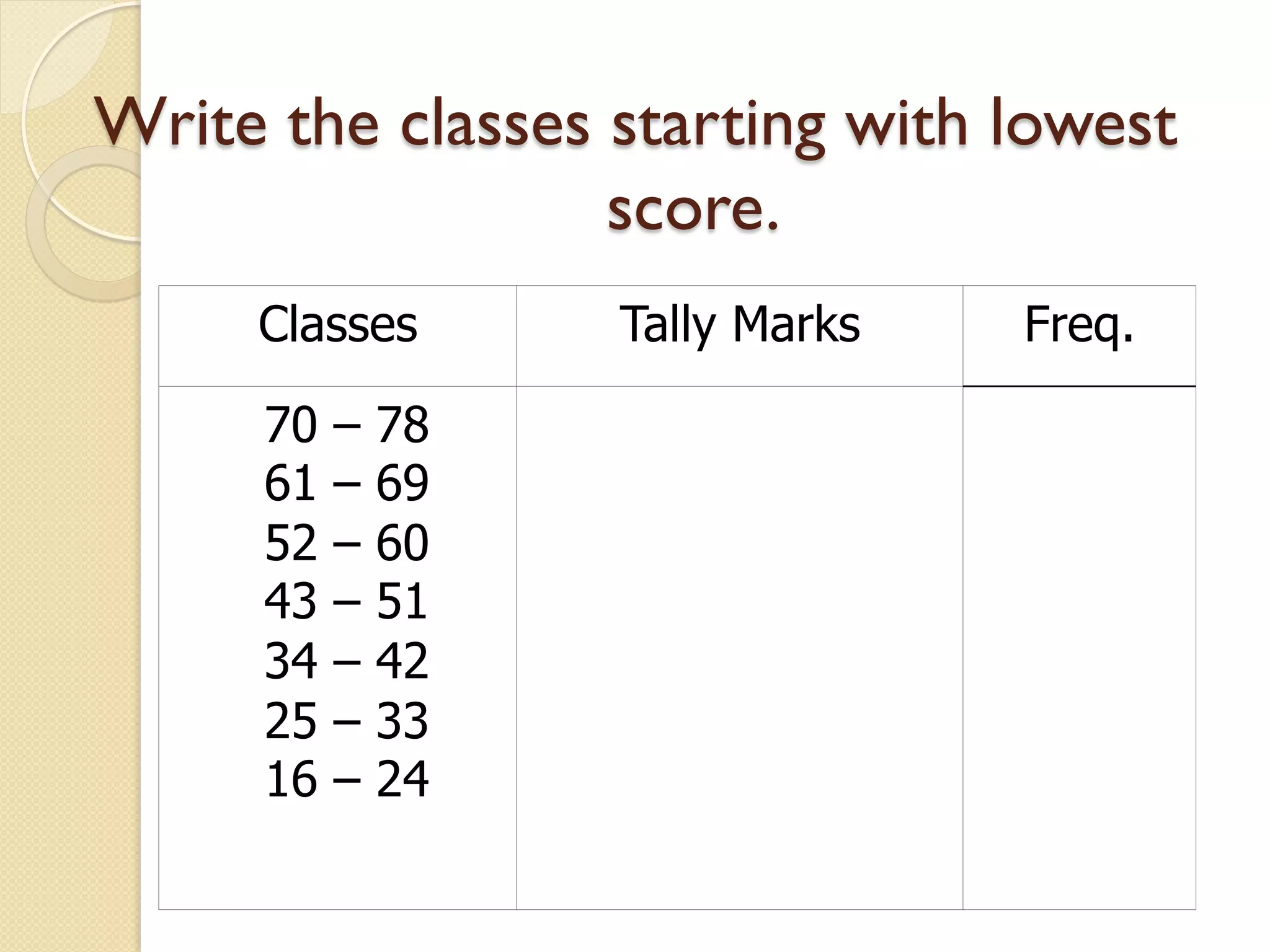
