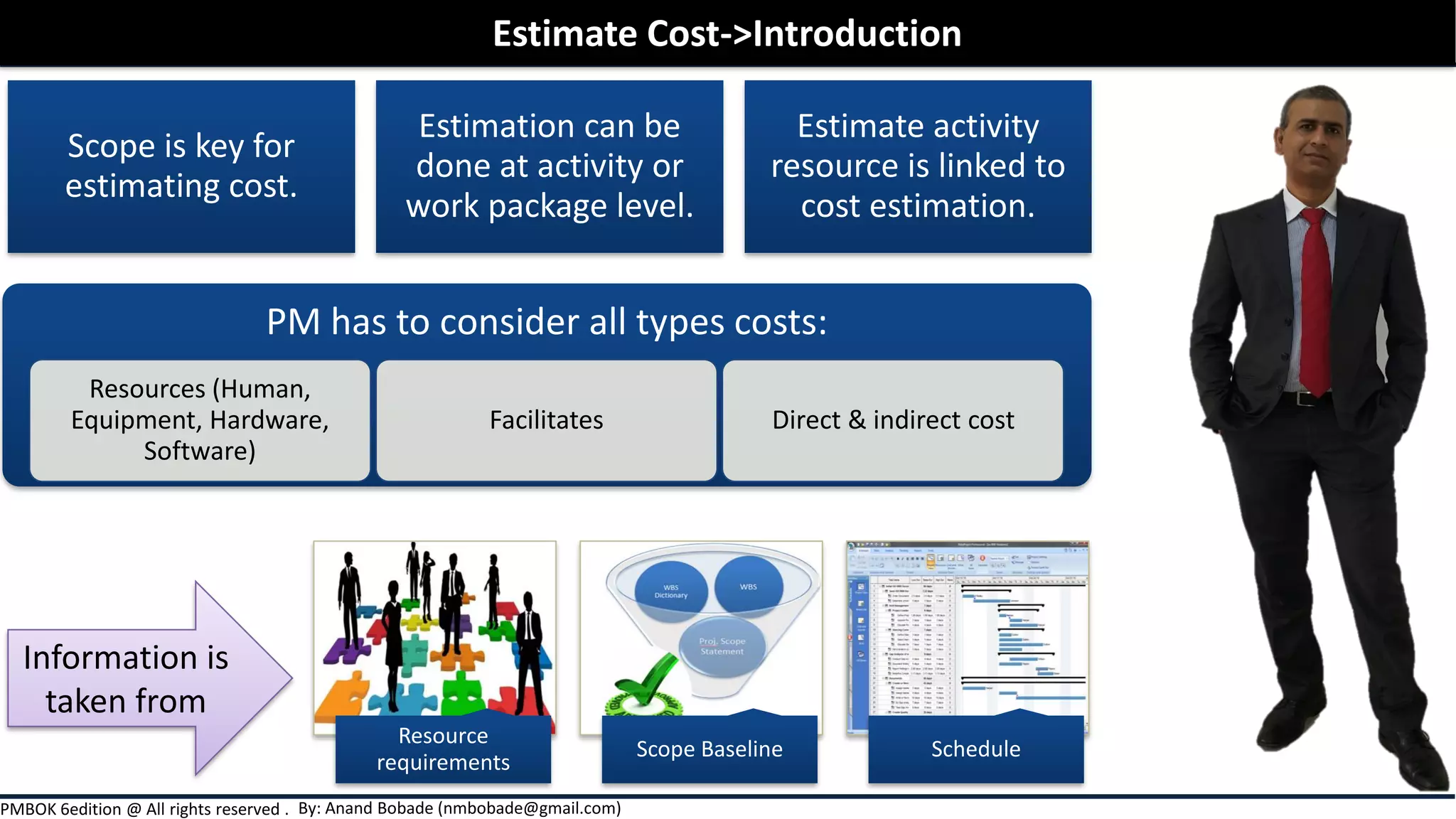
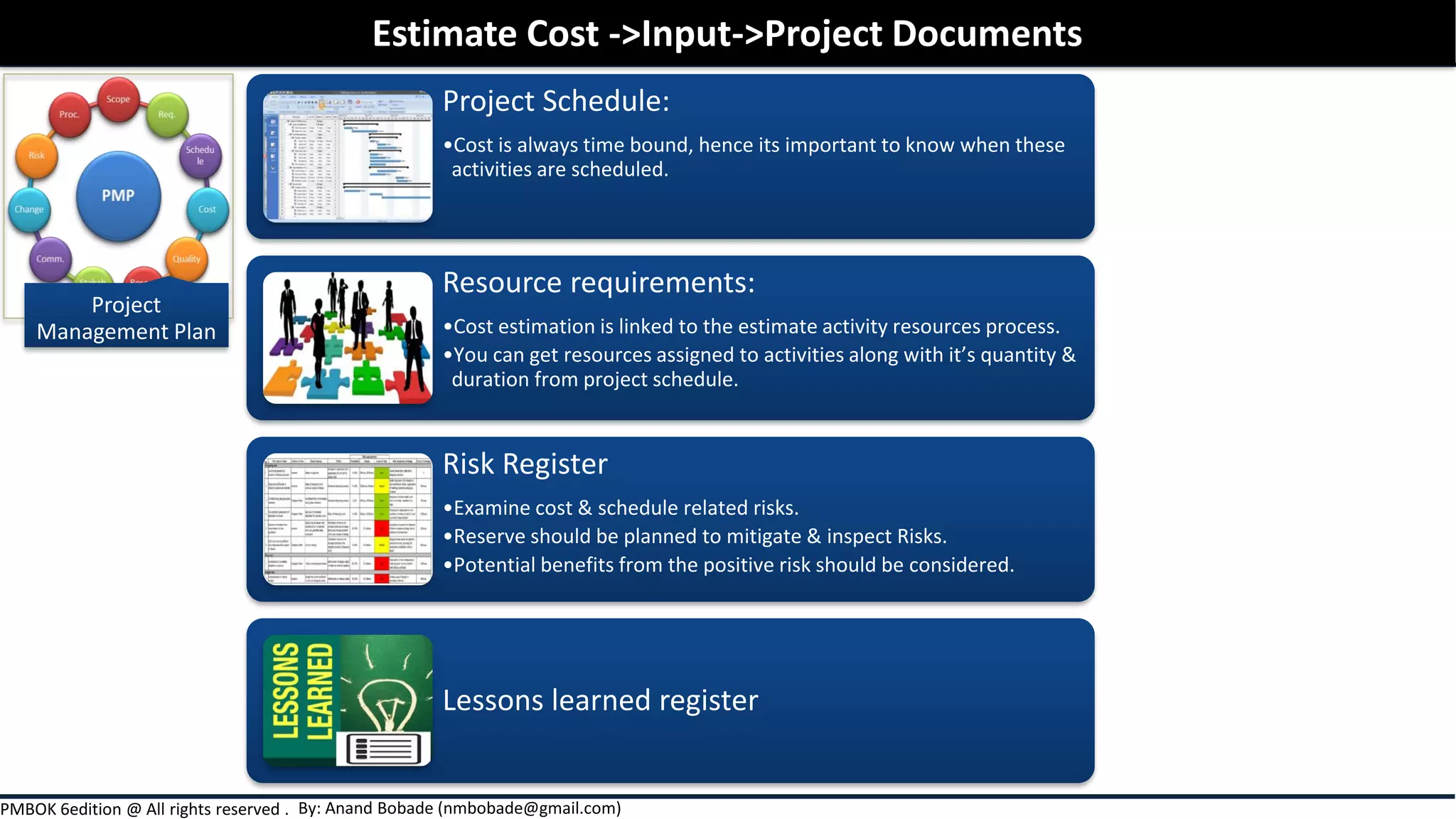
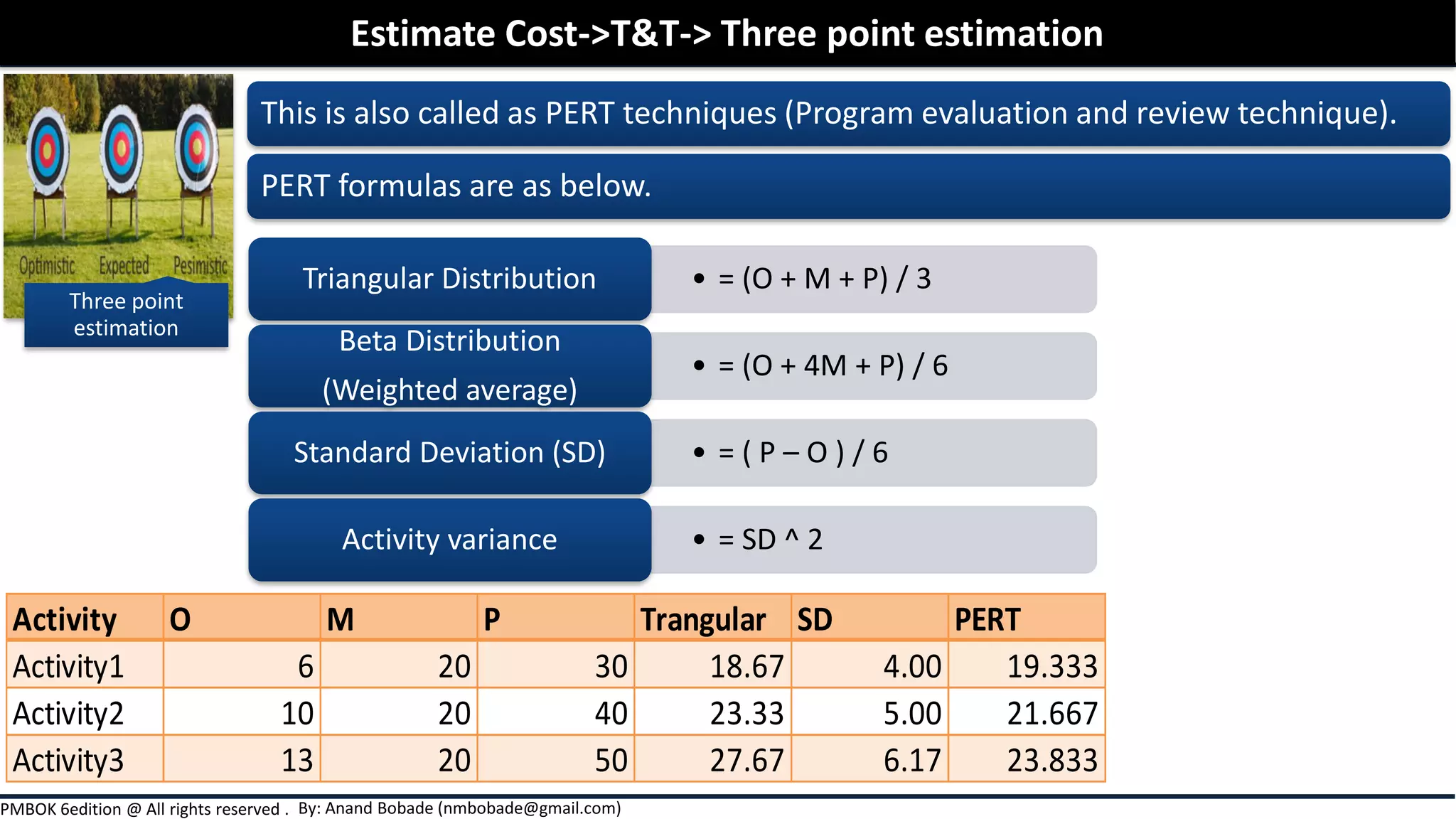
