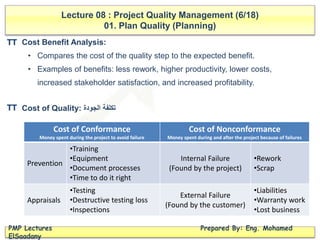
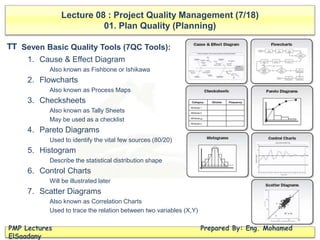
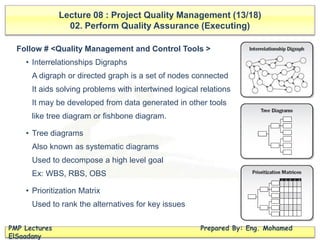
The document discusses project quality management, covering key concepts such as planning quality, performing quality assurance, and controlling quality. It defines terms important for quality assessment, outlines tools and techniques for planning and assurance, and emphasizes the importance of team responsibility for quality. Additionally, it highlights the impacts of poor quality and various quality management strategies, including cost-benefit analysis and continuous improvement practices like Kaizen.