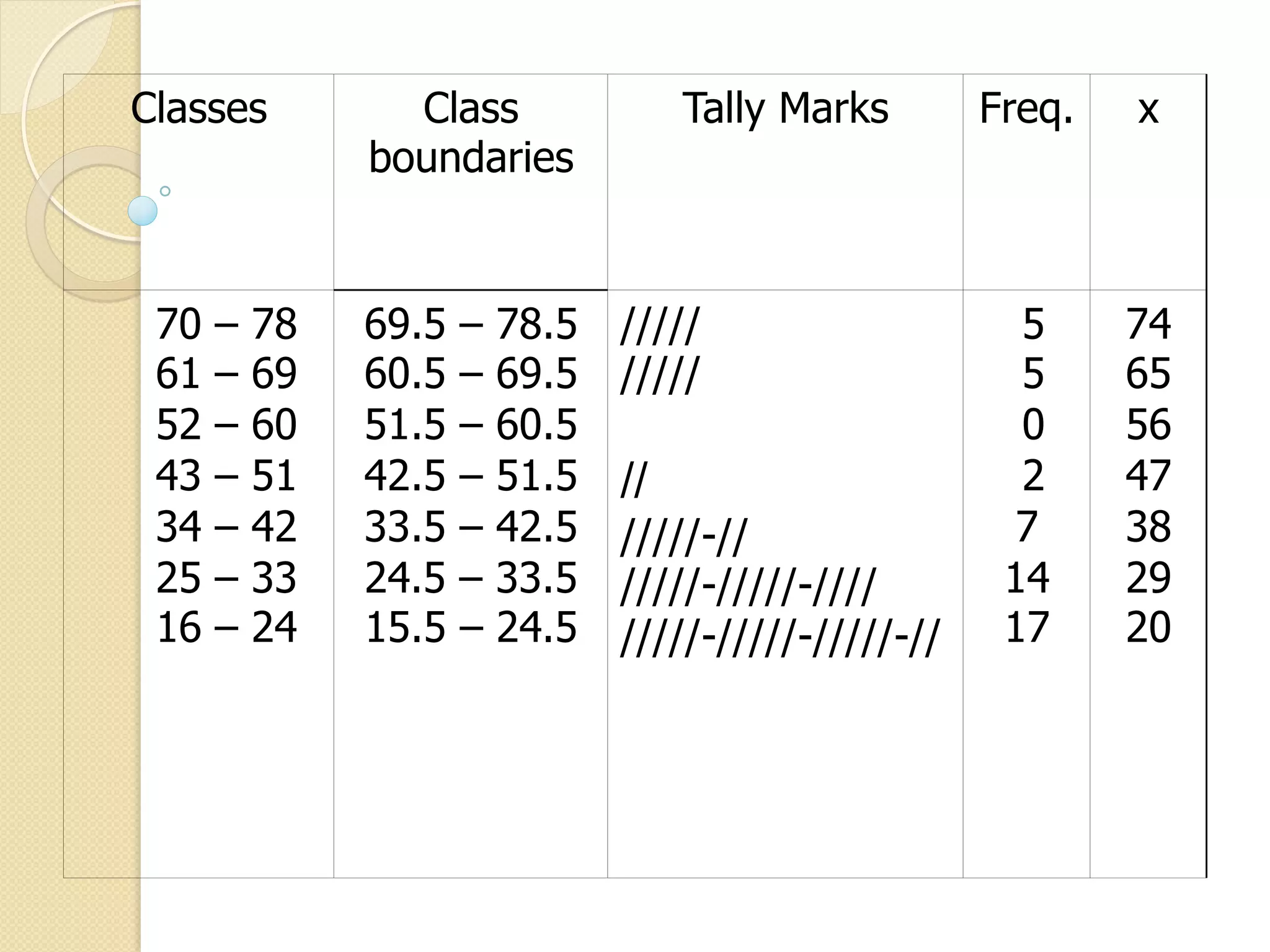
