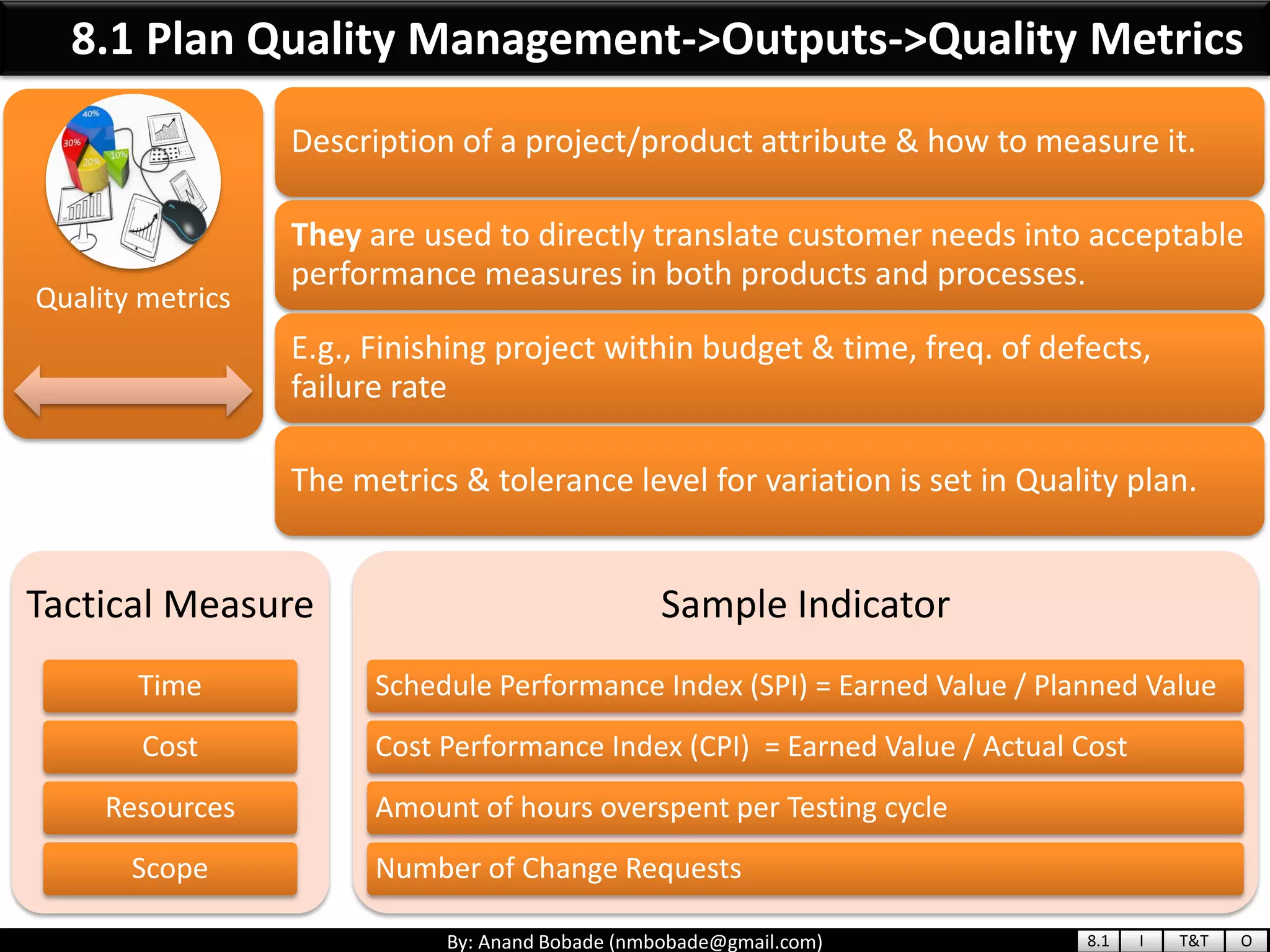
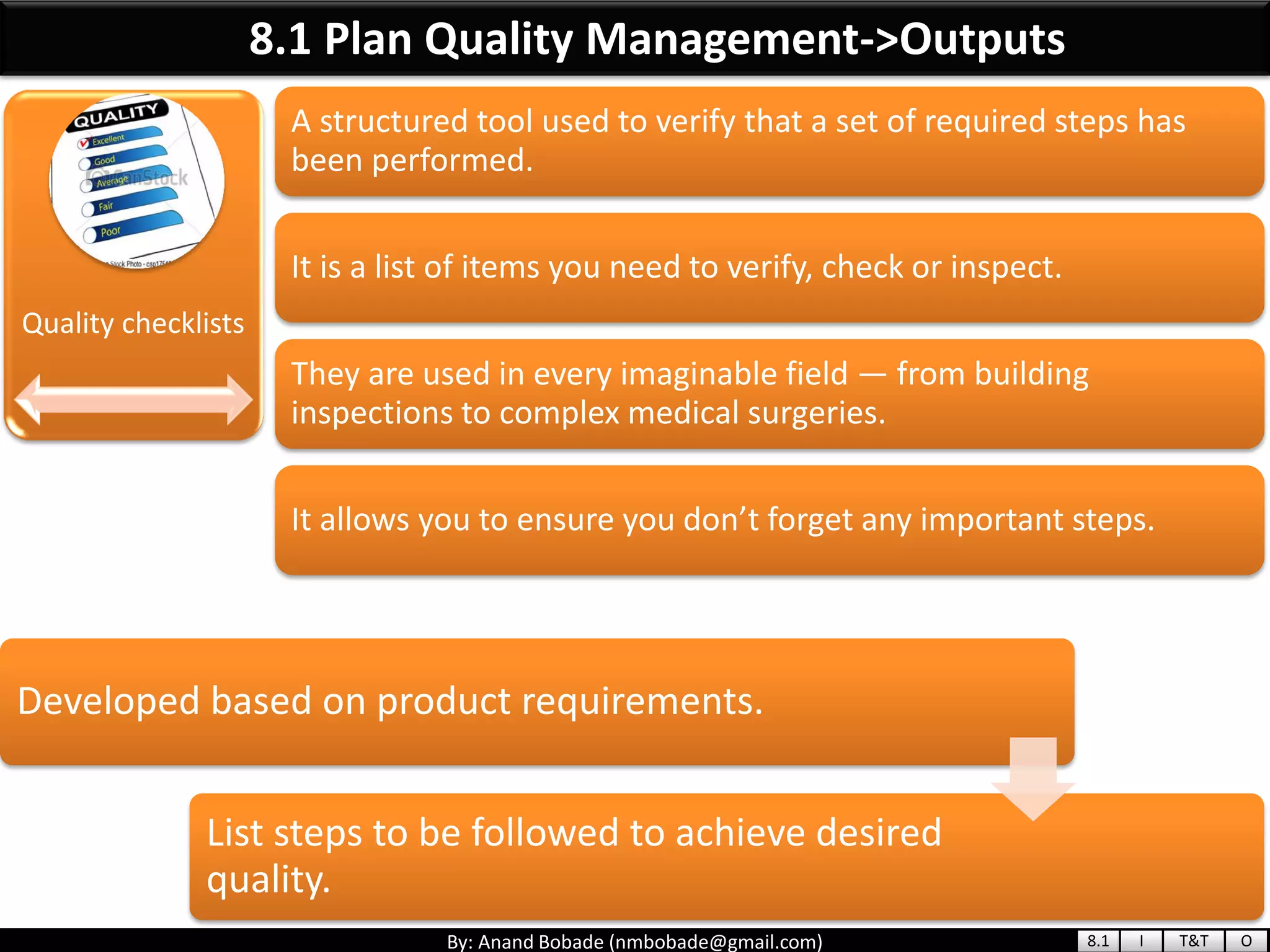
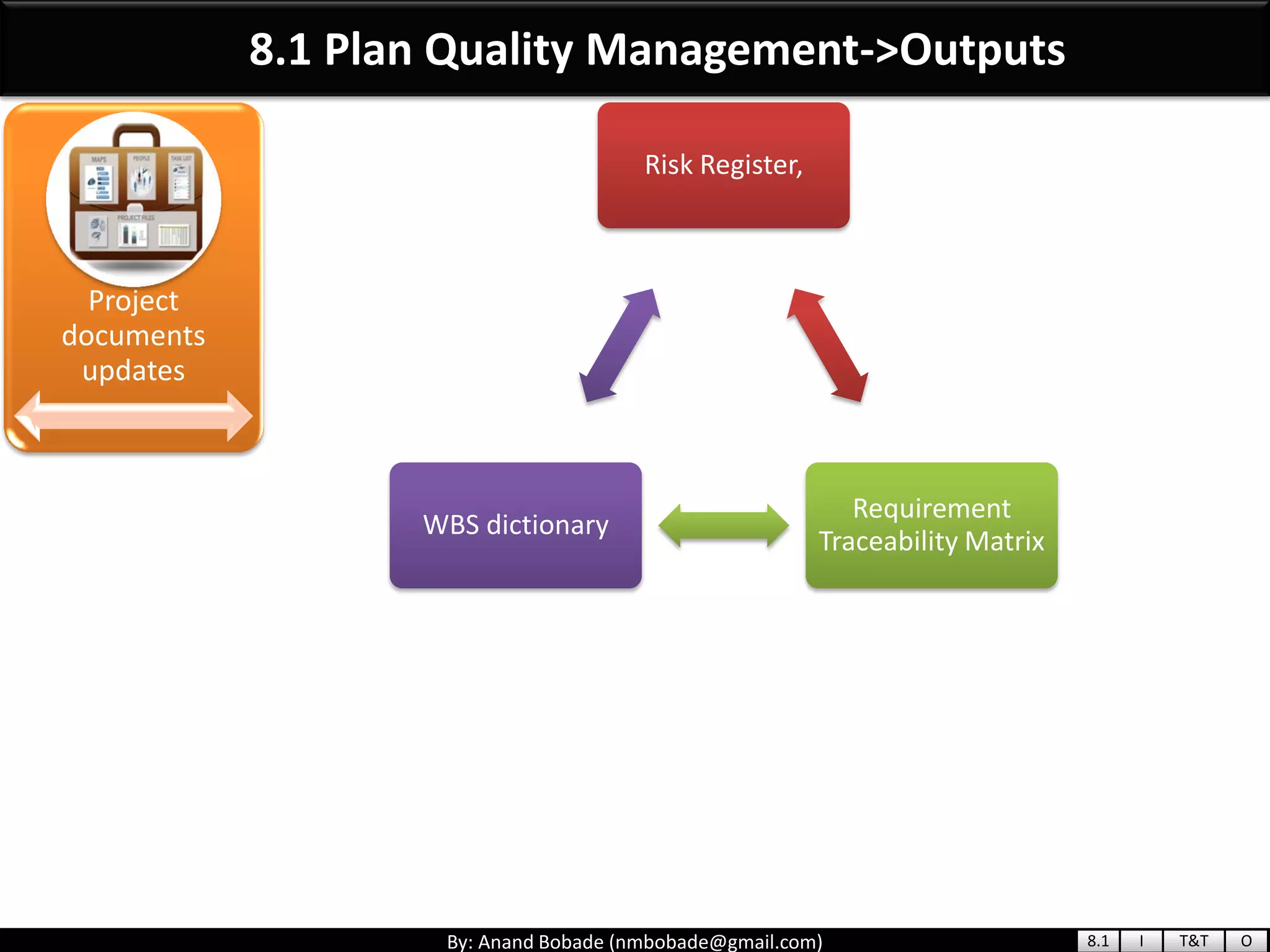
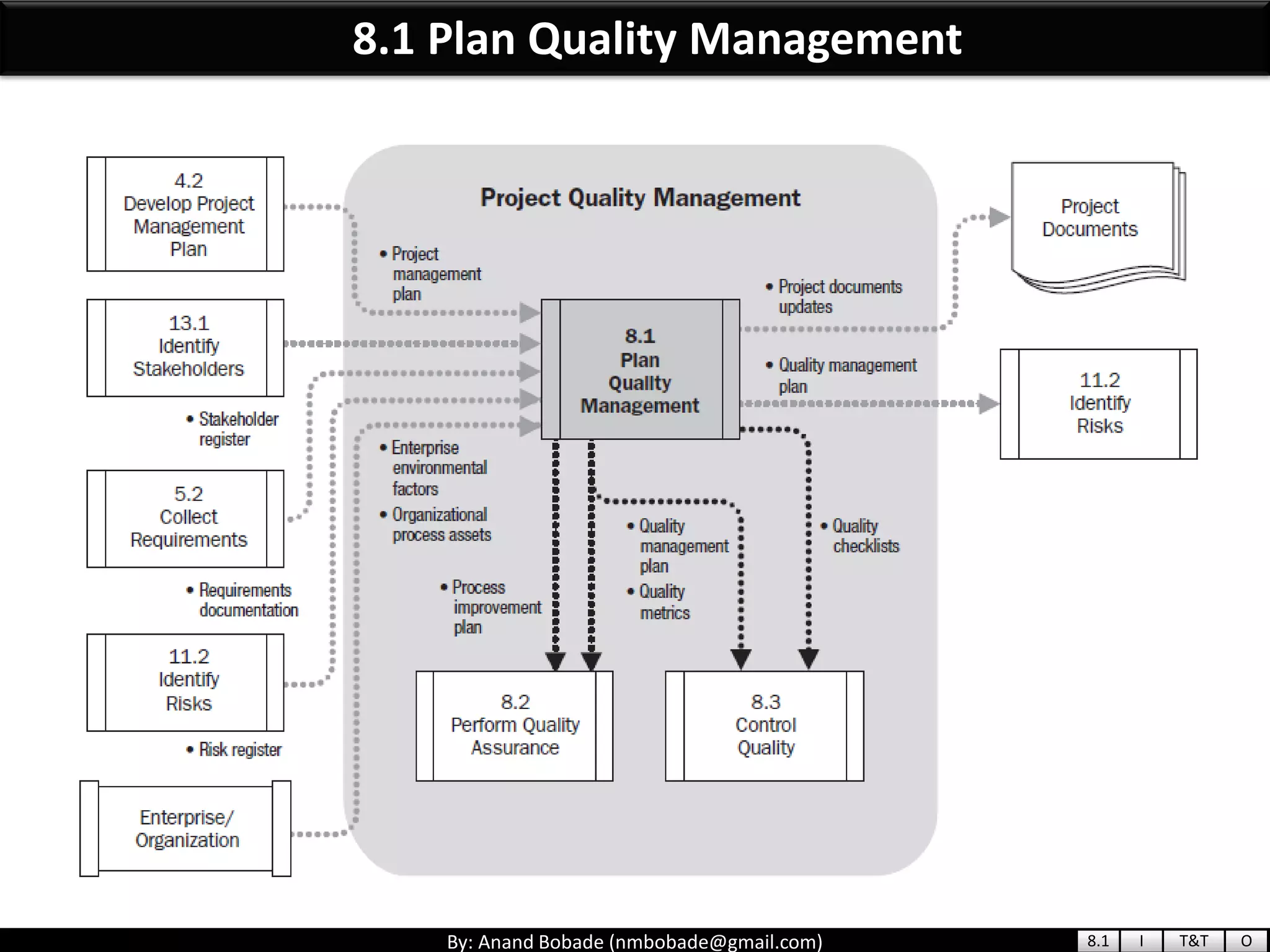
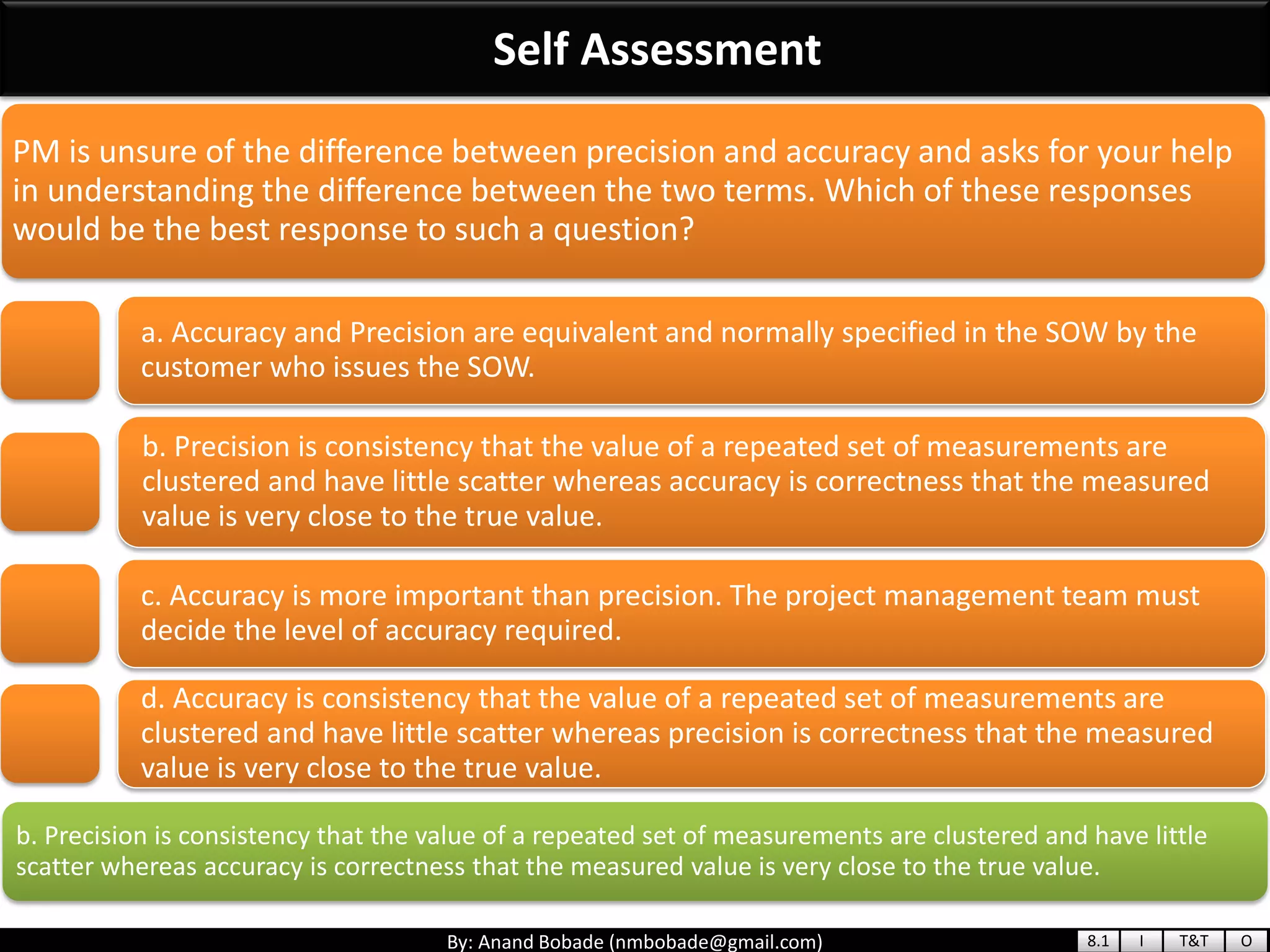
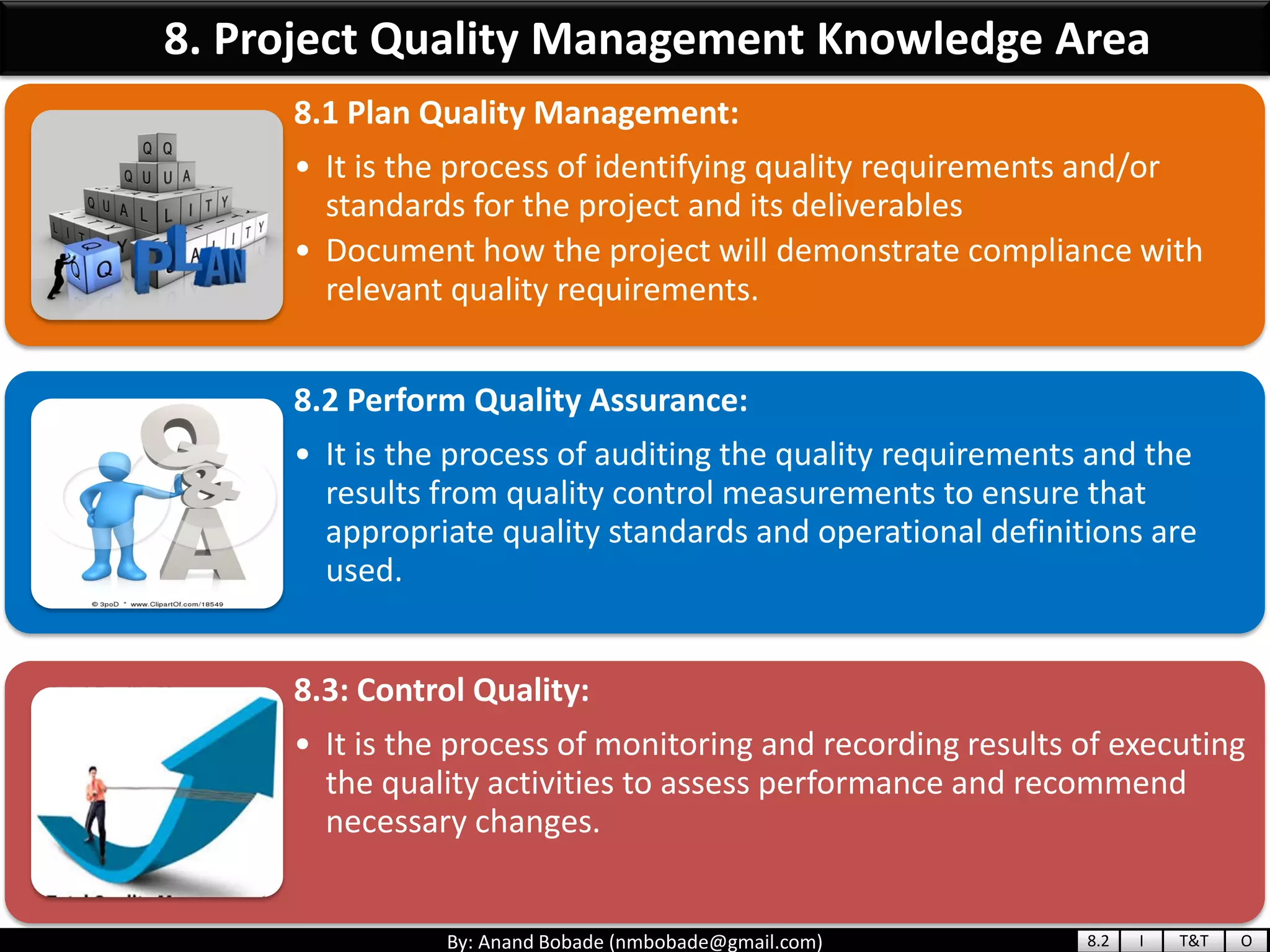