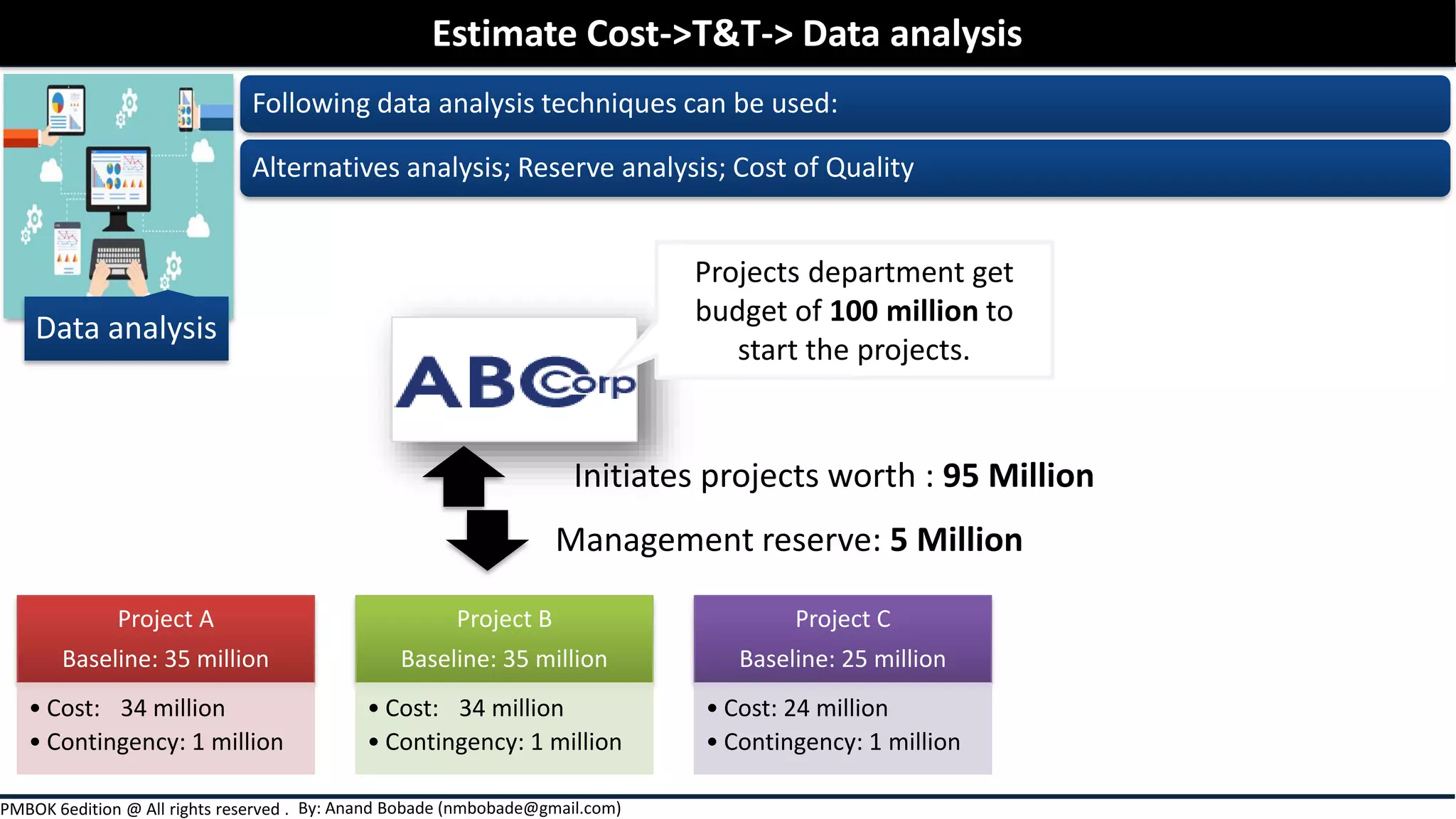
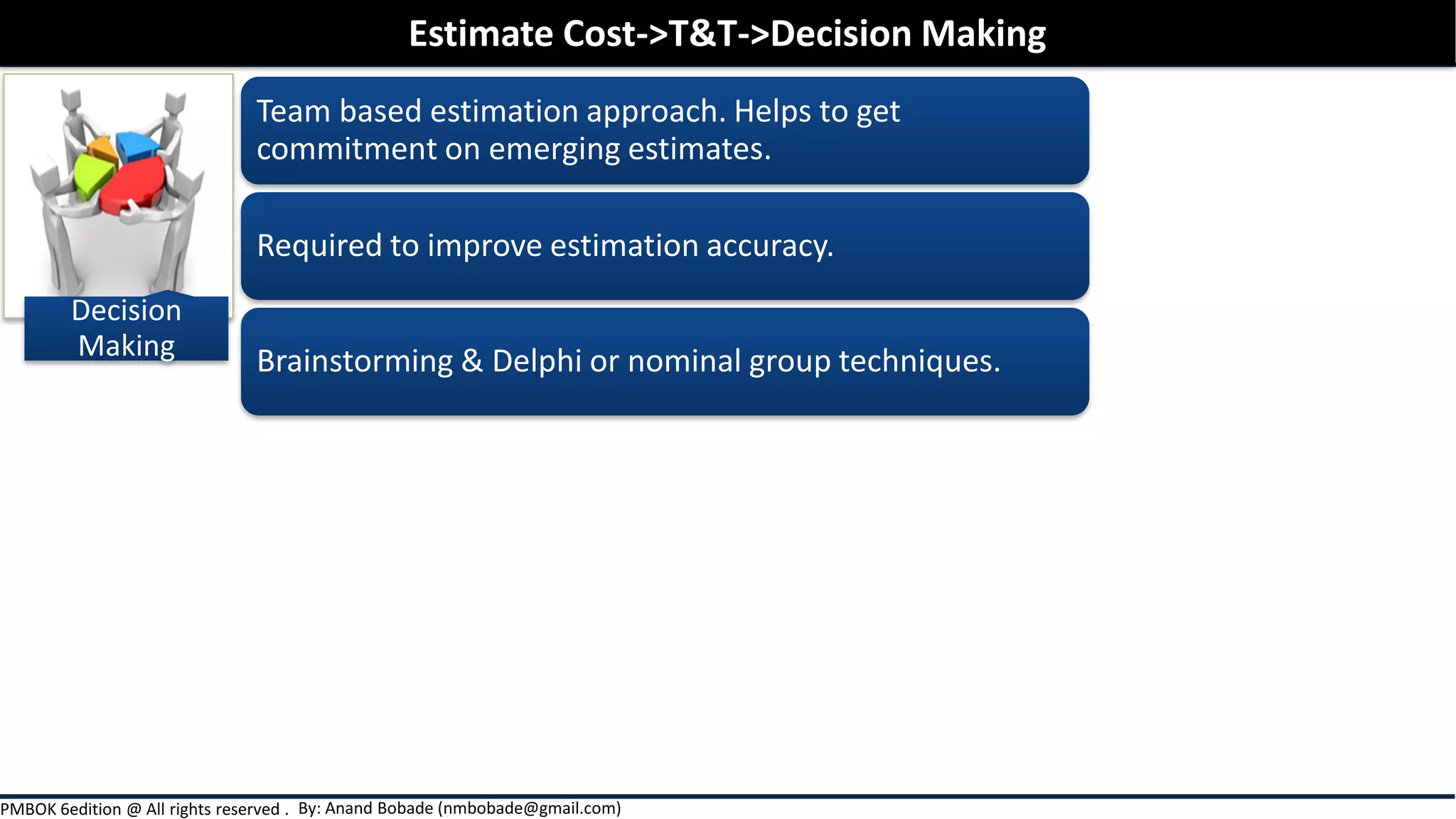
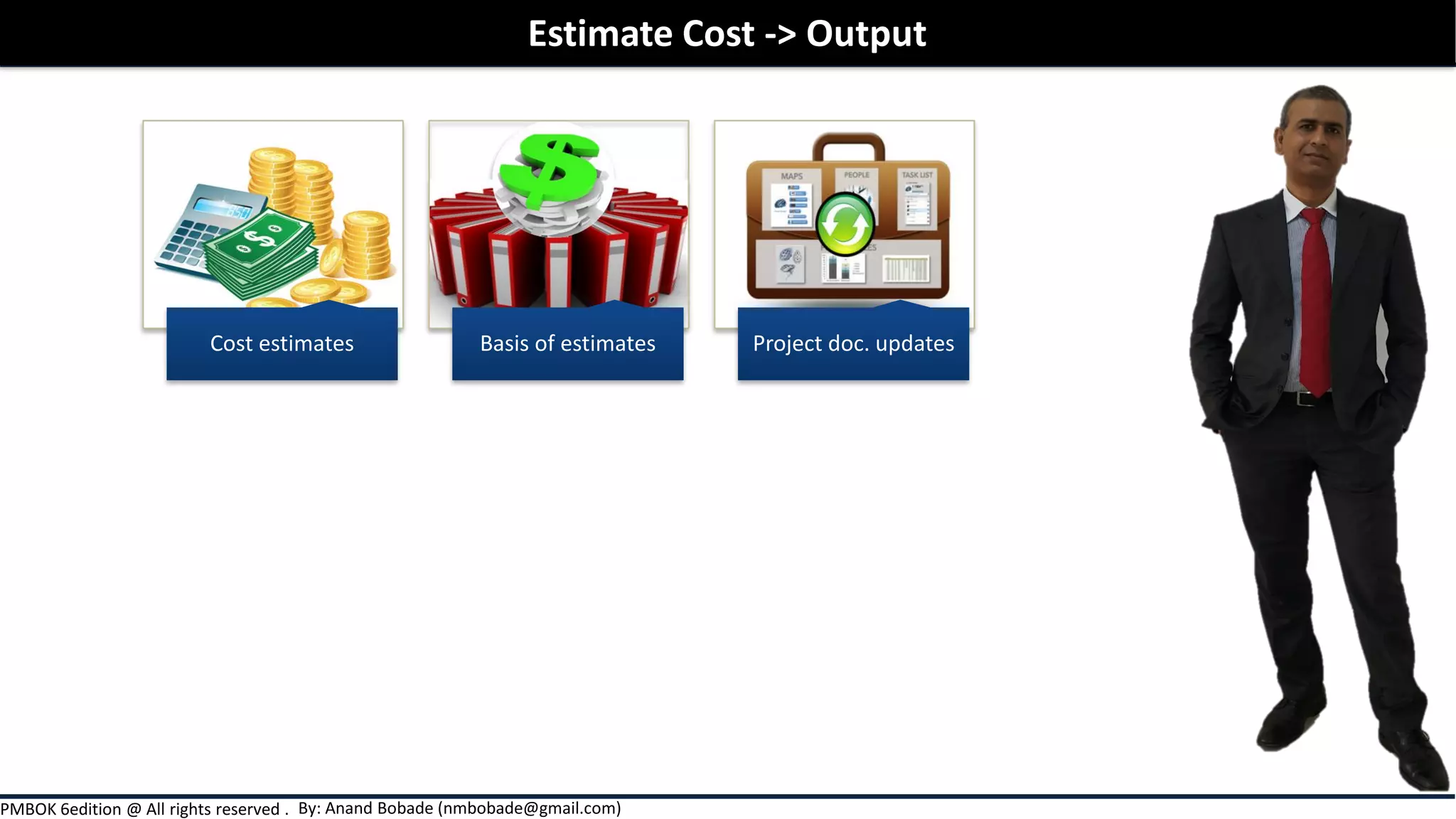
