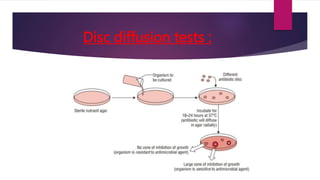
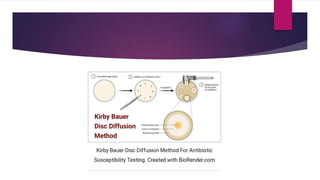
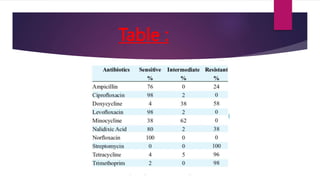
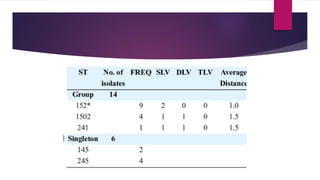
The document discusses antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) performed by clinical laboratory scientists to identify effective antibiotics for bacterial strains. It details two main methods: disc diffusion tests, including the Kirby-Bauer method, and dilution tests to determine minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC). The aim of these tests is to accurately predict the response of microorganisms to antimicrobial therapy.