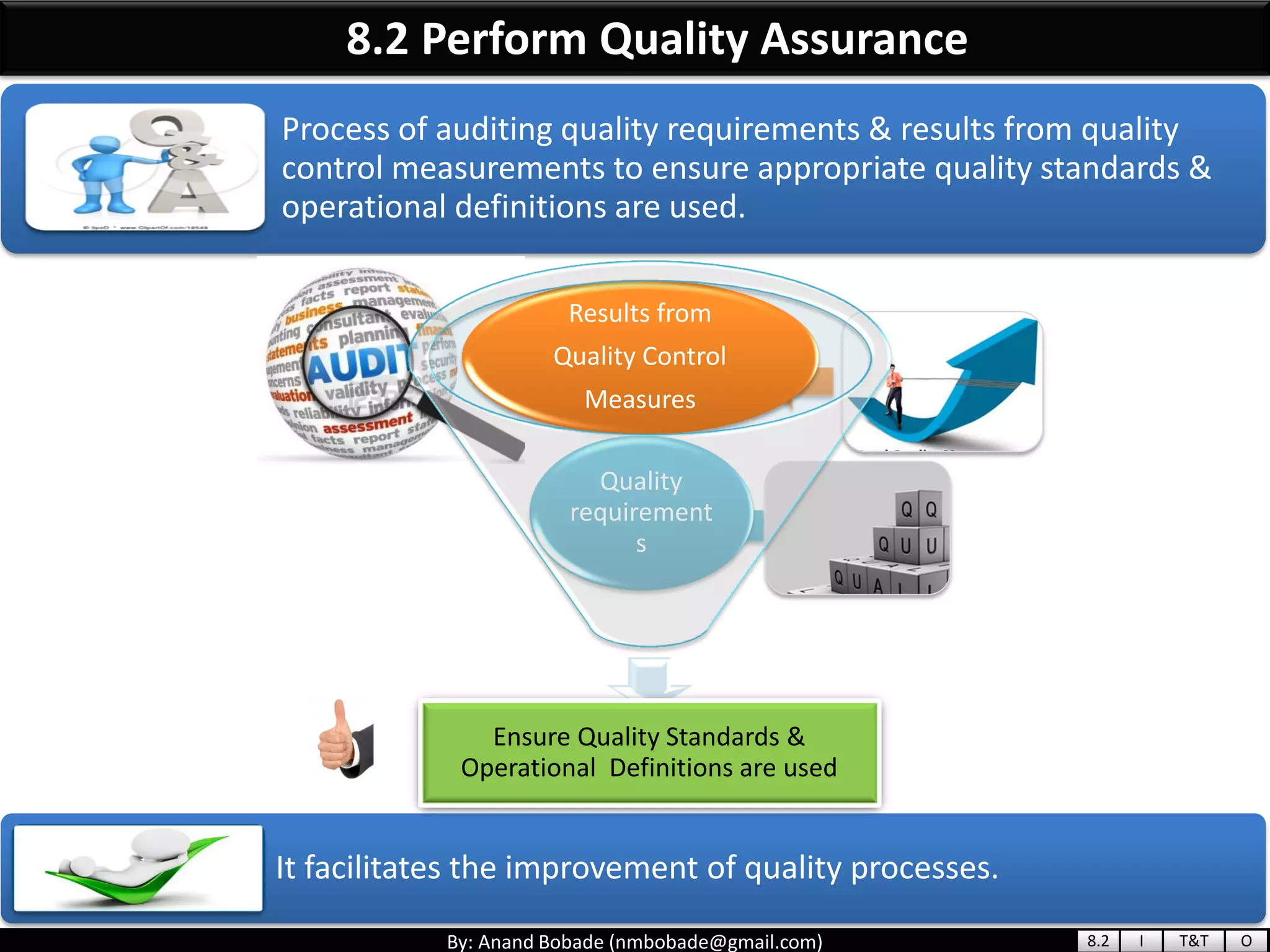
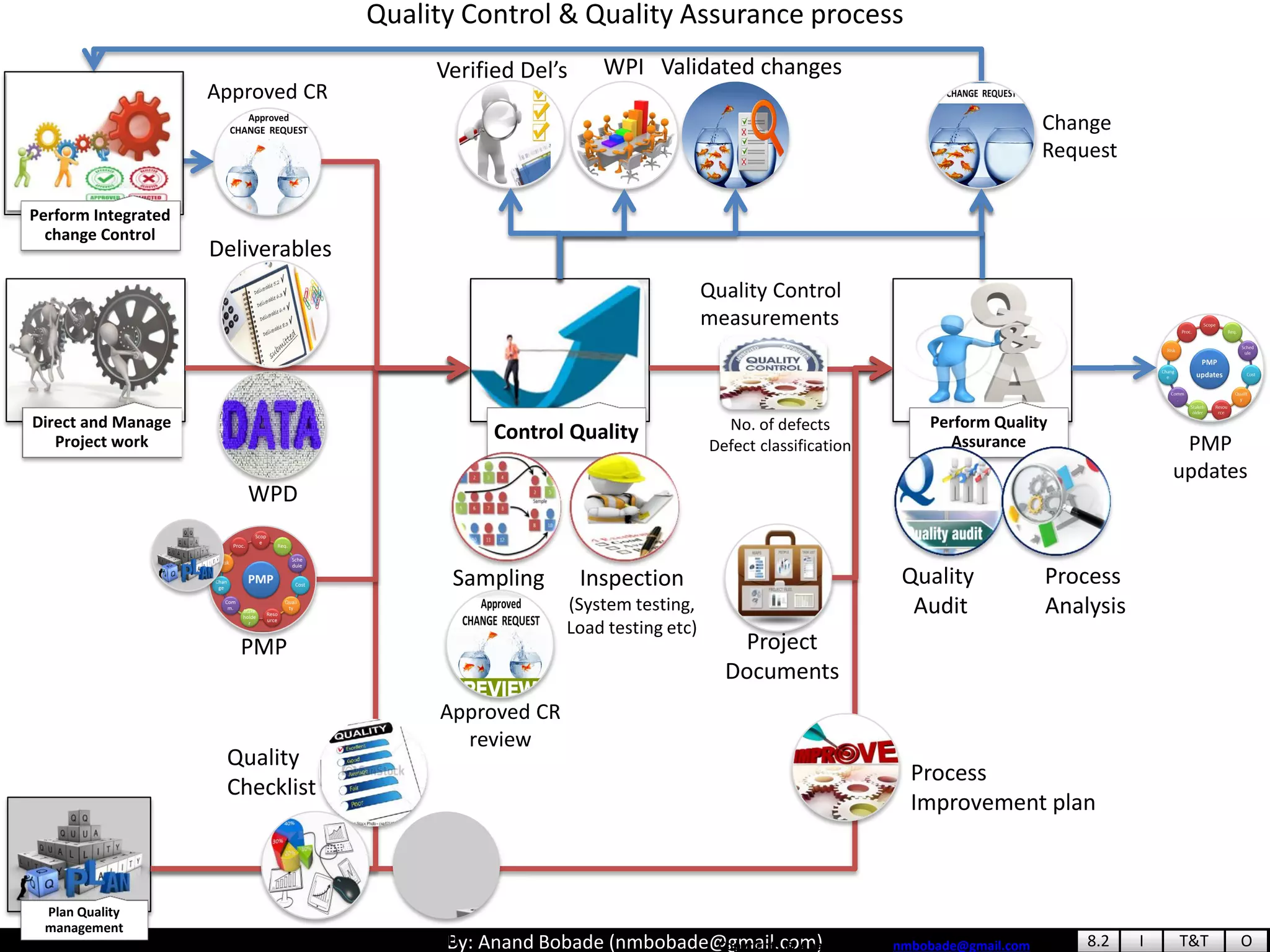
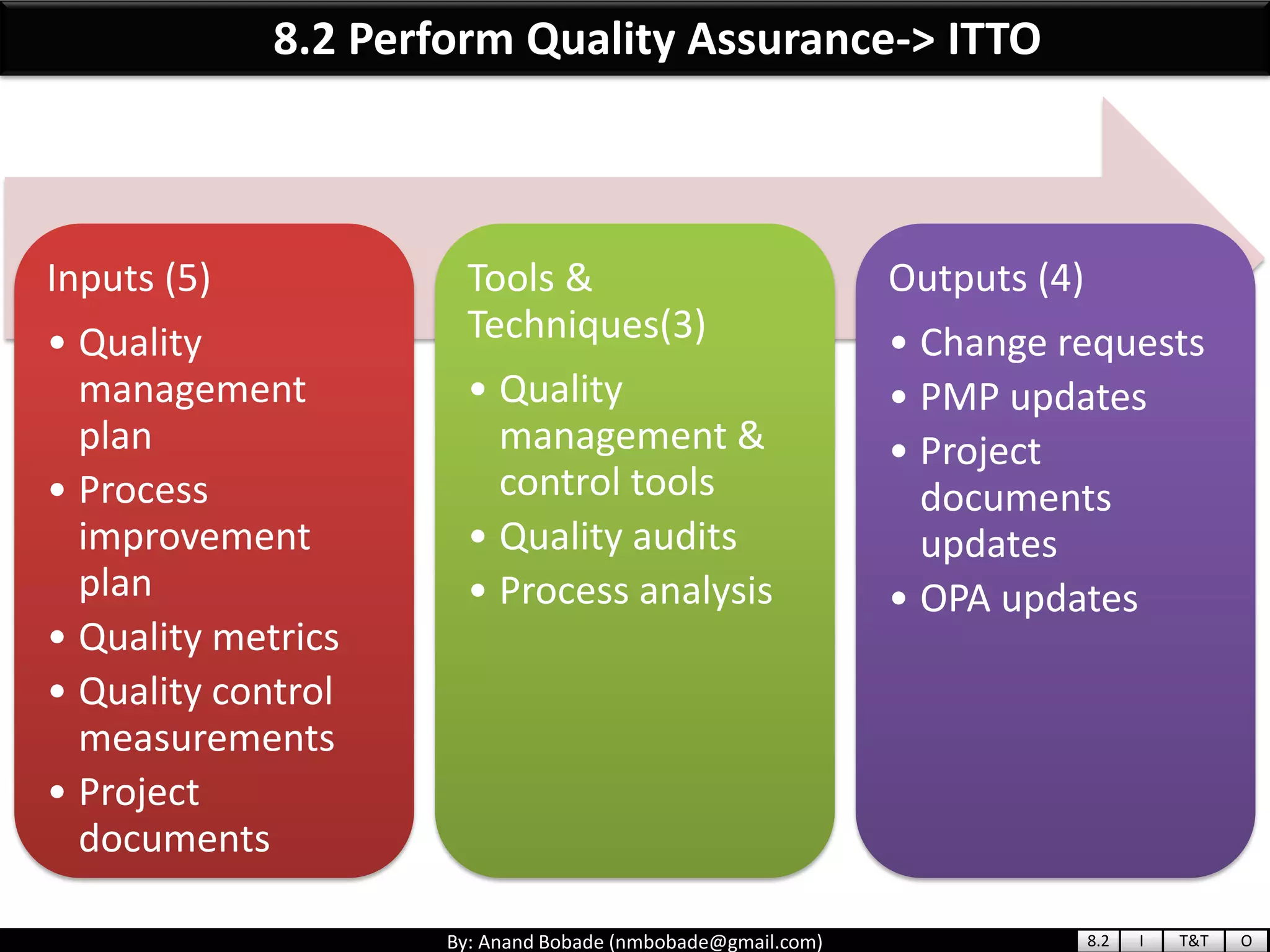
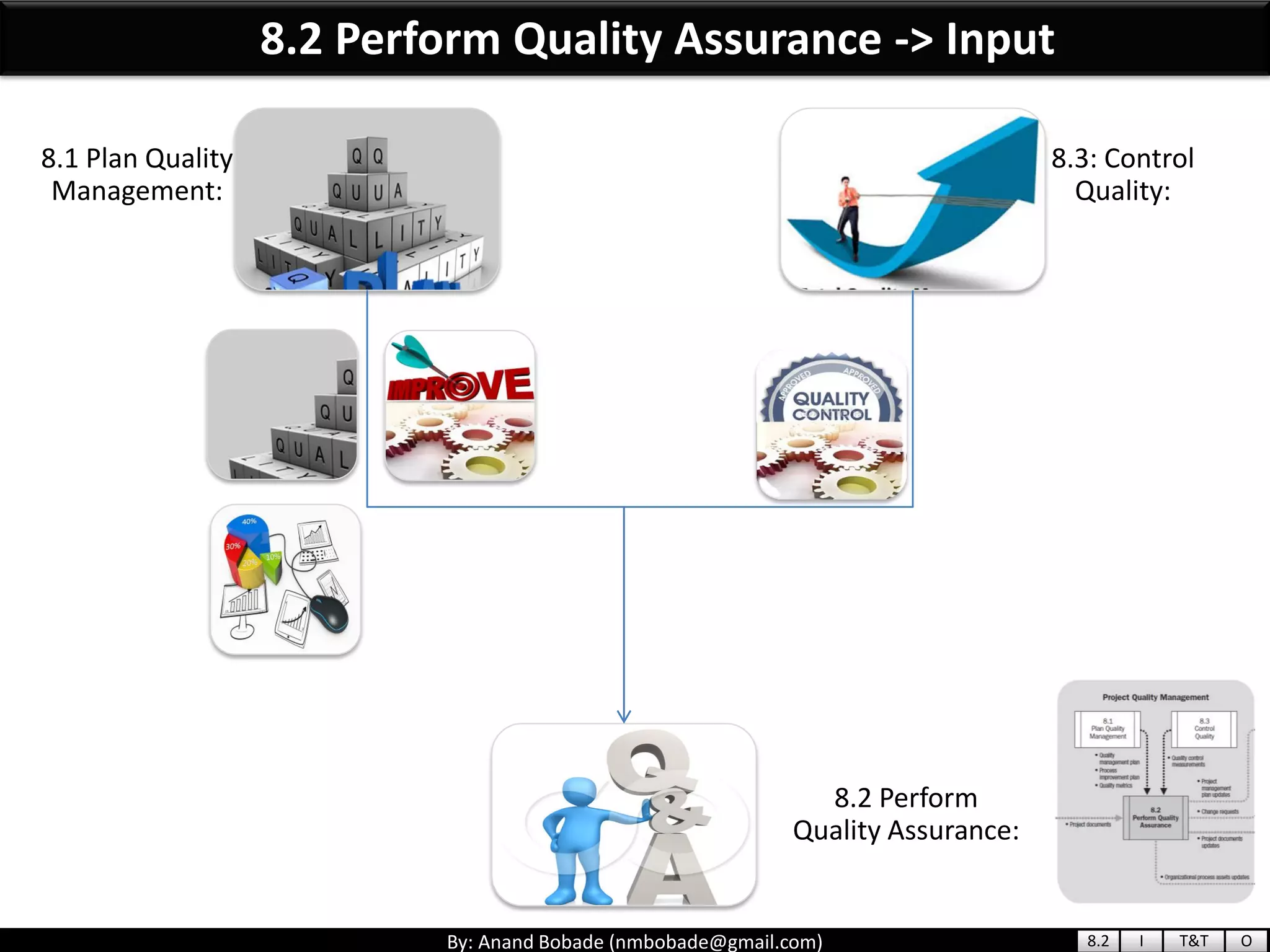
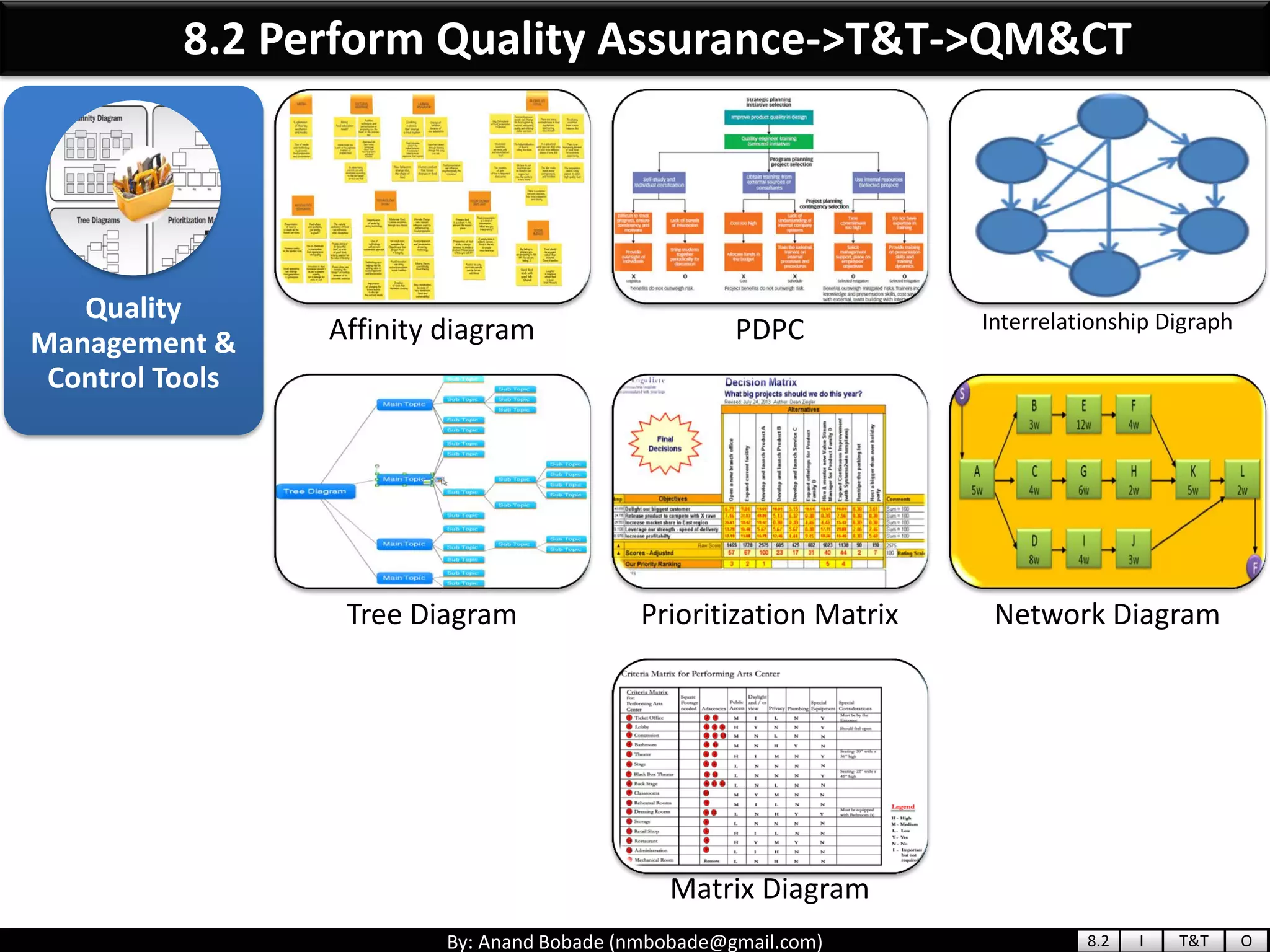
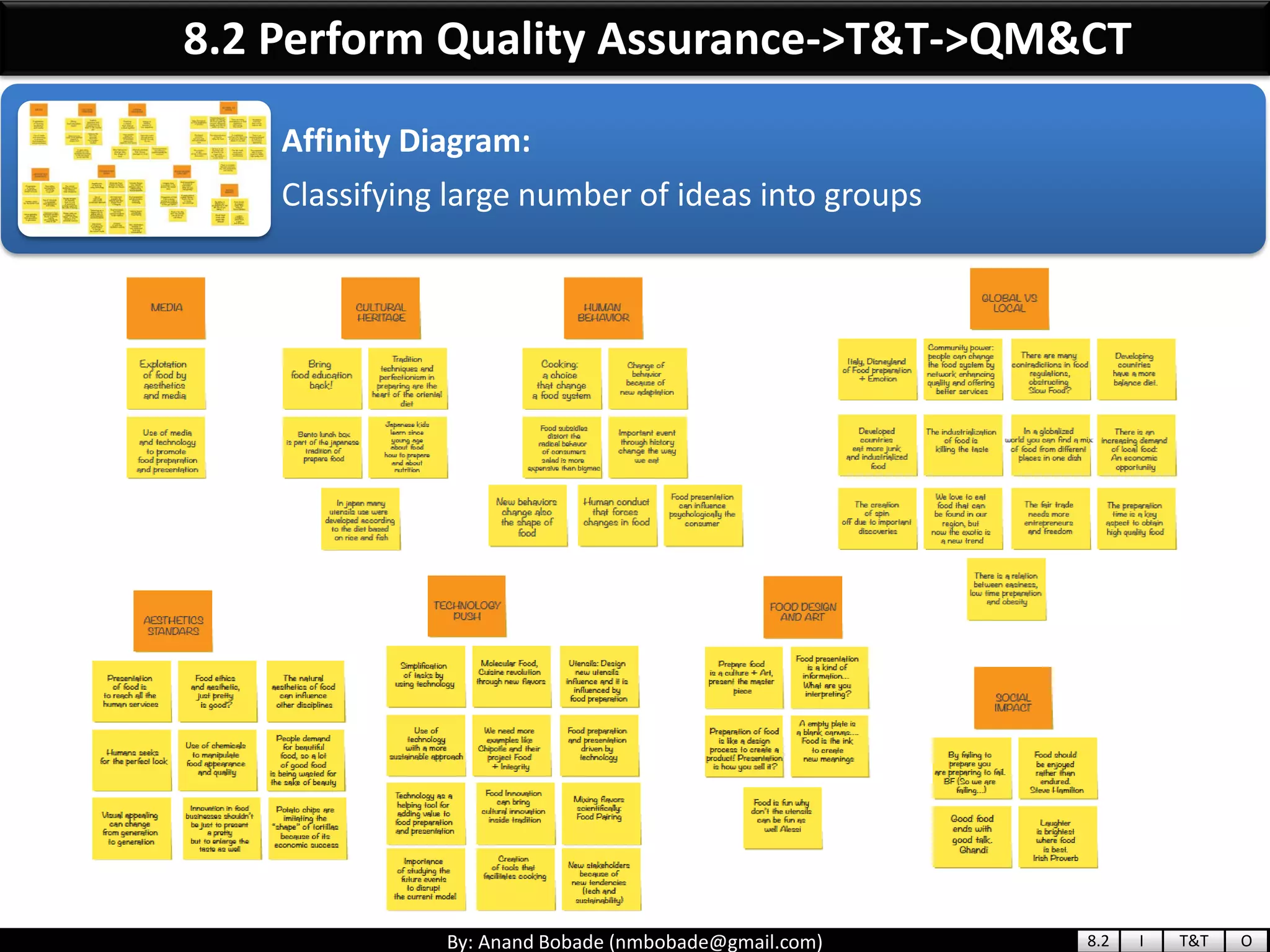
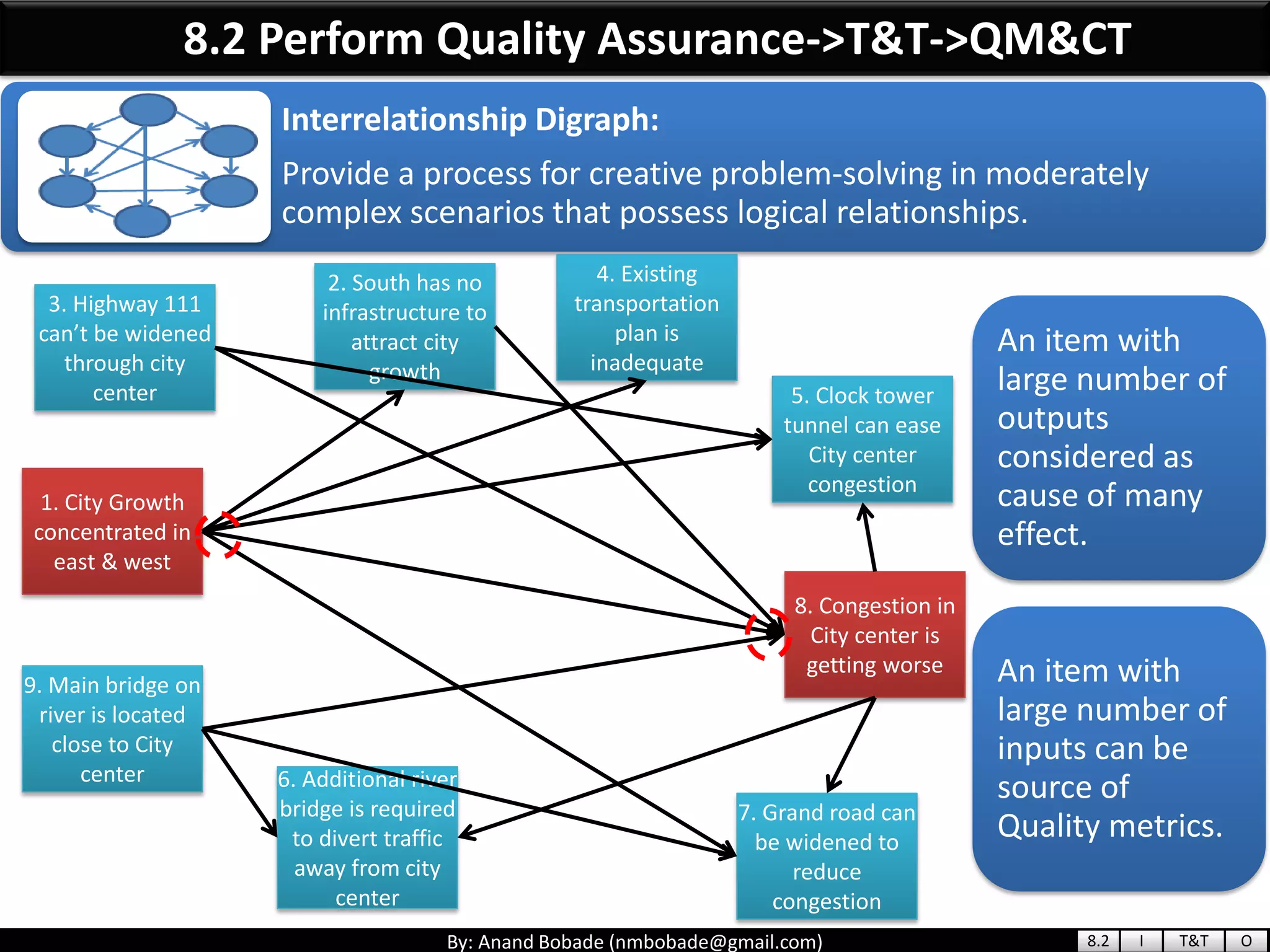
