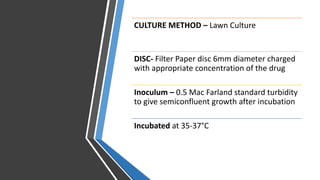
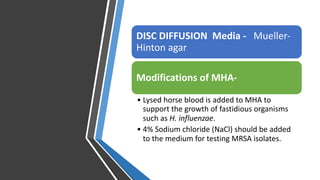
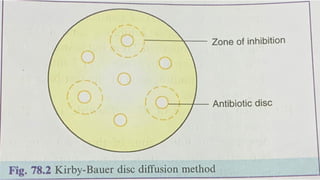
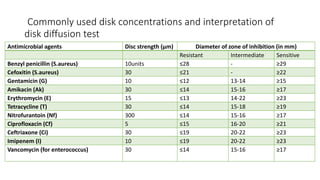
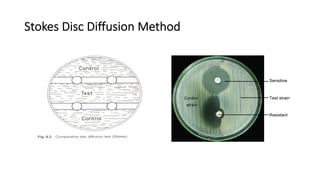
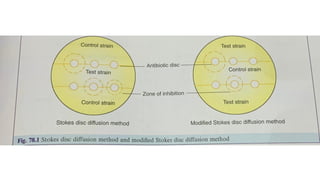
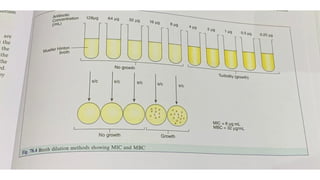
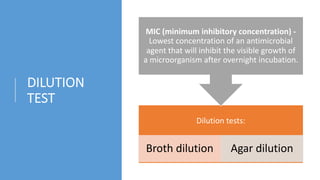
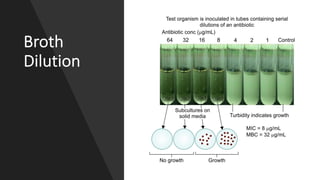
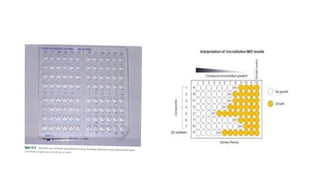
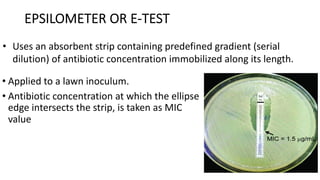
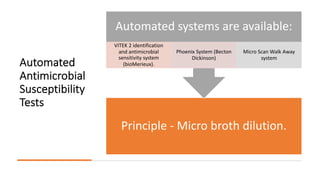
The document discusses antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) methods to determine the susceptibility of pathogenic bacteria, outlining factors affecting results and various testing techniques, including disc diffusion and dilution methods. It highlights the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method as the most widely used and details how to interpret zone sizes for several antibiotics. Additionally, it covers automated systems and molecular methods, such as PCR, for detecting drug-resistant genes.