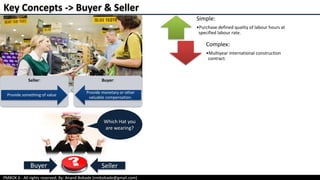
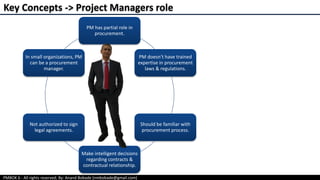
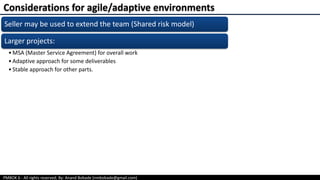
The document provides an overview of project procurement management as outlined in the PMBOK 6th edition, focusing on the roles of the project manager, types of procurement processes, and contract types. It discusses factors influencing procurement decisions, centralized versus decentralized procurement, and emerging trends impacting procurement practices. Additionally, it outlines various contract types, including fixed price and cost reimbursable contracts, along with the procurement management processes of planning, conducting, and controlling procurement.