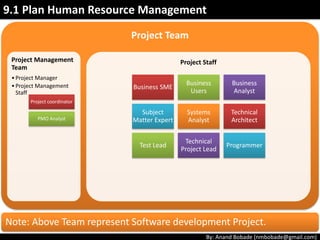
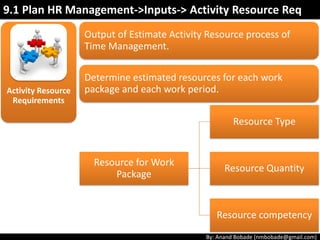
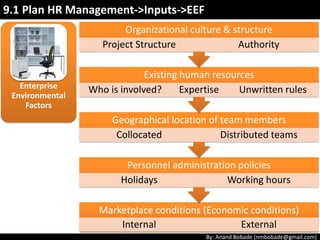
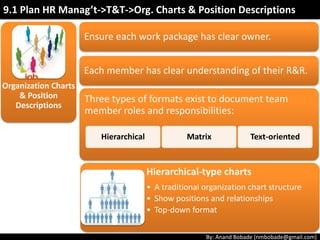
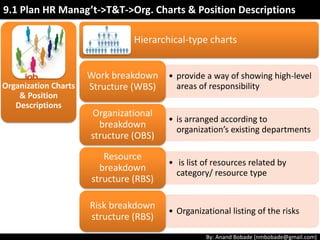
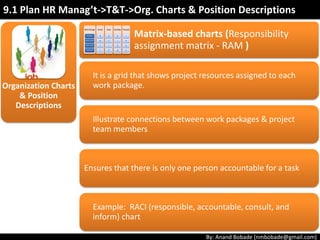
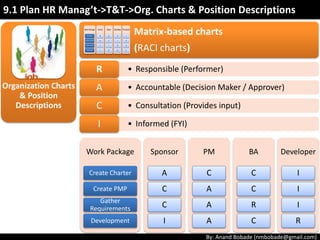
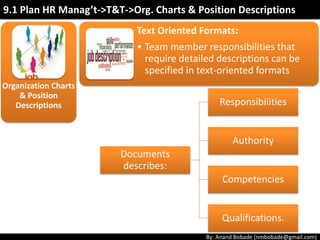
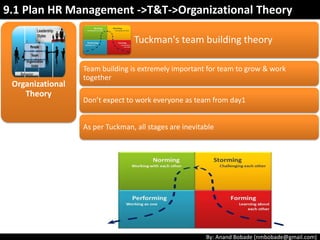
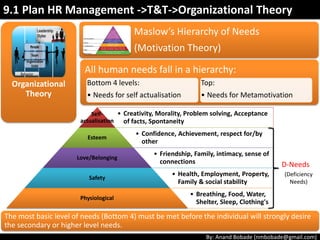
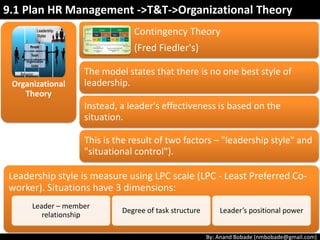
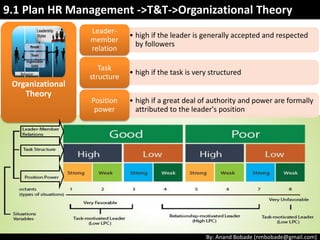
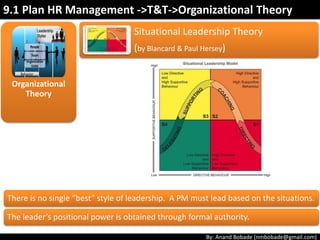
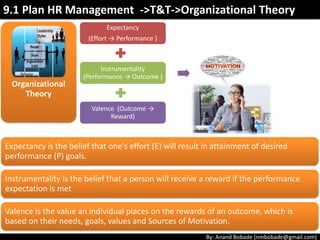
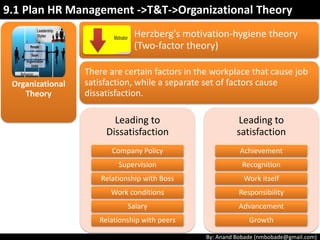
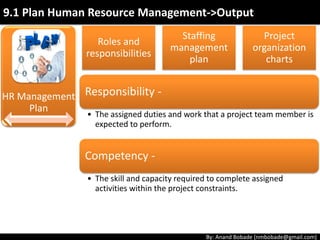
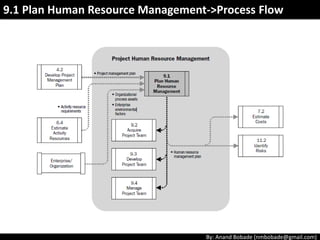
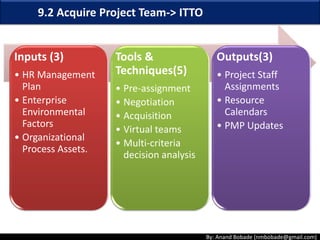
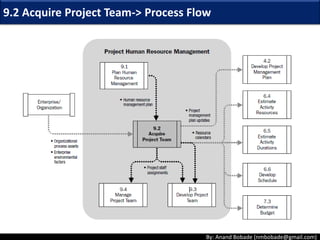