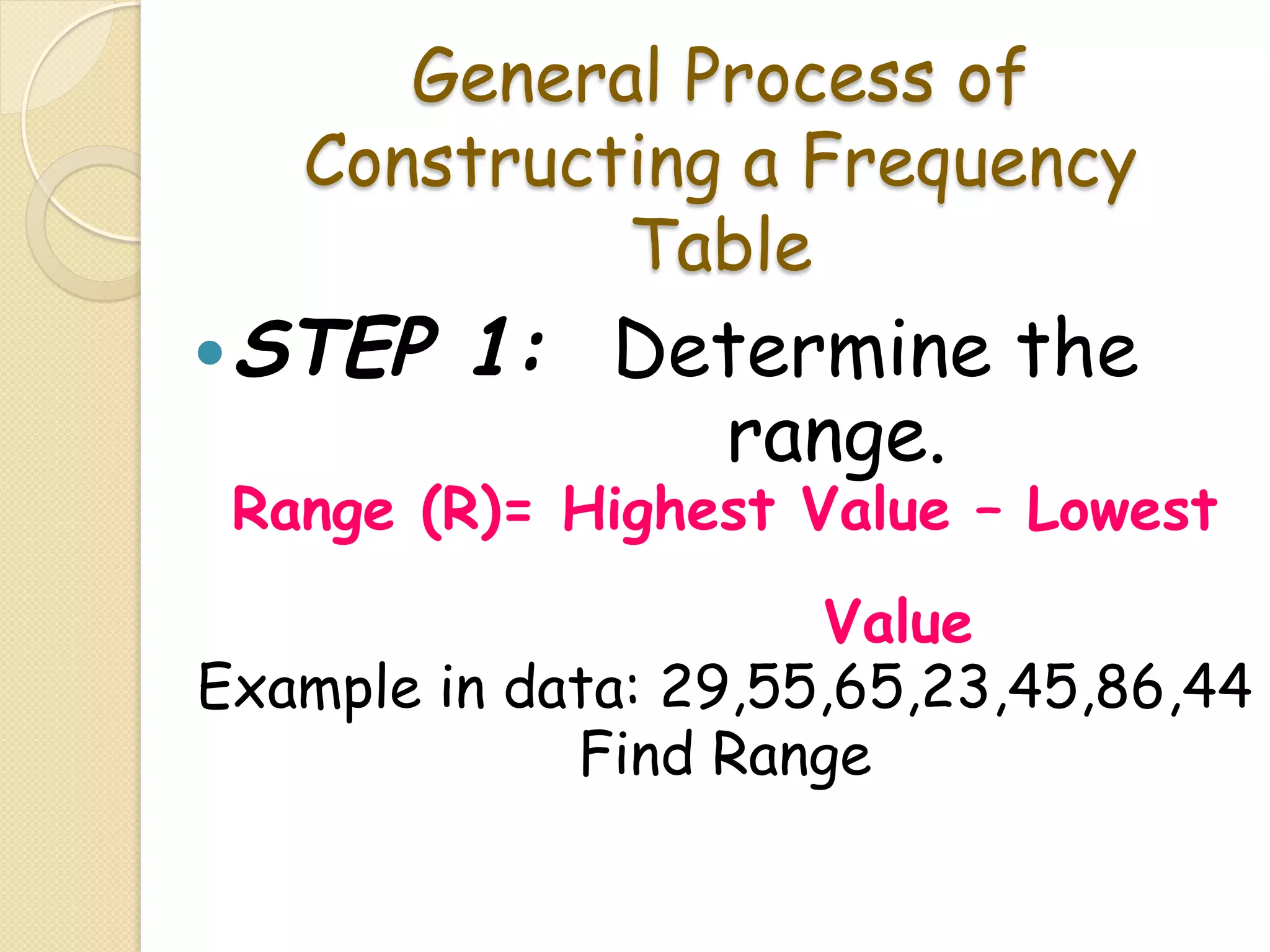