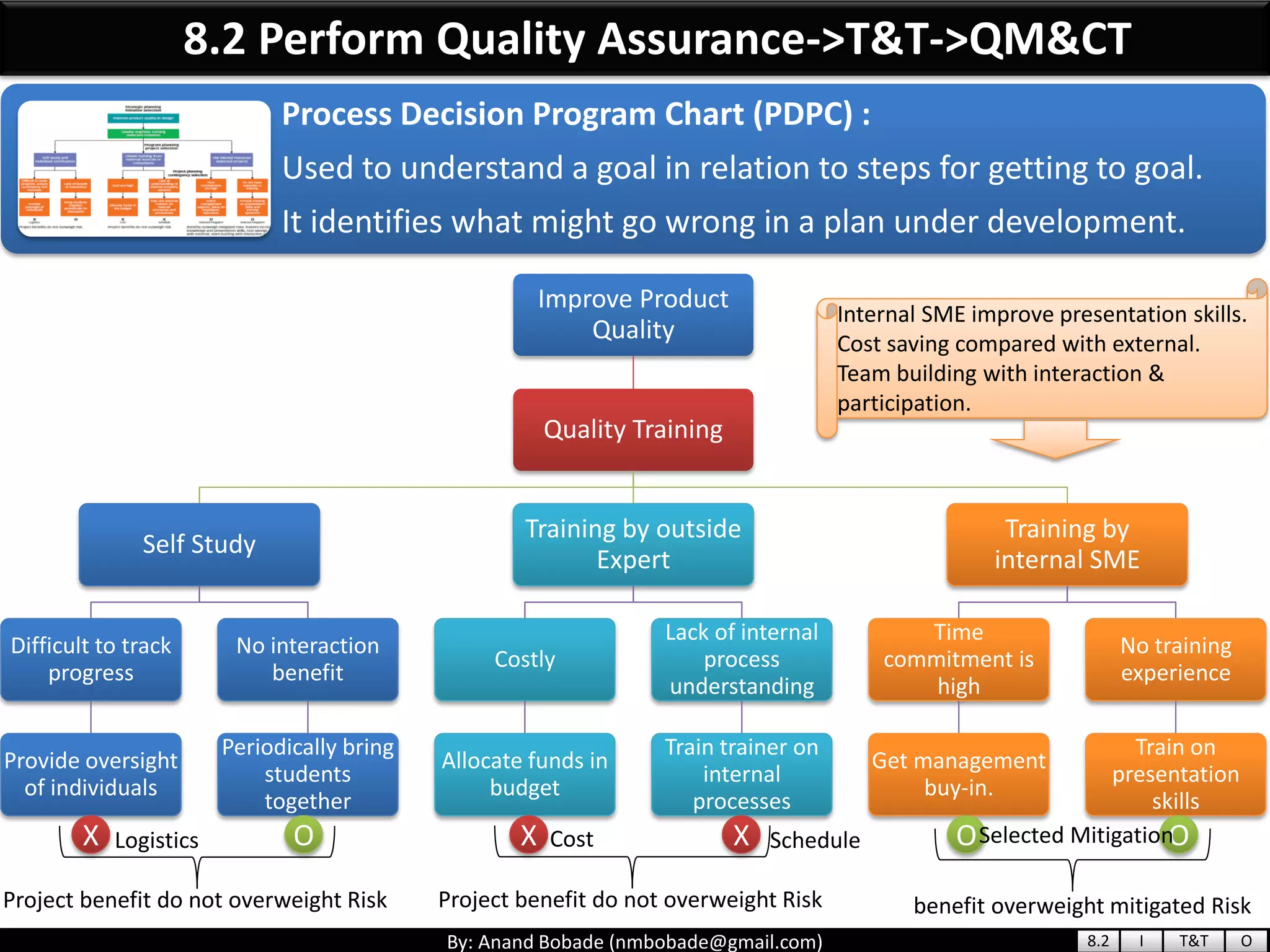
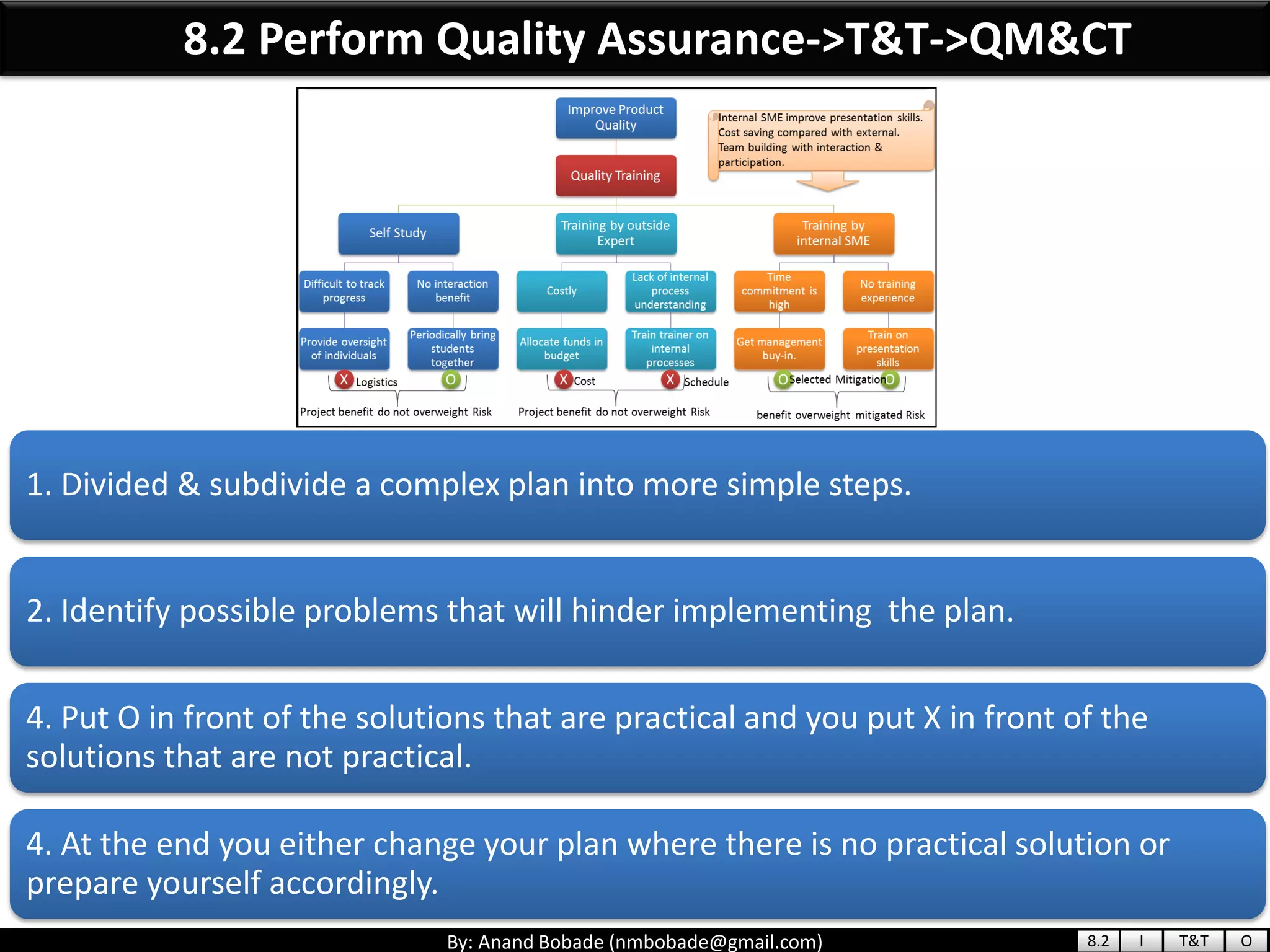
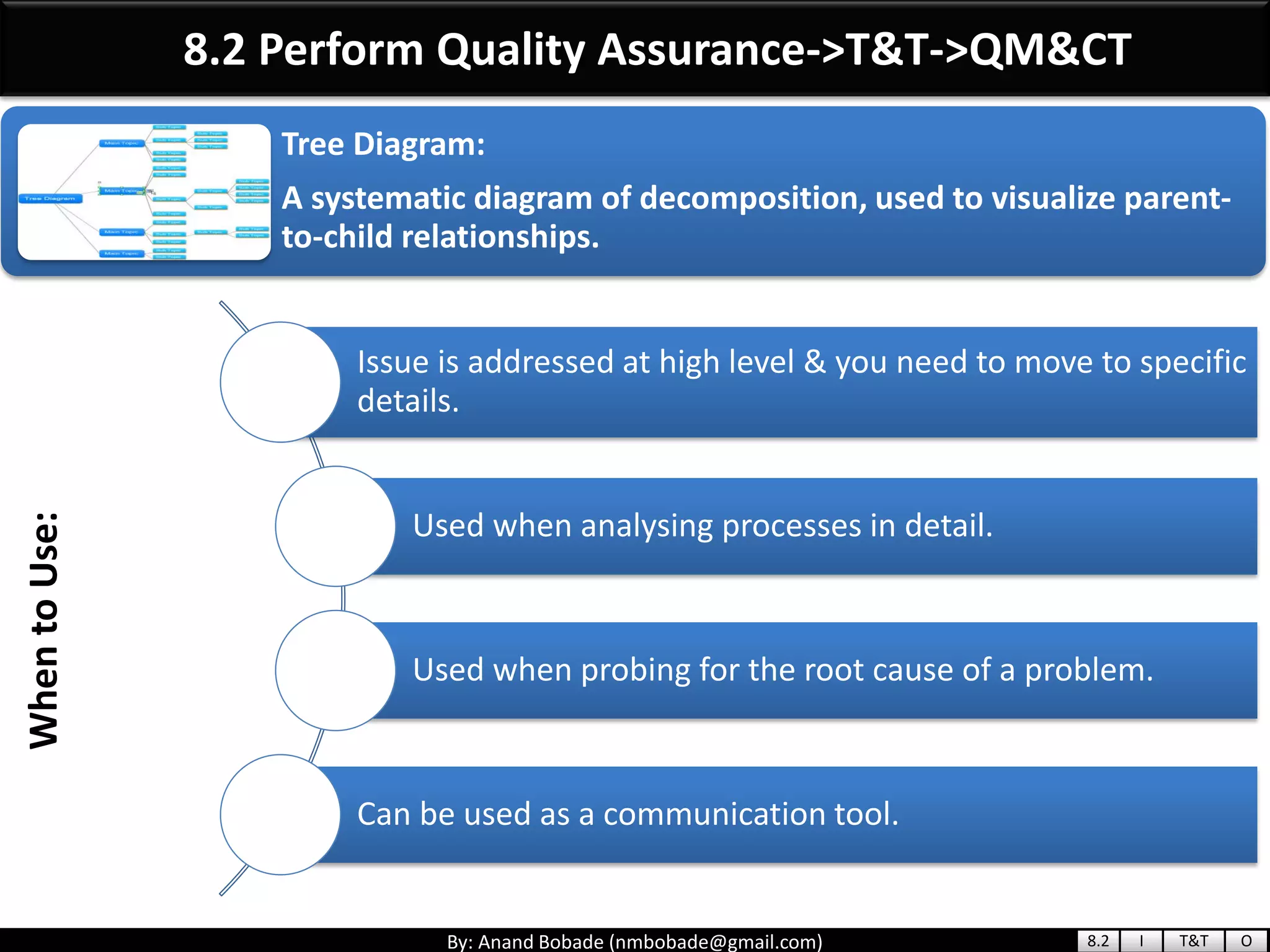
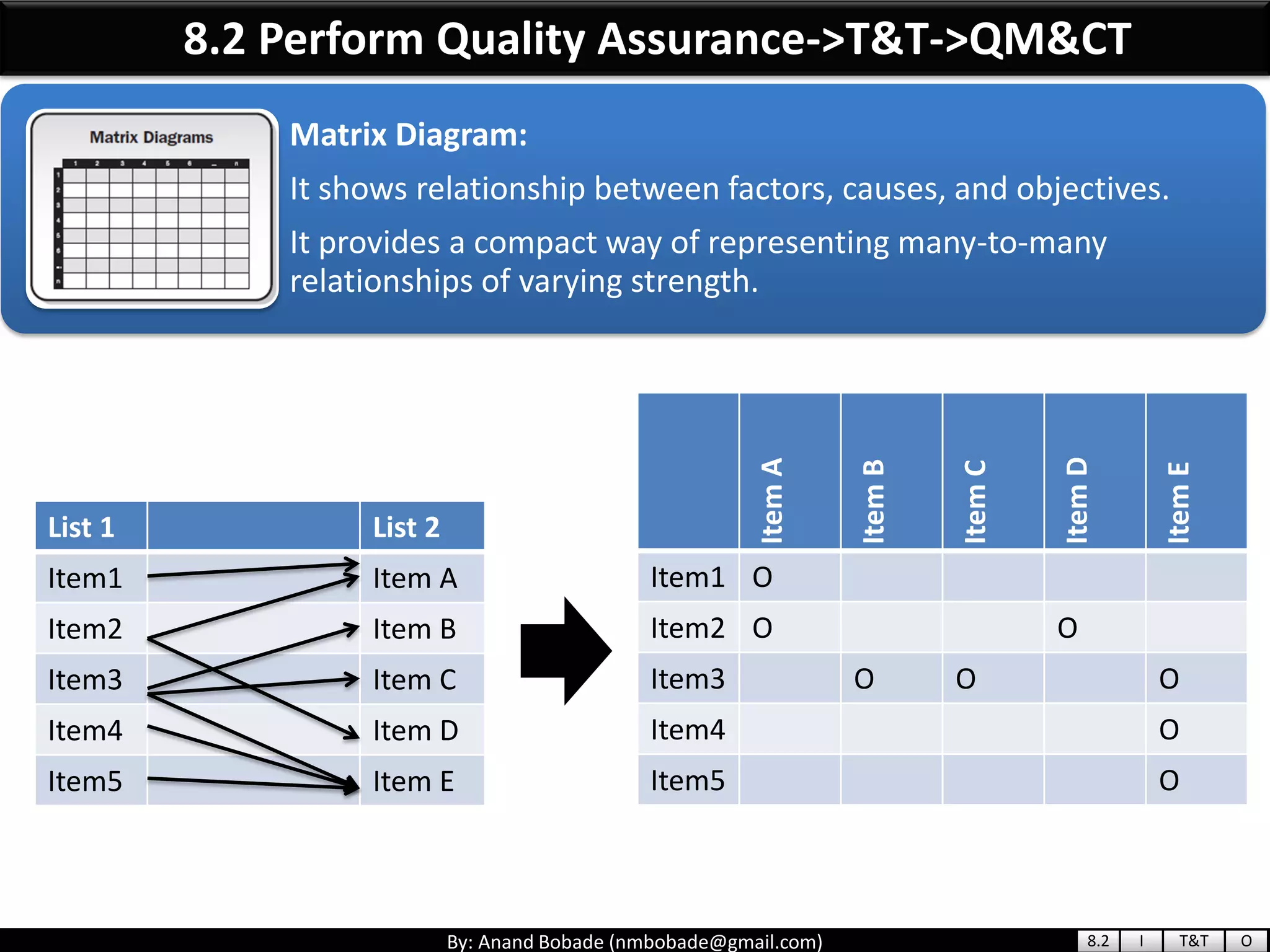
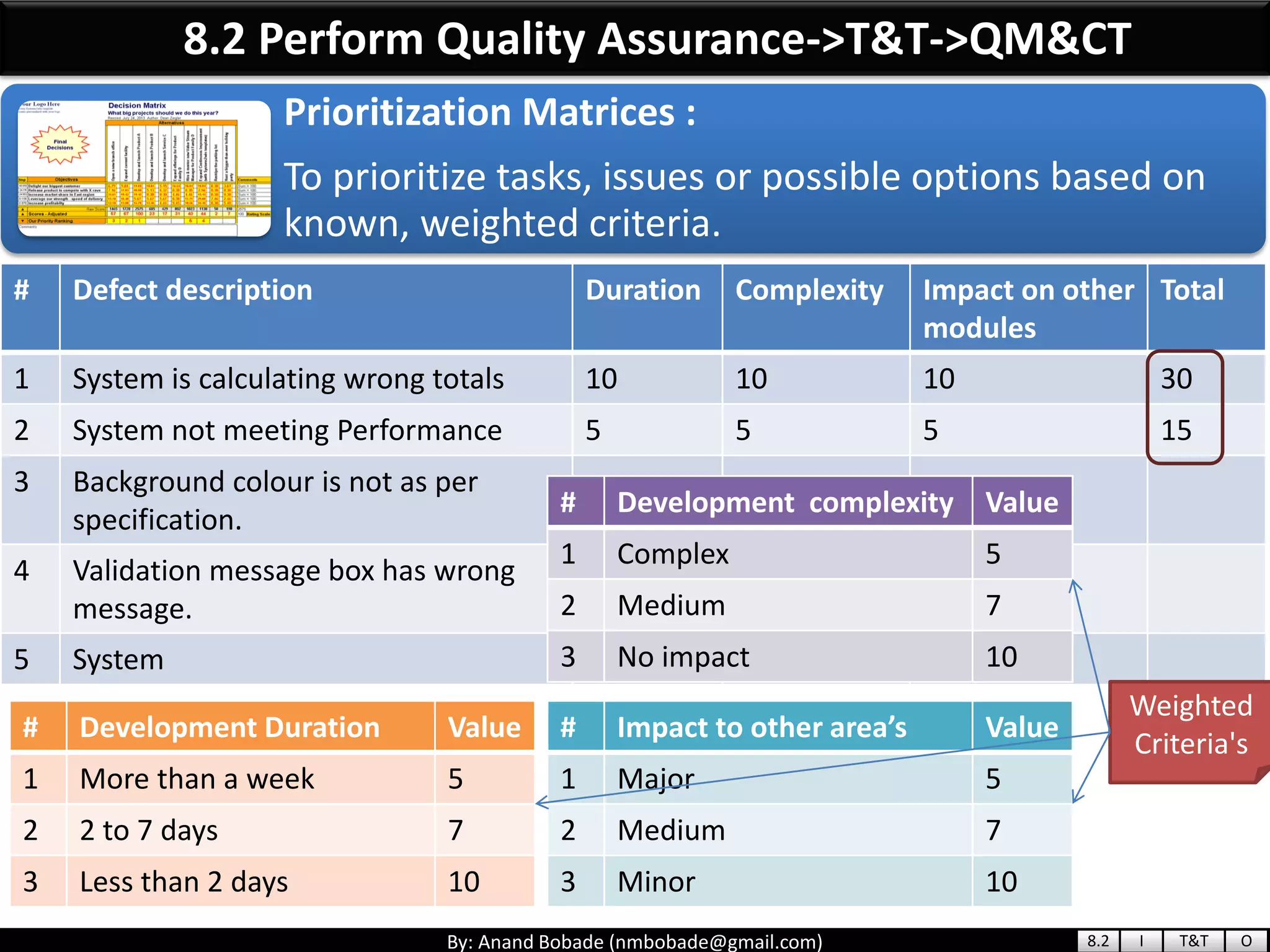
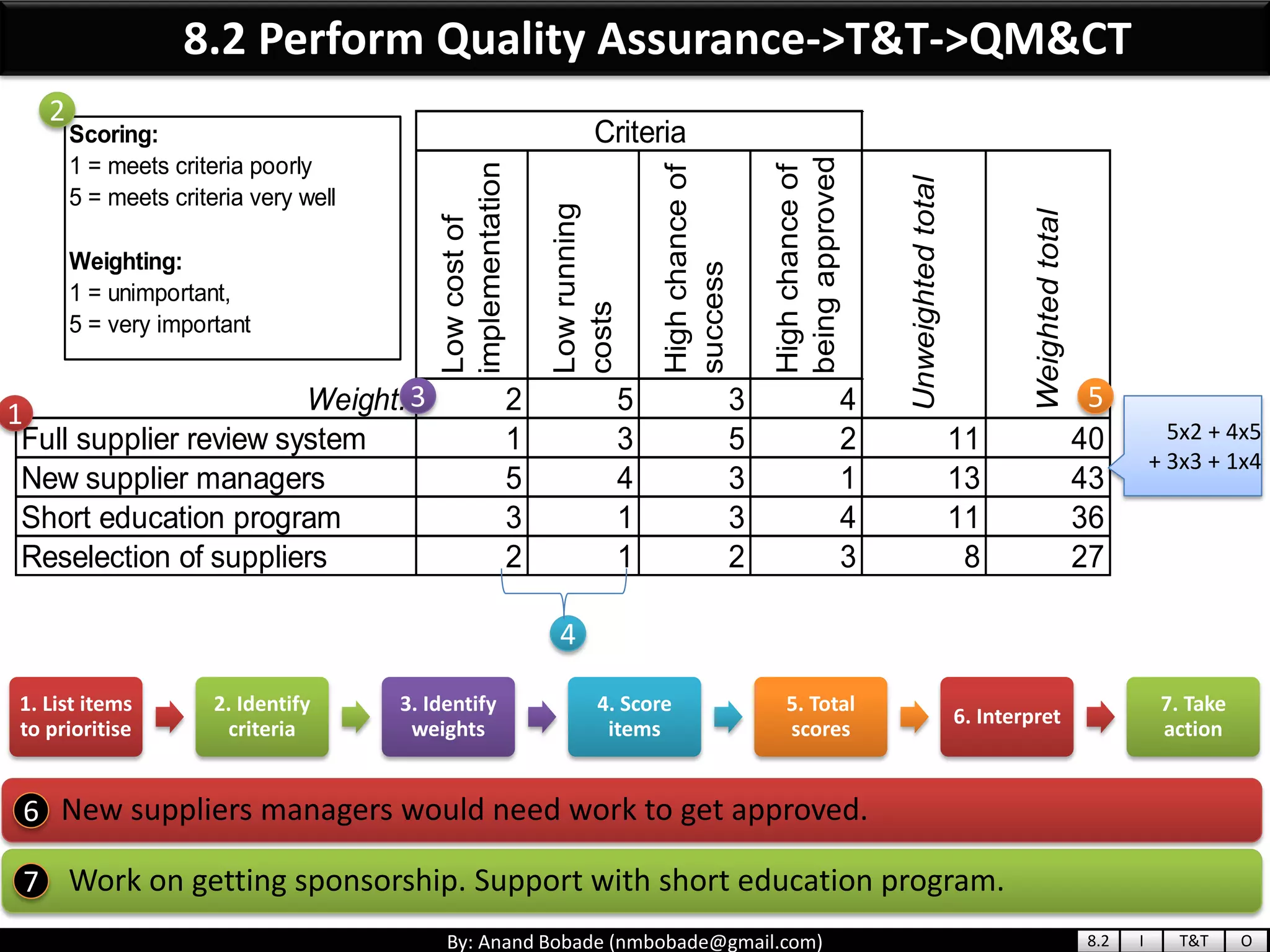
