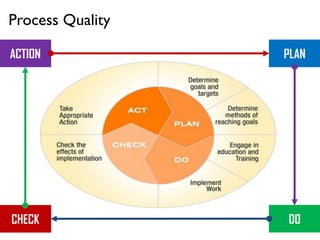
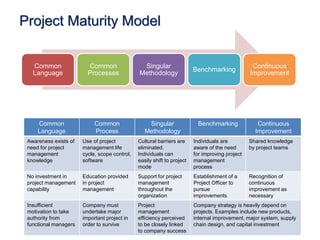
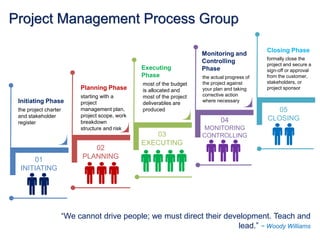
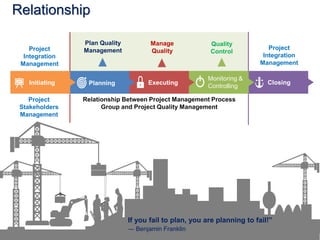
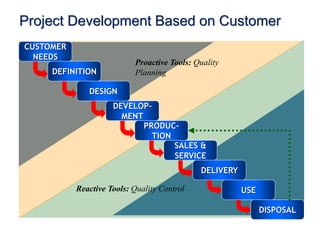
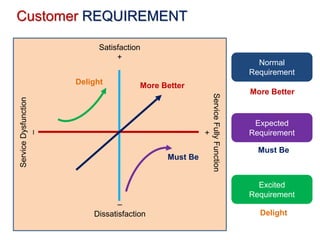
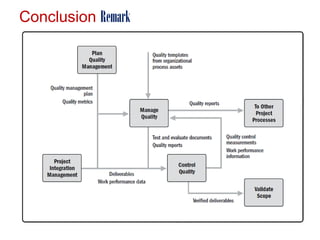
This document discusses project quality management. It begins by defining what a project and its key characteristics are, such as being temporary with a defined start and end, unique, and involving people who don't usually work together. It then discusses different dimensions of quality, including product, service, people, process, and environmental quality. The document outlines the five process groups in project management and explains how quality management fits within these groups through planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing quality. Finally, it provides overviews of key quality management processes, including plan quality management, manage quality, and control quality.