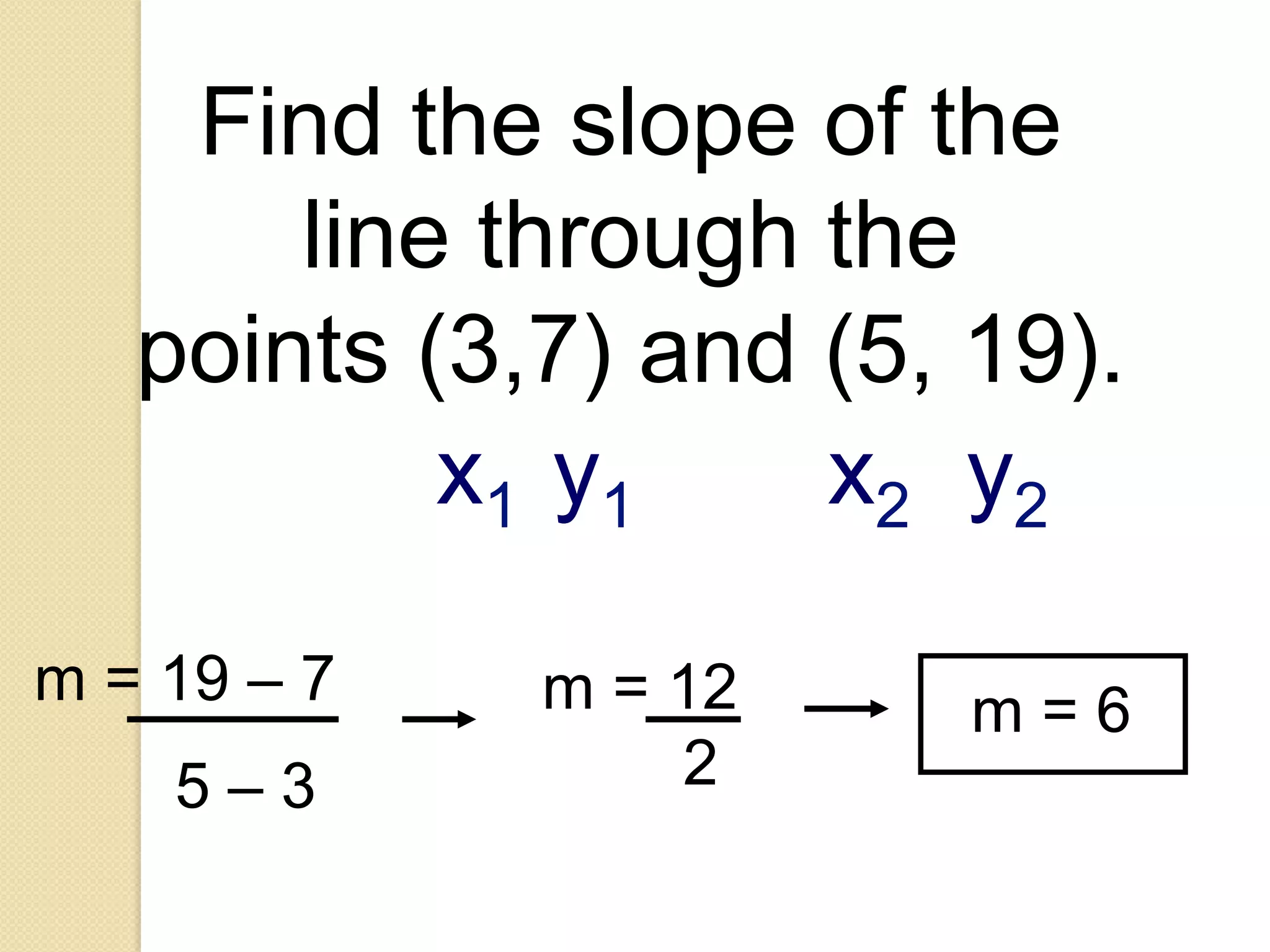