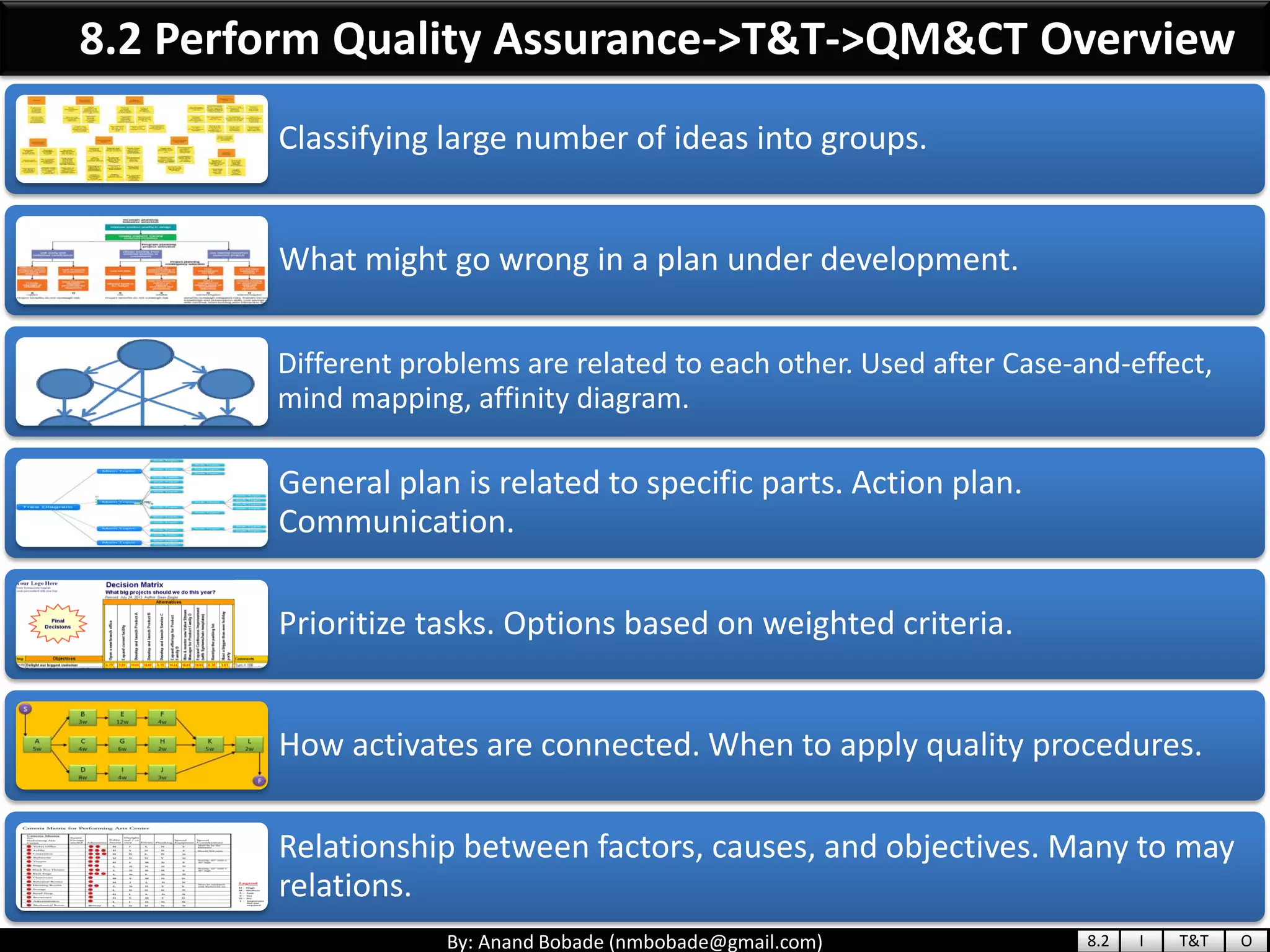
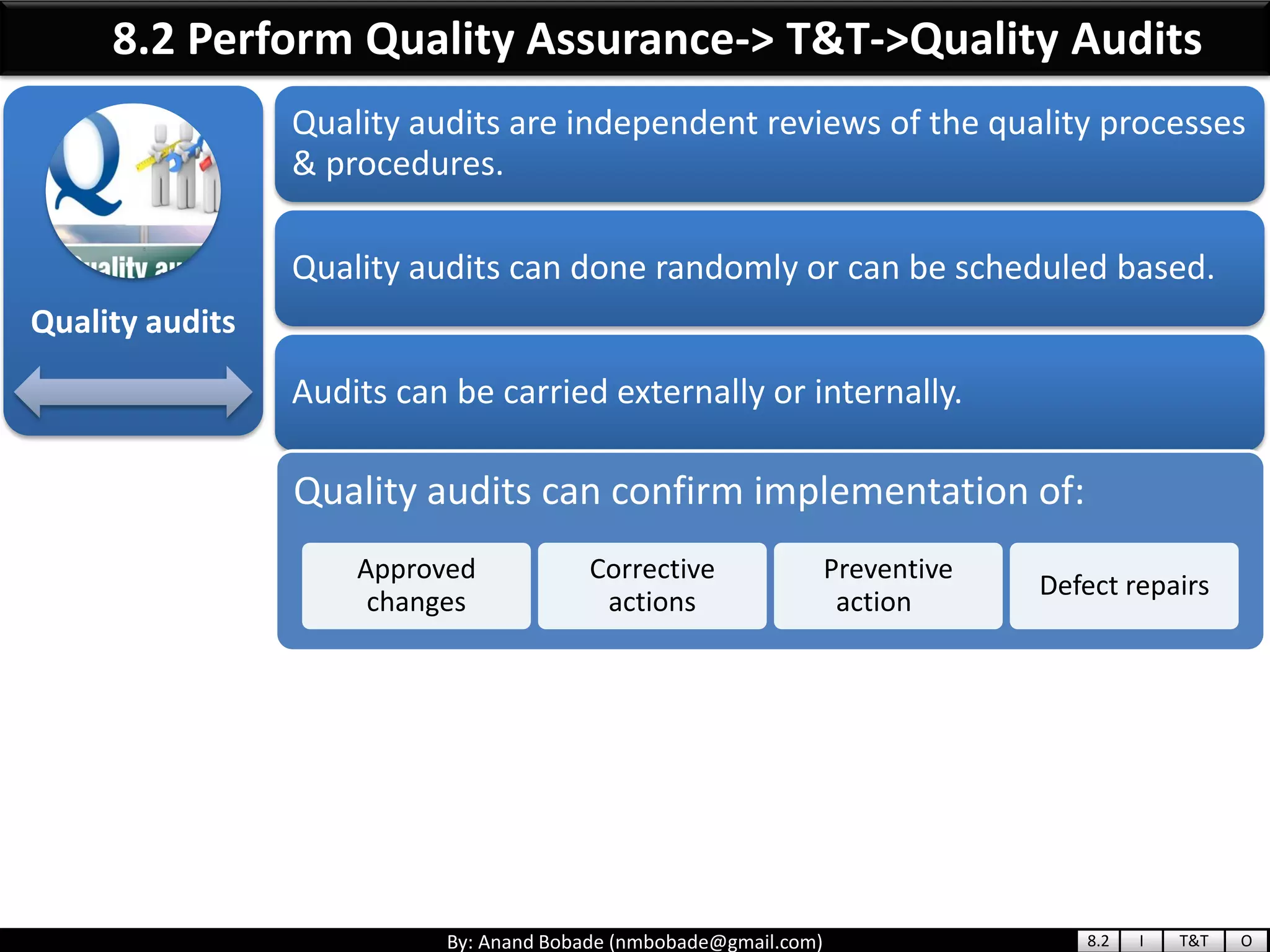
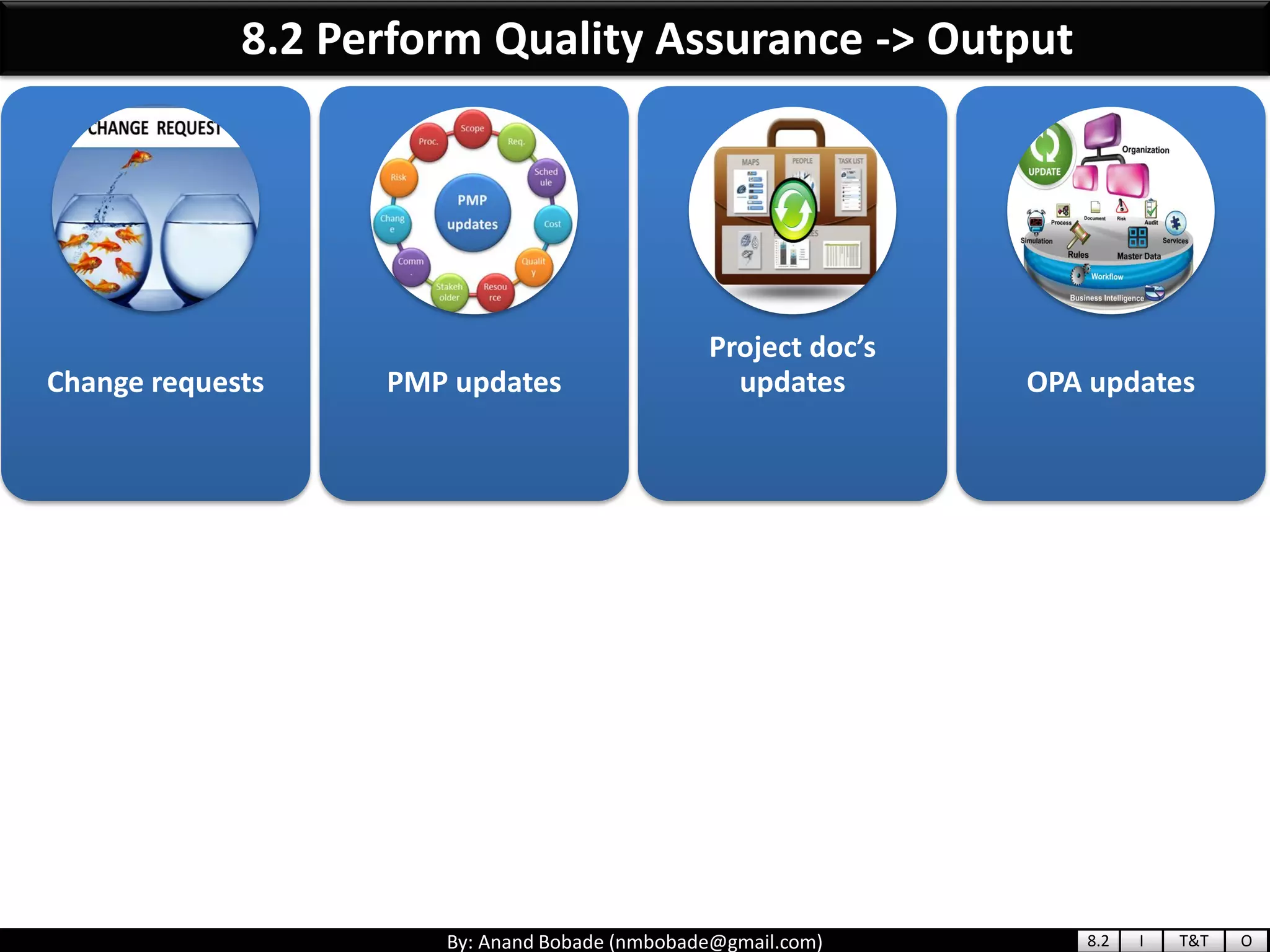
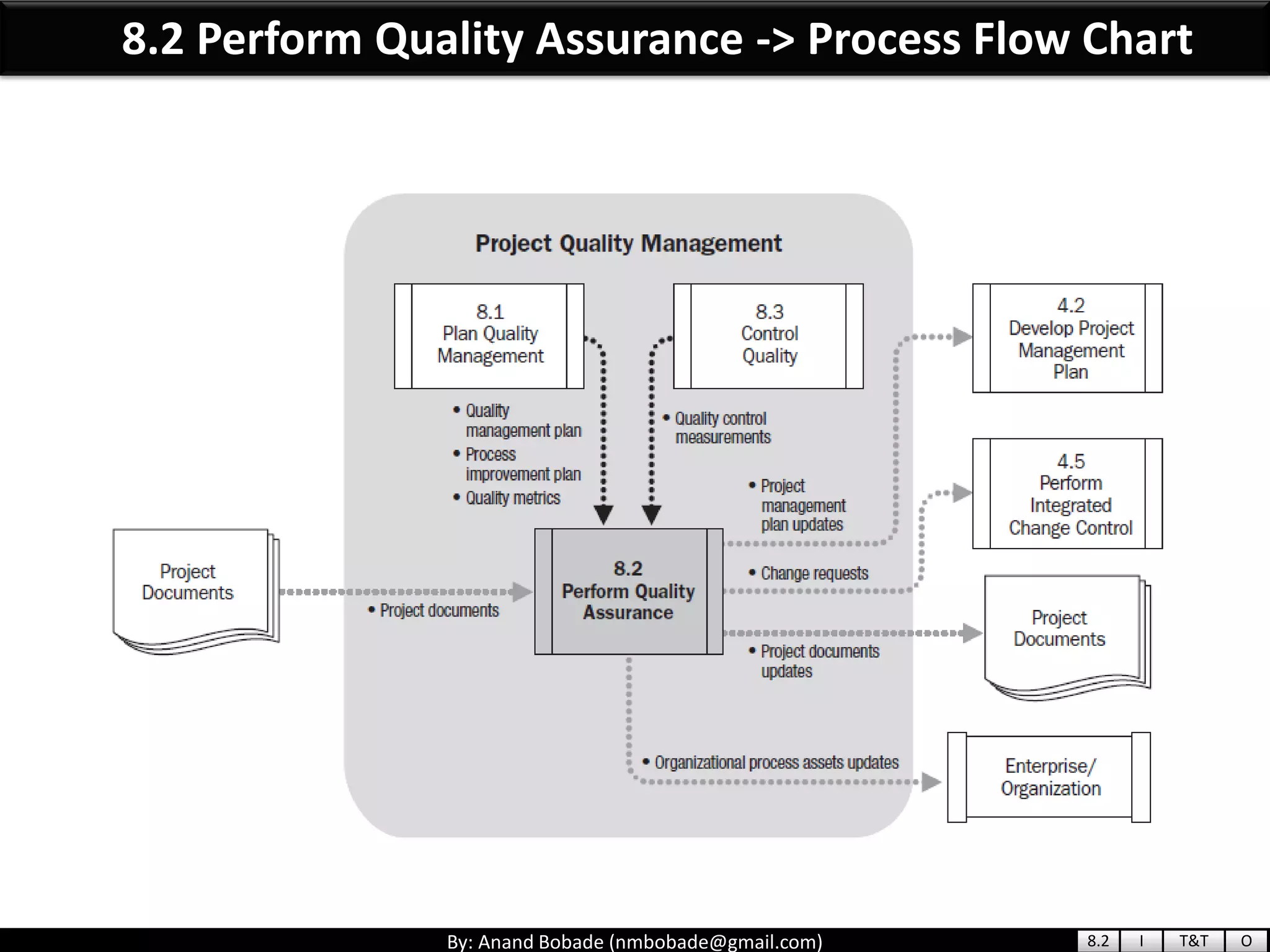
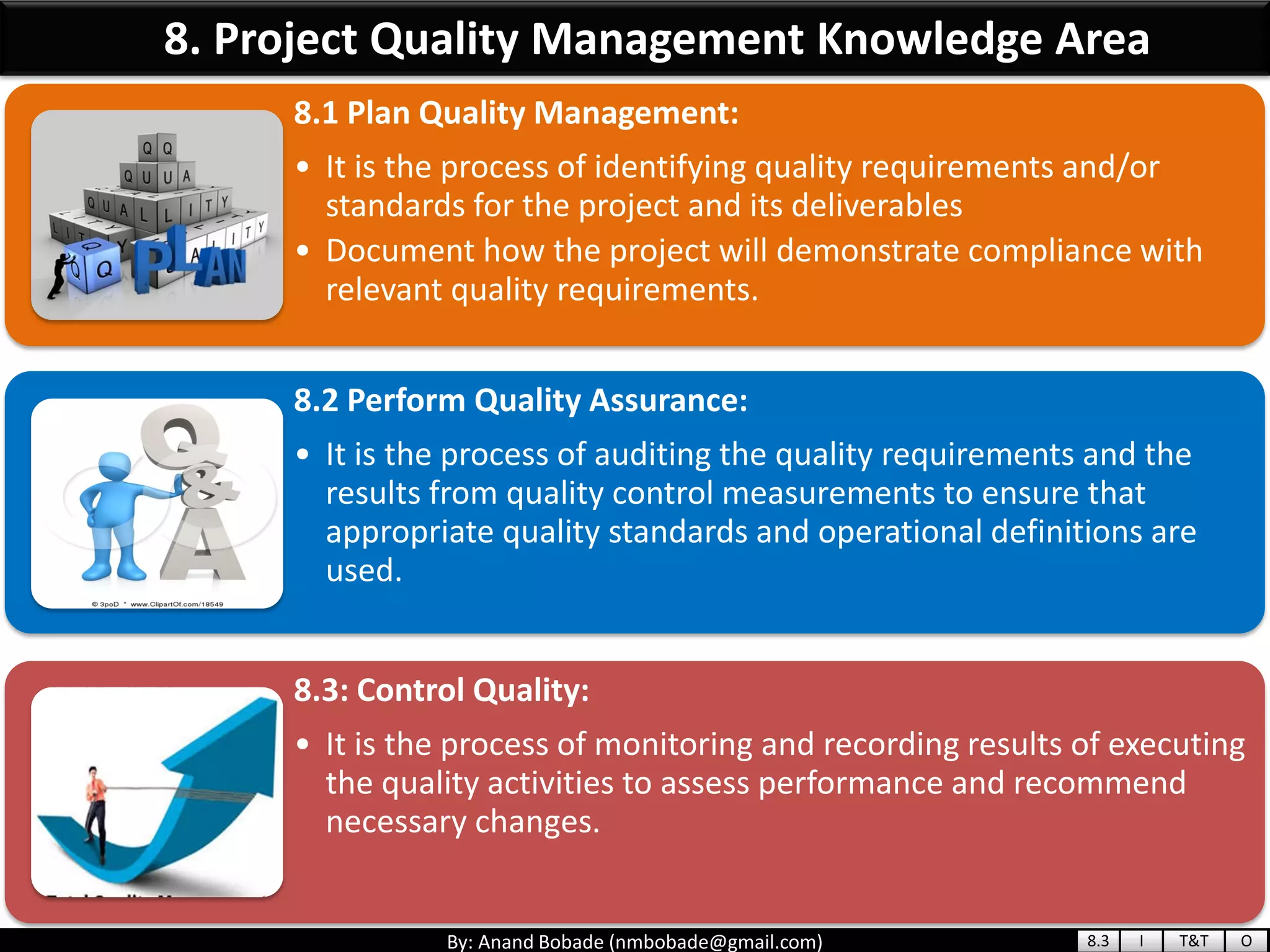
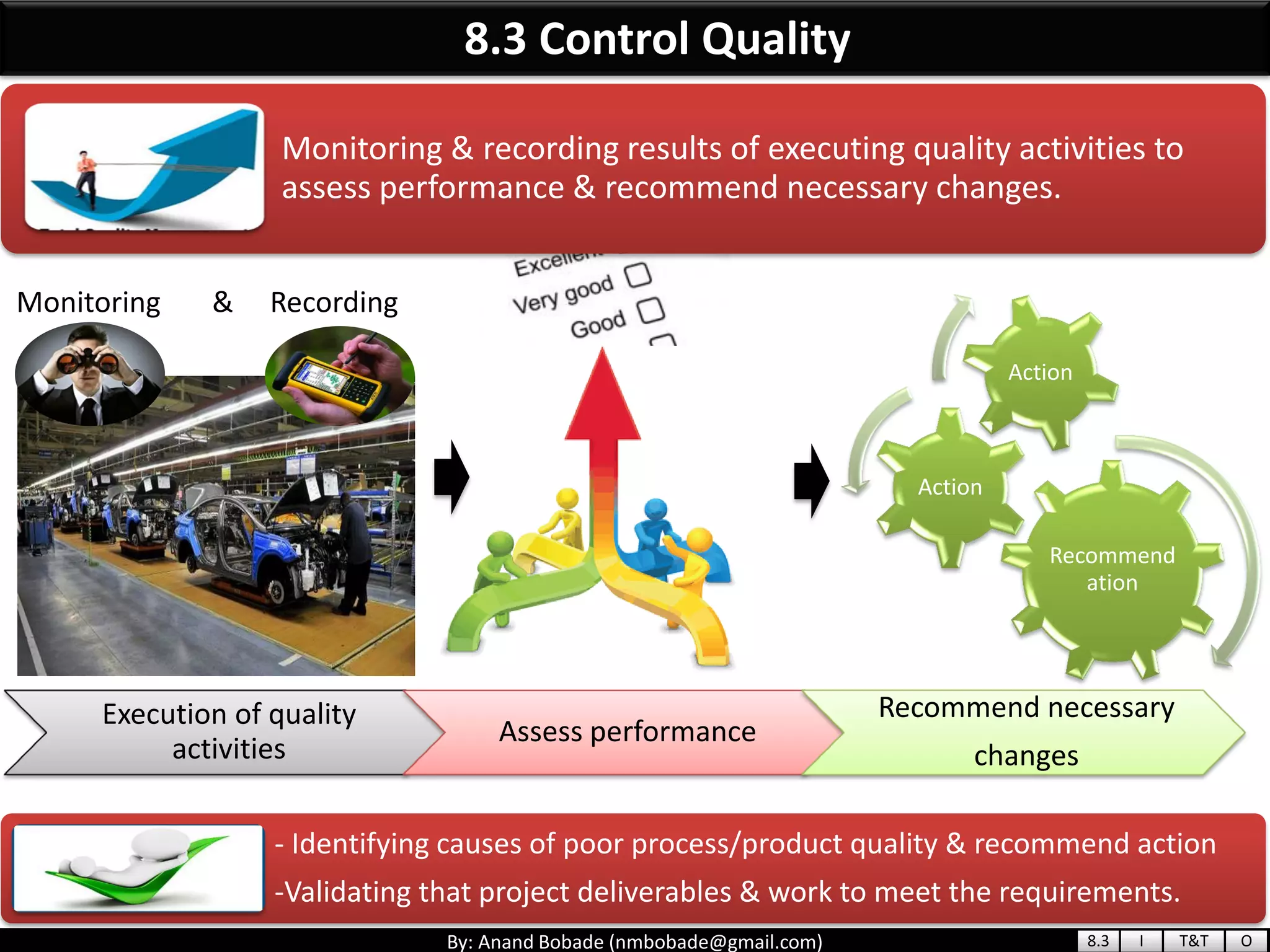
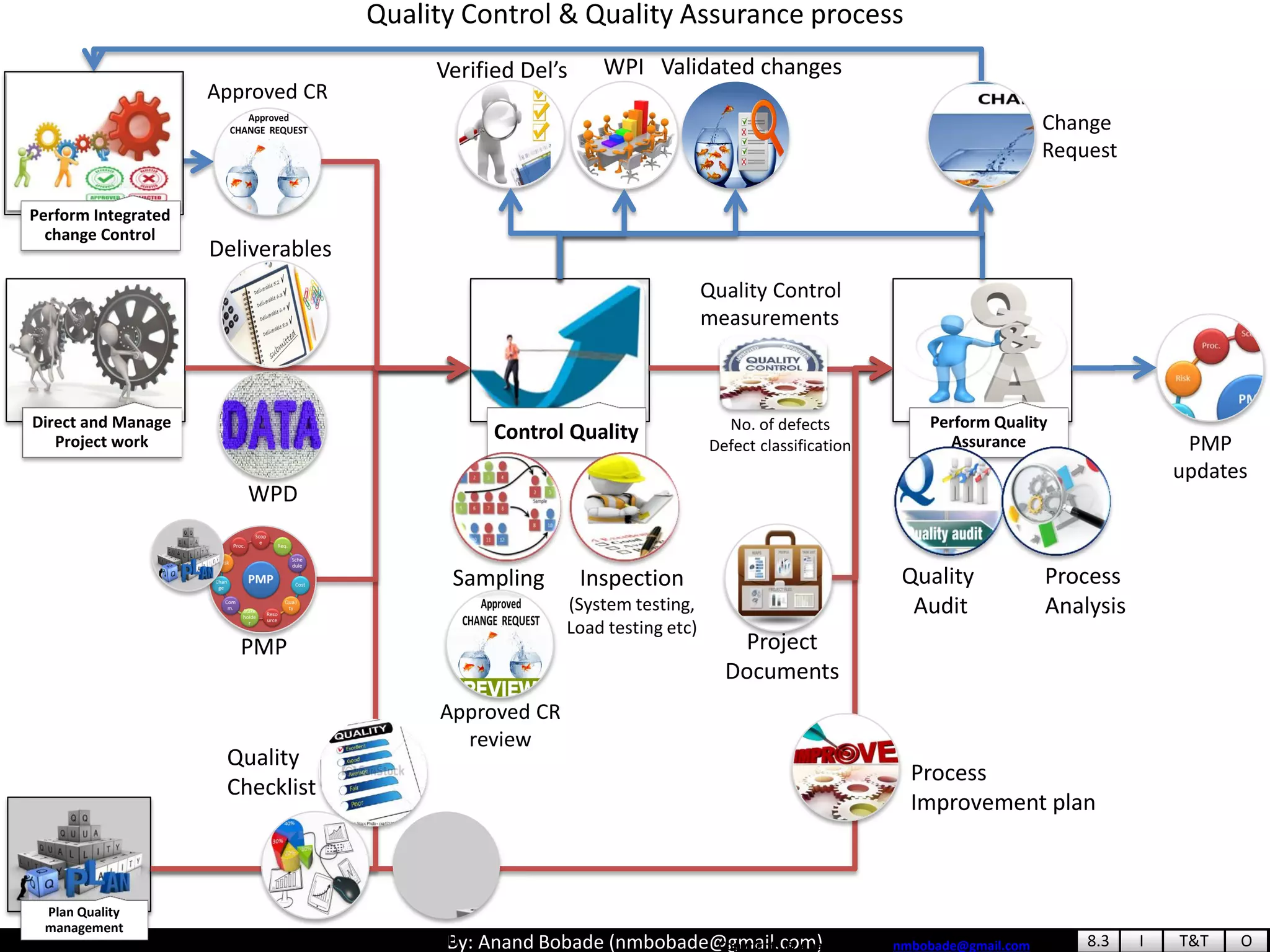