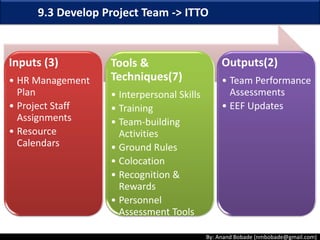
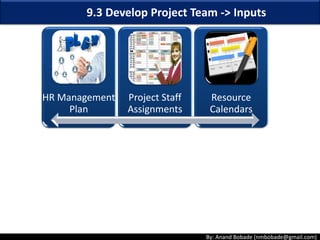
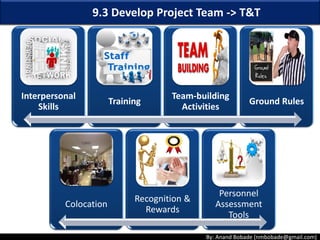
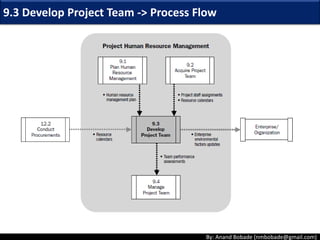
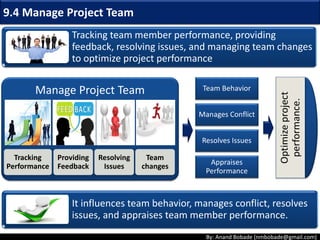
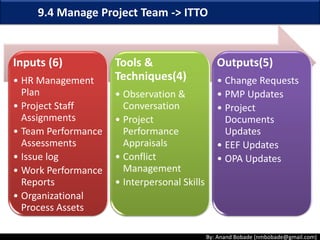
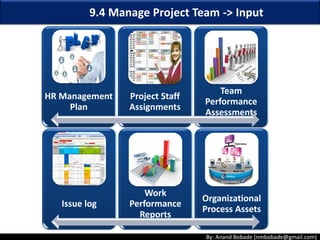
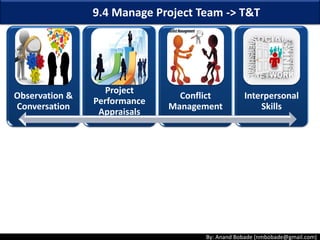
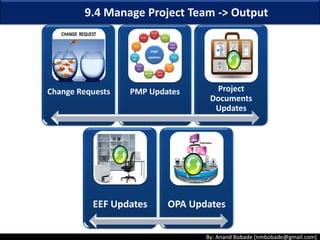
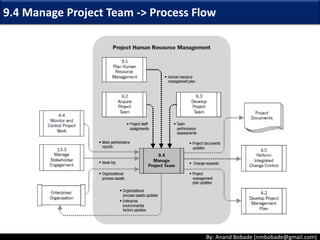
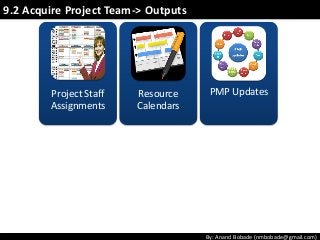
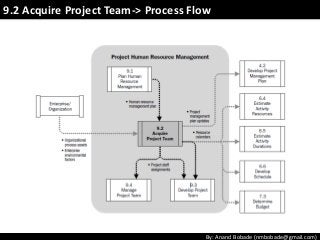
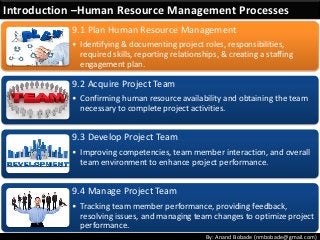
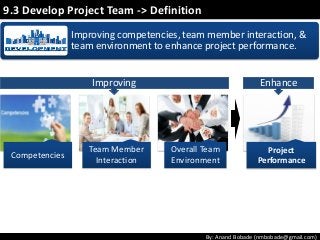
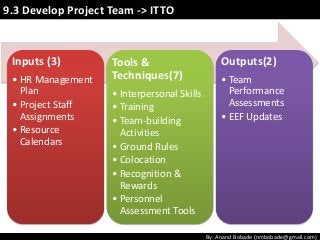
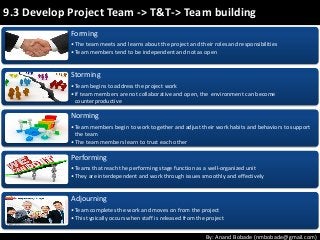
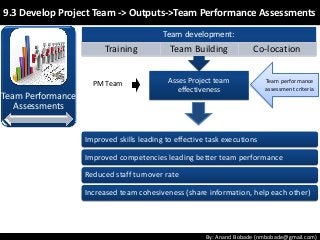
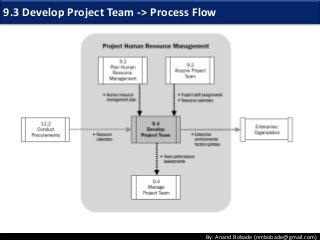
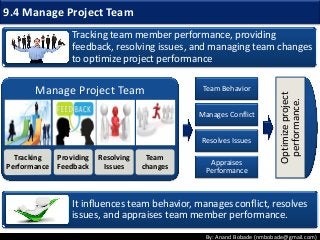