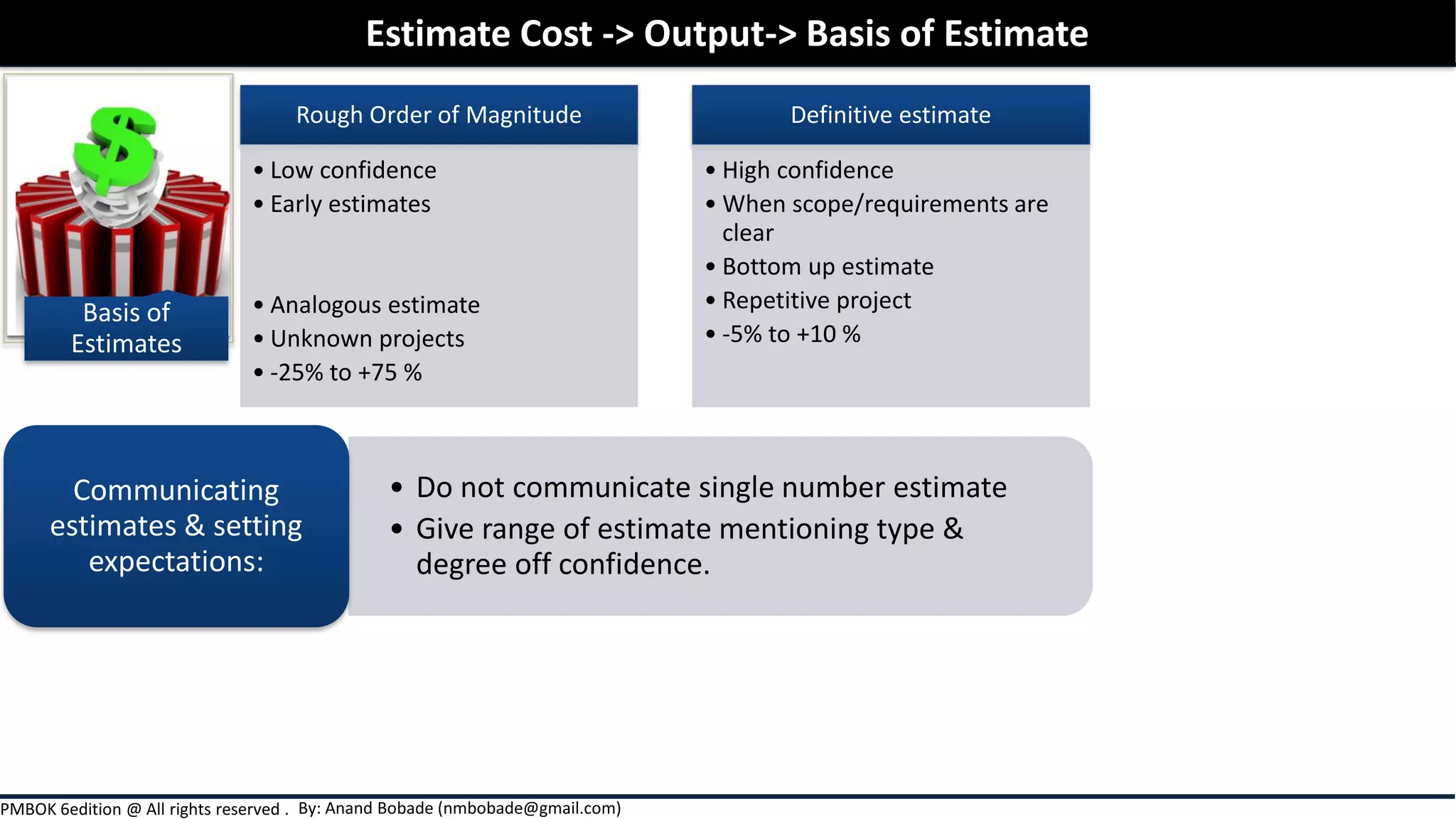
Chapter 7 of the PMBOK Guide focuses on project cost management, detailing the processes involved in estimating costs, determining budgets, and controlling costs throughout a project. It covers various estimation techniques such as expert judgment, analogous, parametric, and bottom-up estimating, as well as the importance of considering risks and uncertainties in cost estimates. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of thorough documentation and communication of estimates to enhance accuracy and stakeholder expectations.