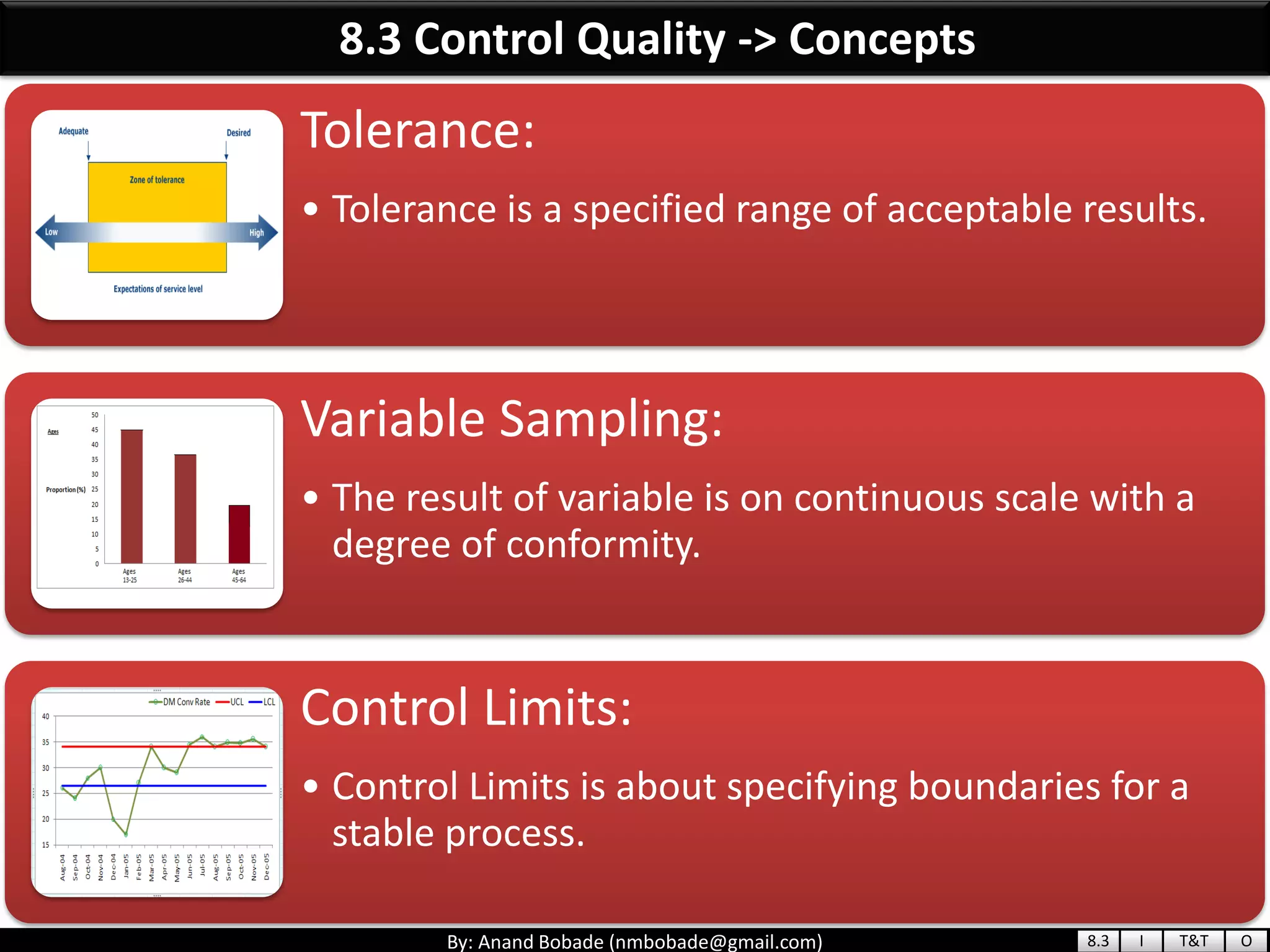
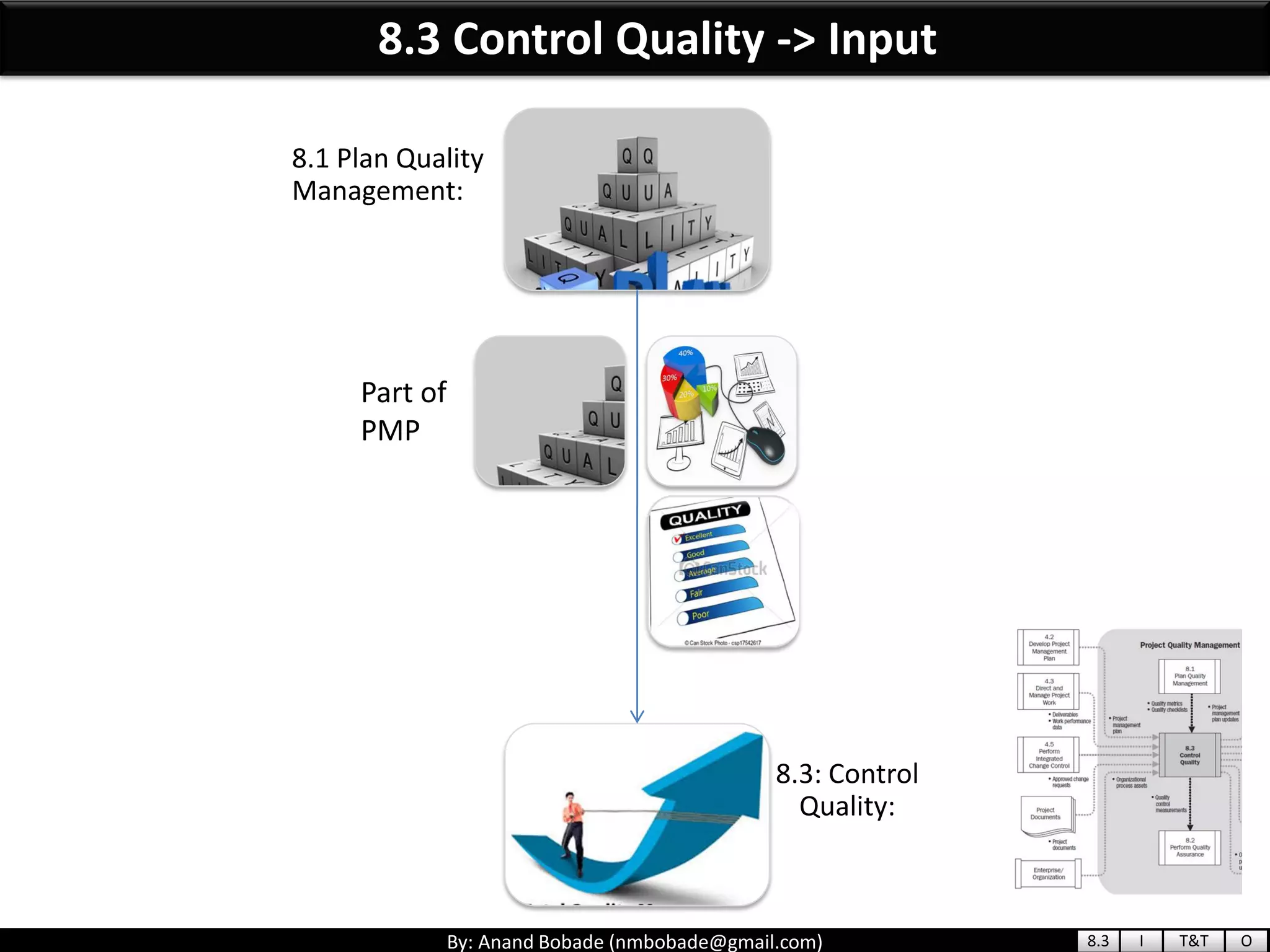
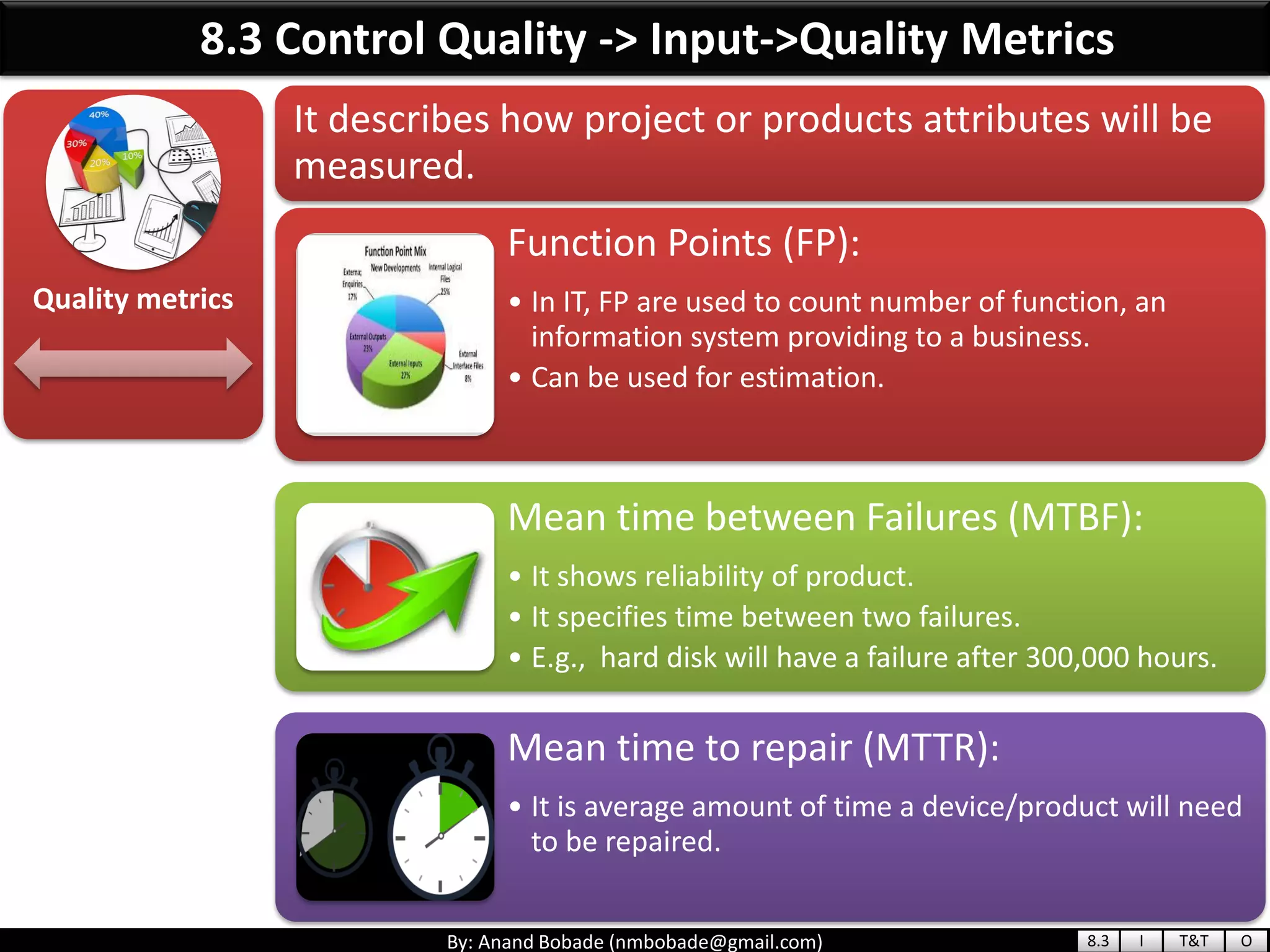
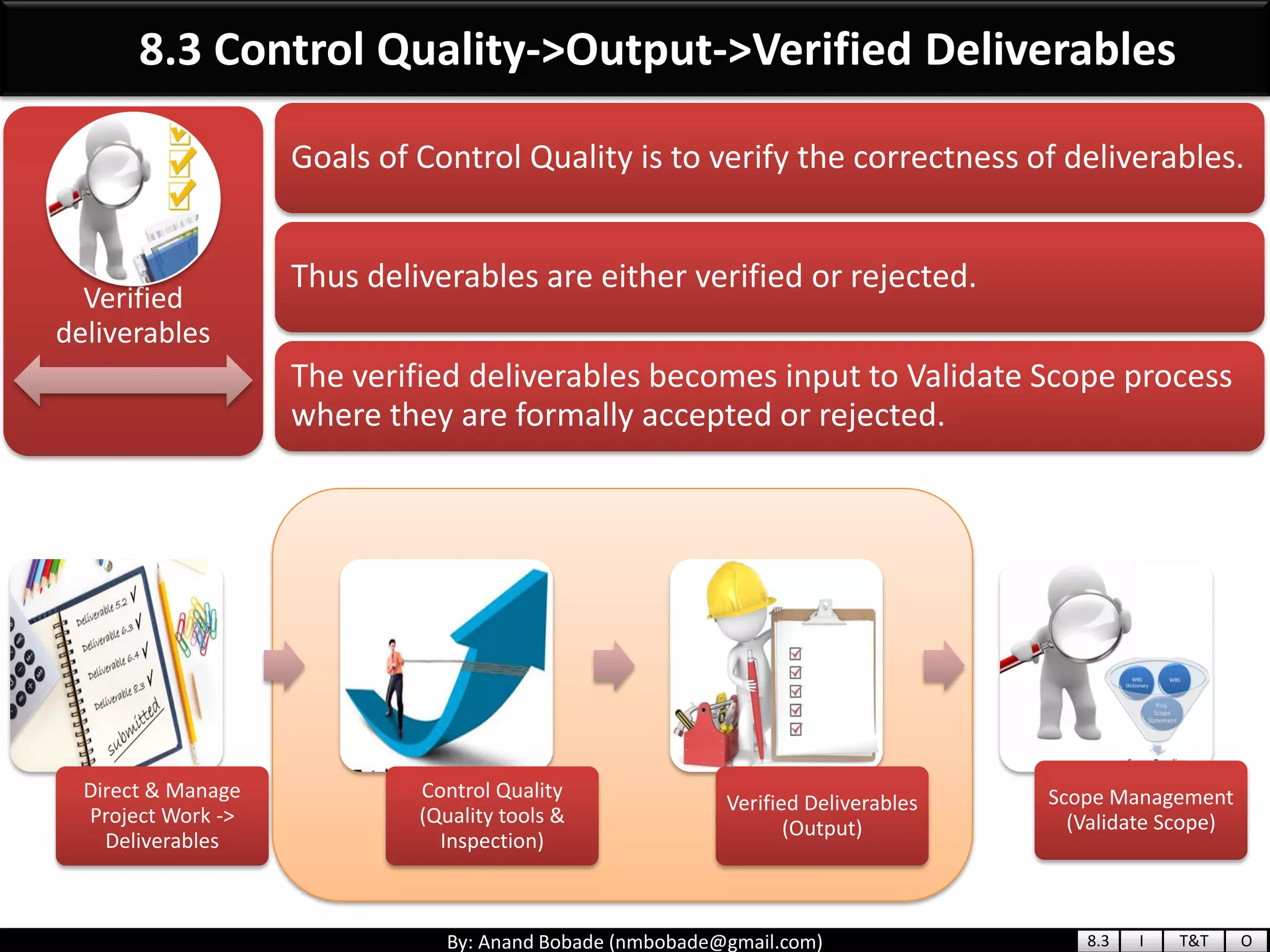
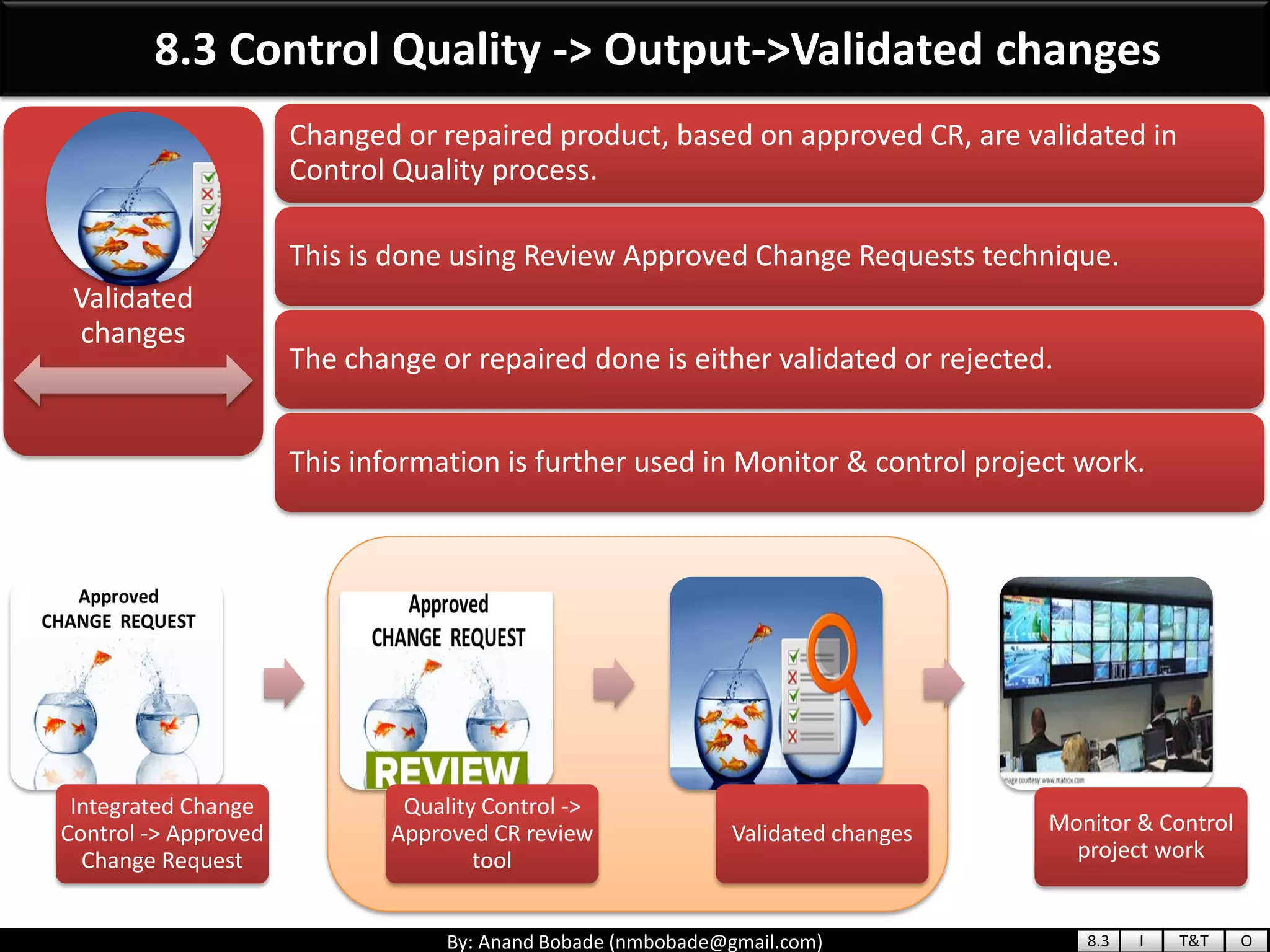
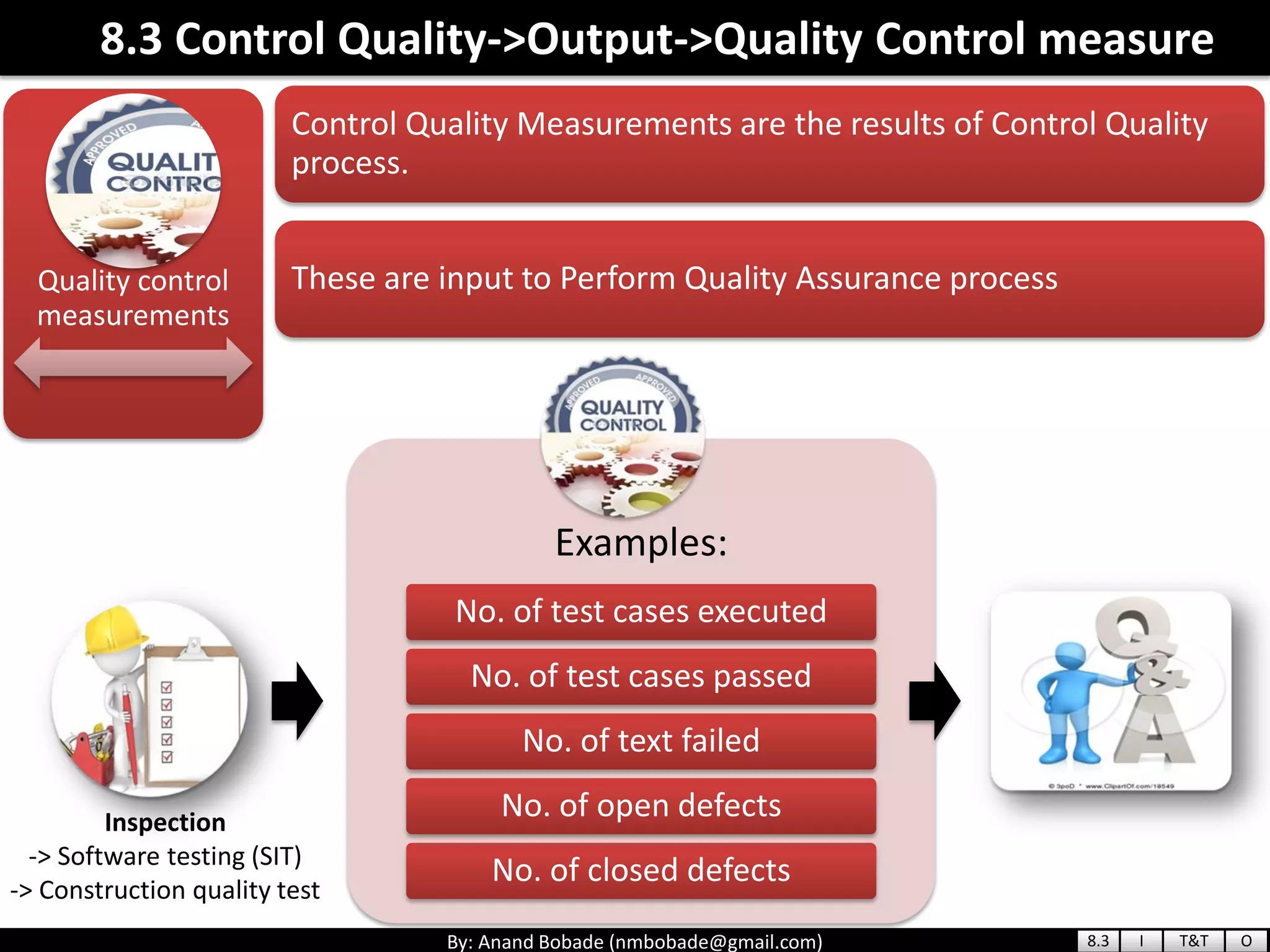
