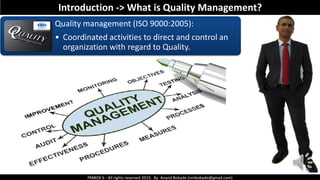
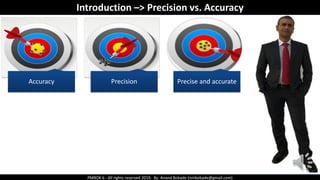
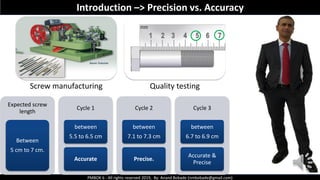
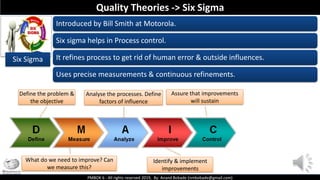
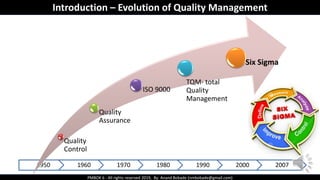
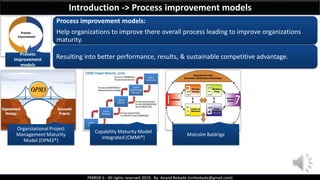
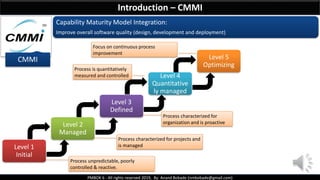
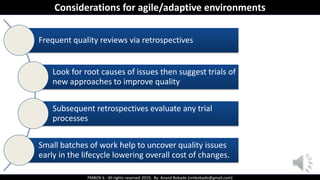
The document discusses Project Quality Management as outlined in the PMBOK 6th edition, focusing on definitions of quality, quality management processes, and various quality theories including Six Sigma and Total Quality Management. It emphasizes the importance of meeting customer requirements, continuous improvement, and the difference between quality and grade. The content is structured to guide project managers in ensuring quality is integral to project planning and execution.