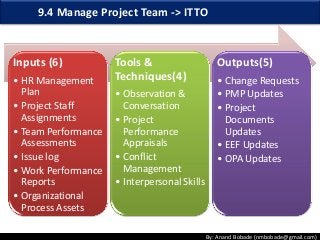
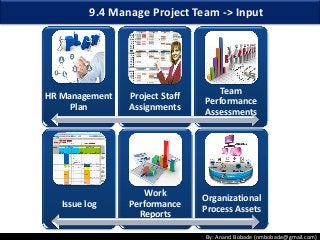
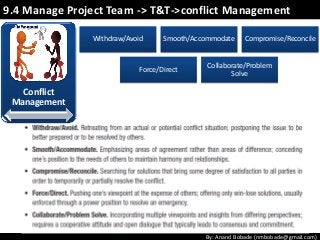
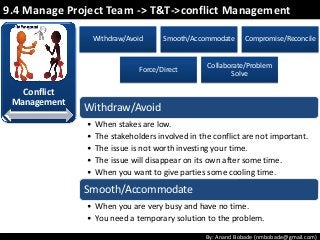
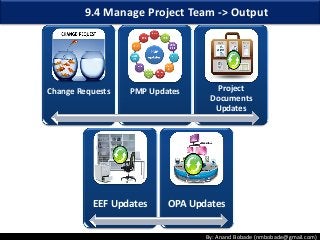
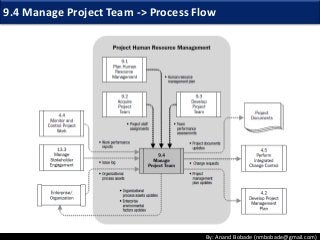
The document discusses the processes of human resource management in project management, focusing on planning, acquiring, developing, and managing the project team. It highlights key components such as the identification of roles and responsibilities, staffing engagement plans, and team development strategies, along with various organizational theories relevant to team dynamics. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of tracking performance and resolving issues to optimize project outcomes.