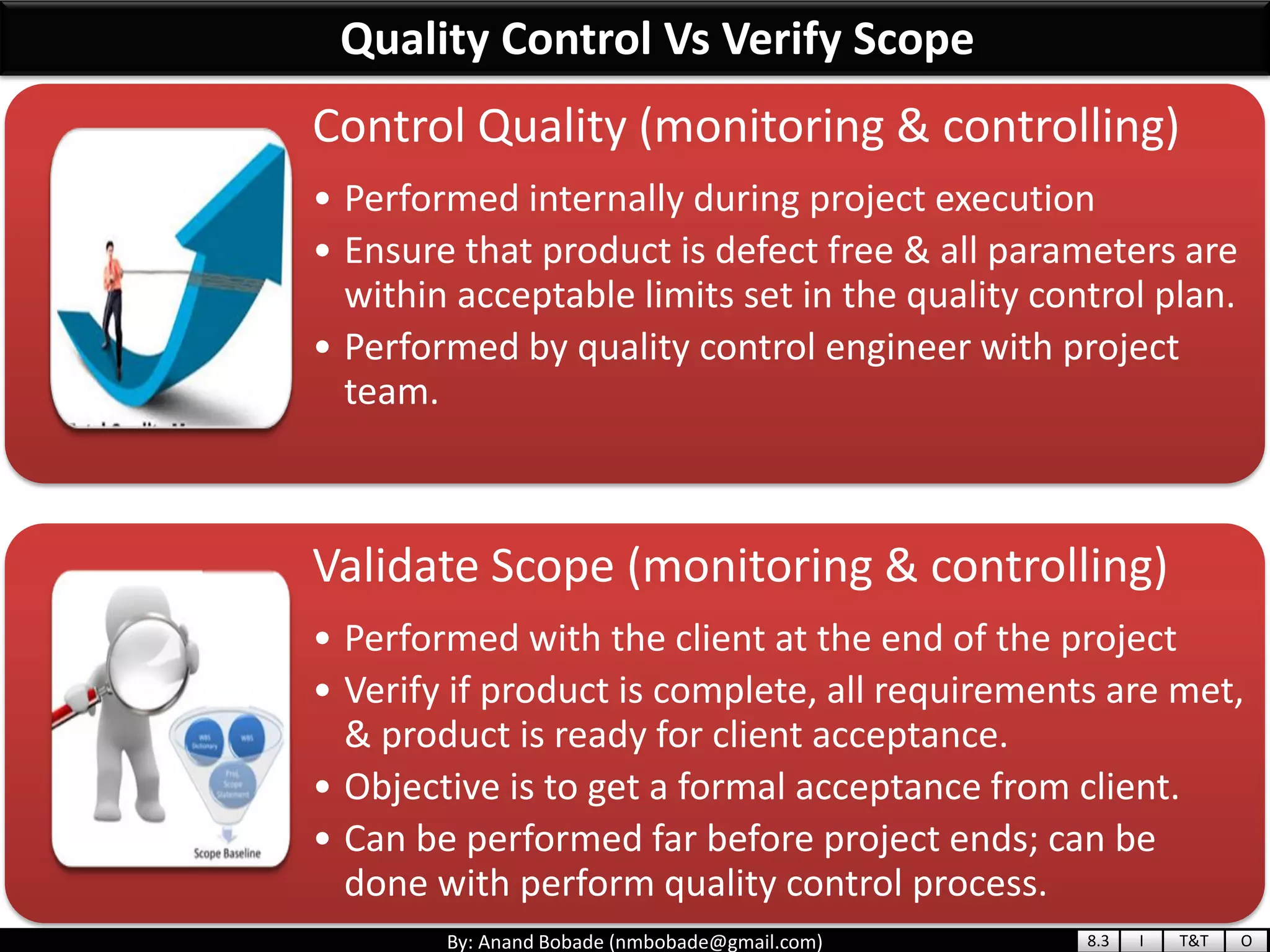
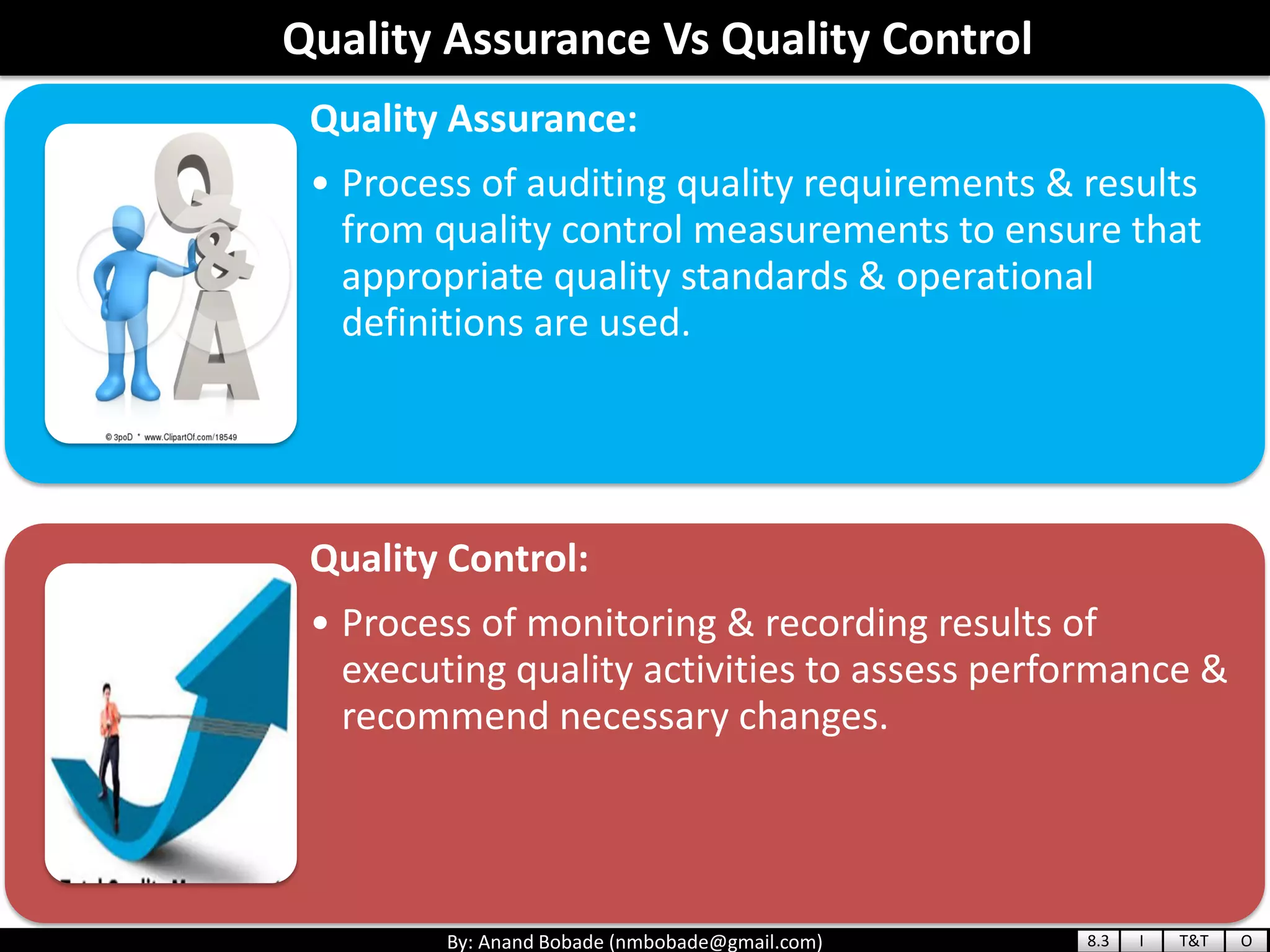
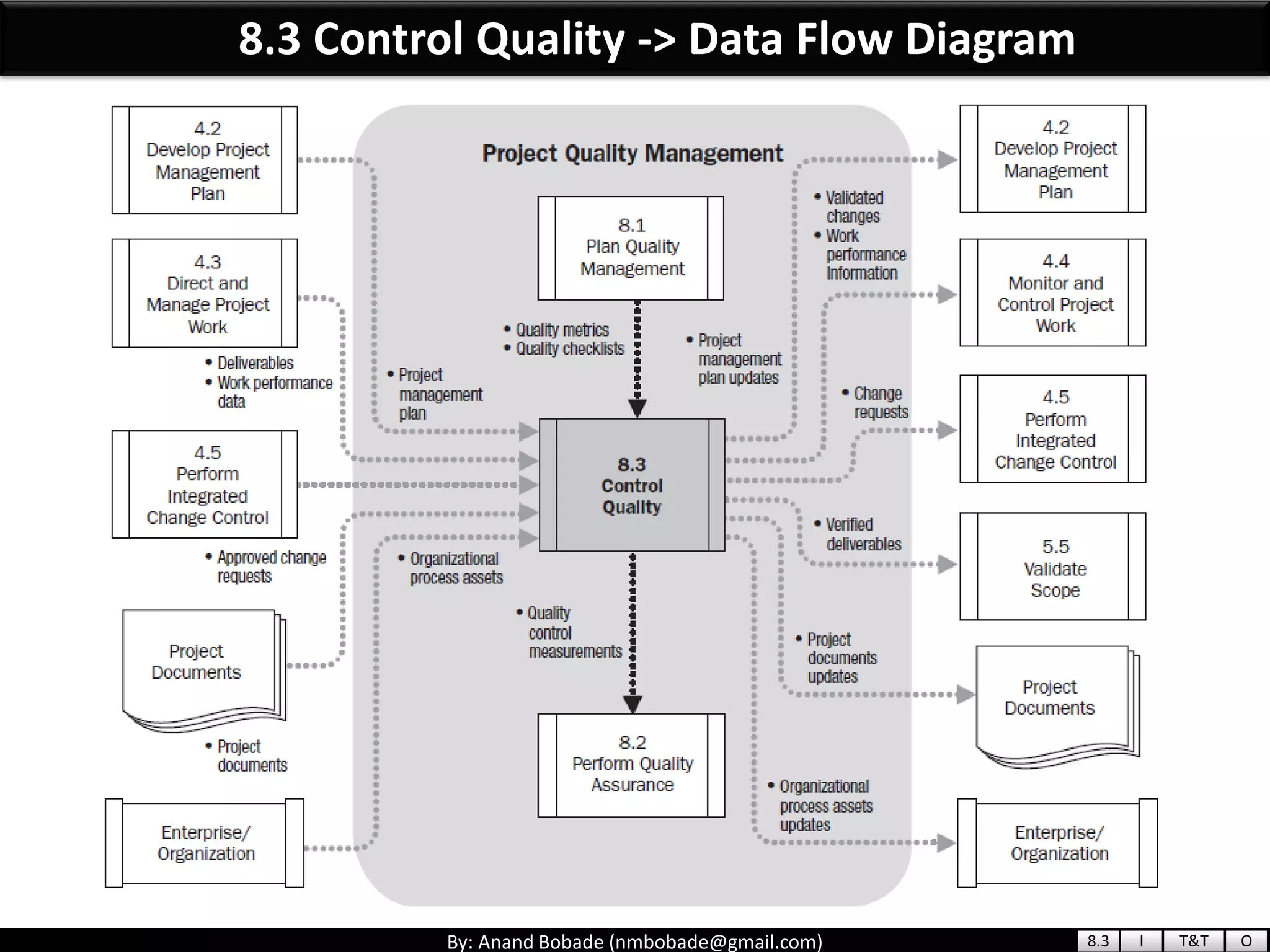
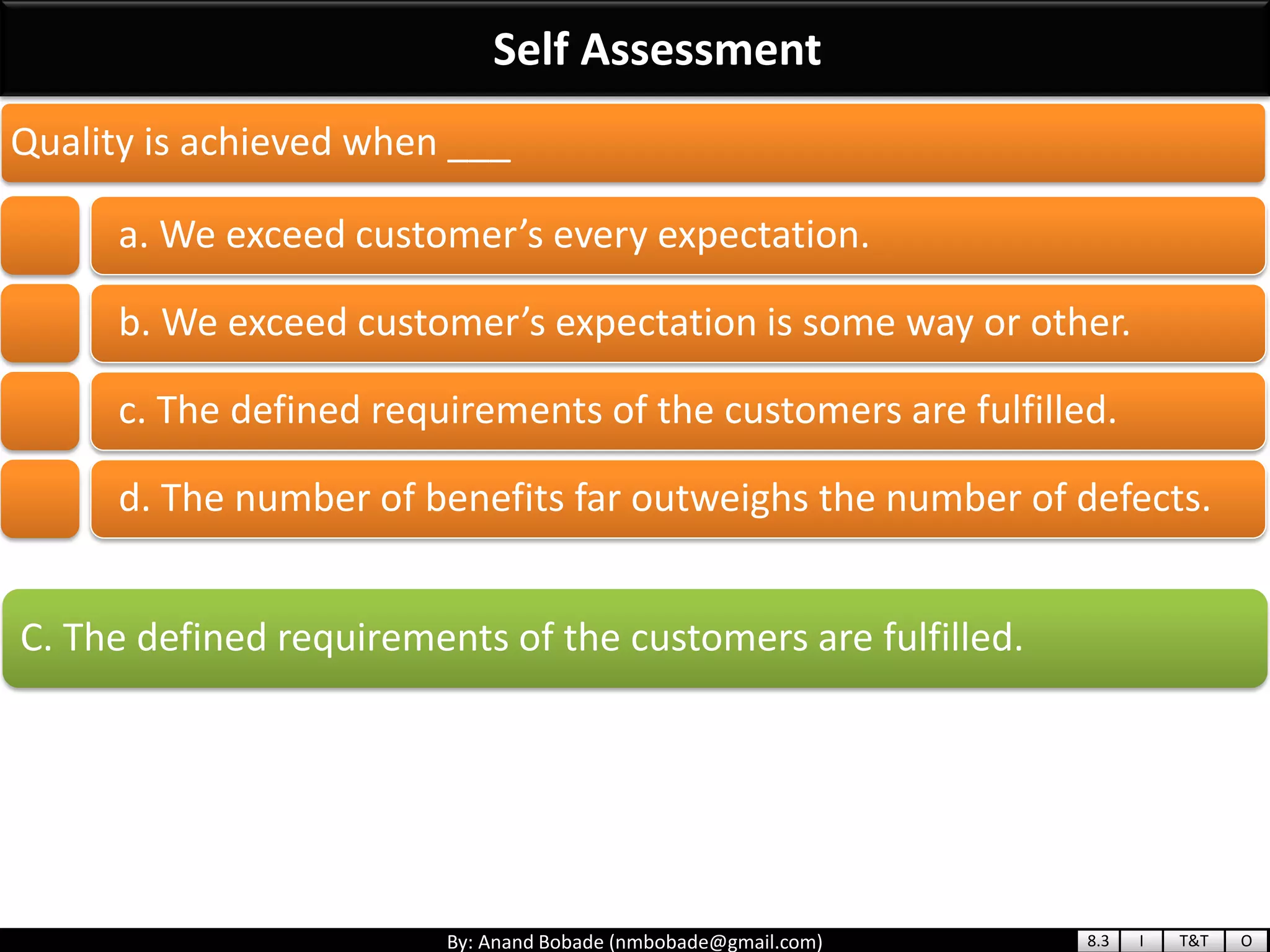
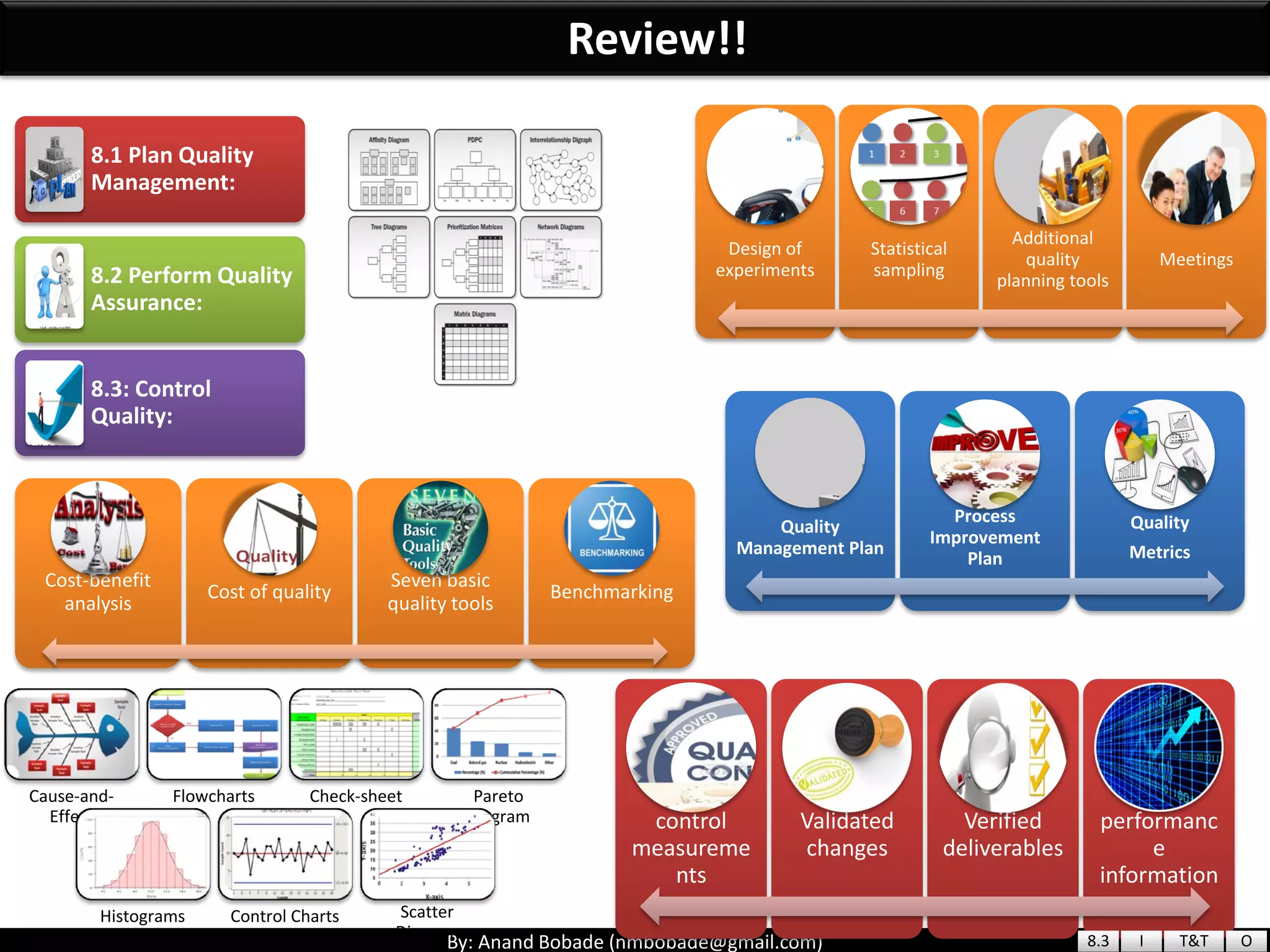
The document provides information about quality management concepts for project management and preparation for the PMP exam. It discusses key quality management processes including plan quality management, perform quality assurance, and control quality. Specific techniques covered include cost-benefit analysis, cost of quality analysis, the seven basic quality tools such as flowcharts and histograms, benchmarking, design of experiments, and statistical sampling. Quality theories including Six Sigma, total quality management, ISO standards, the 80/20 principle, and zero defects are also summarized.