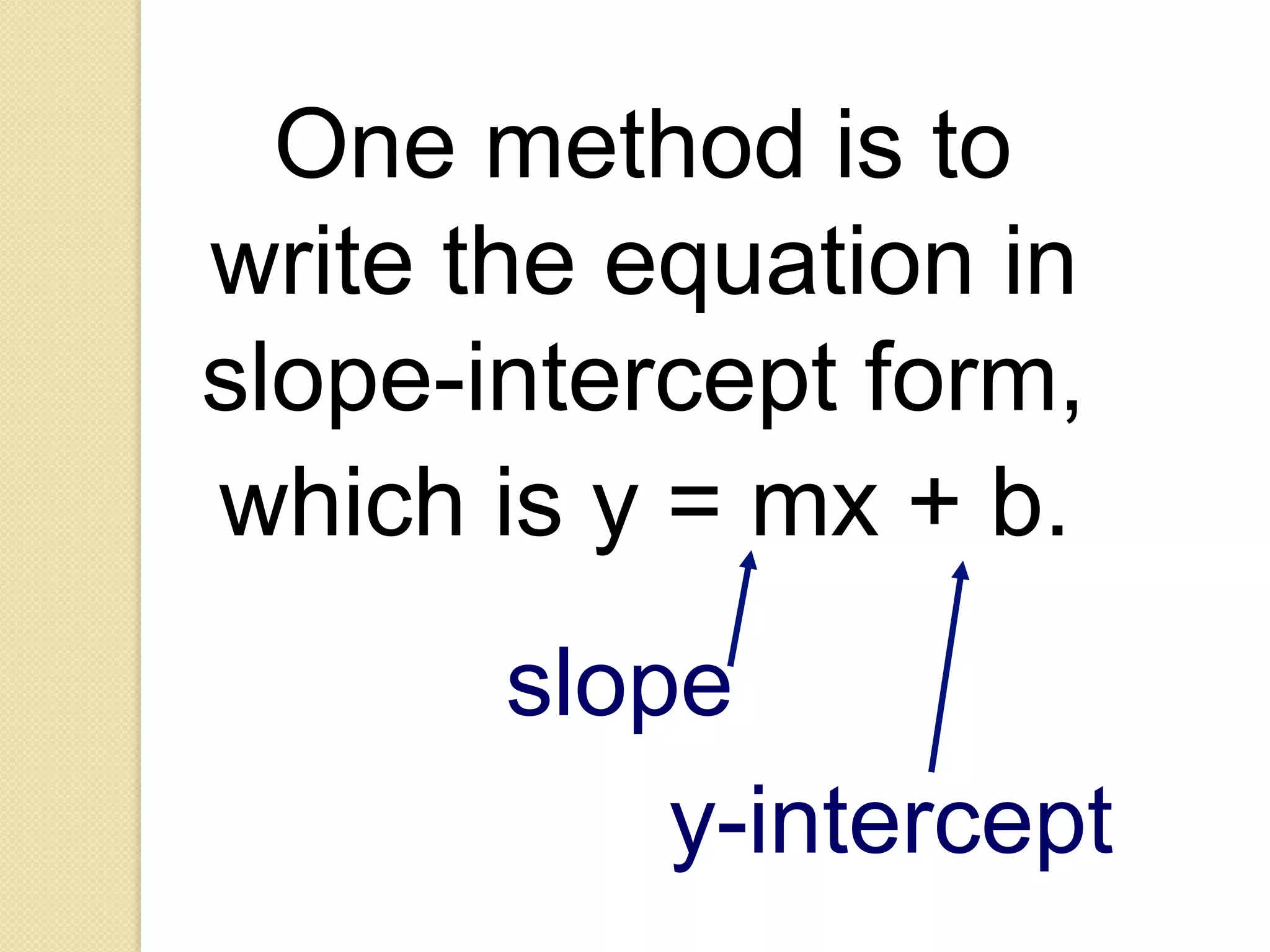
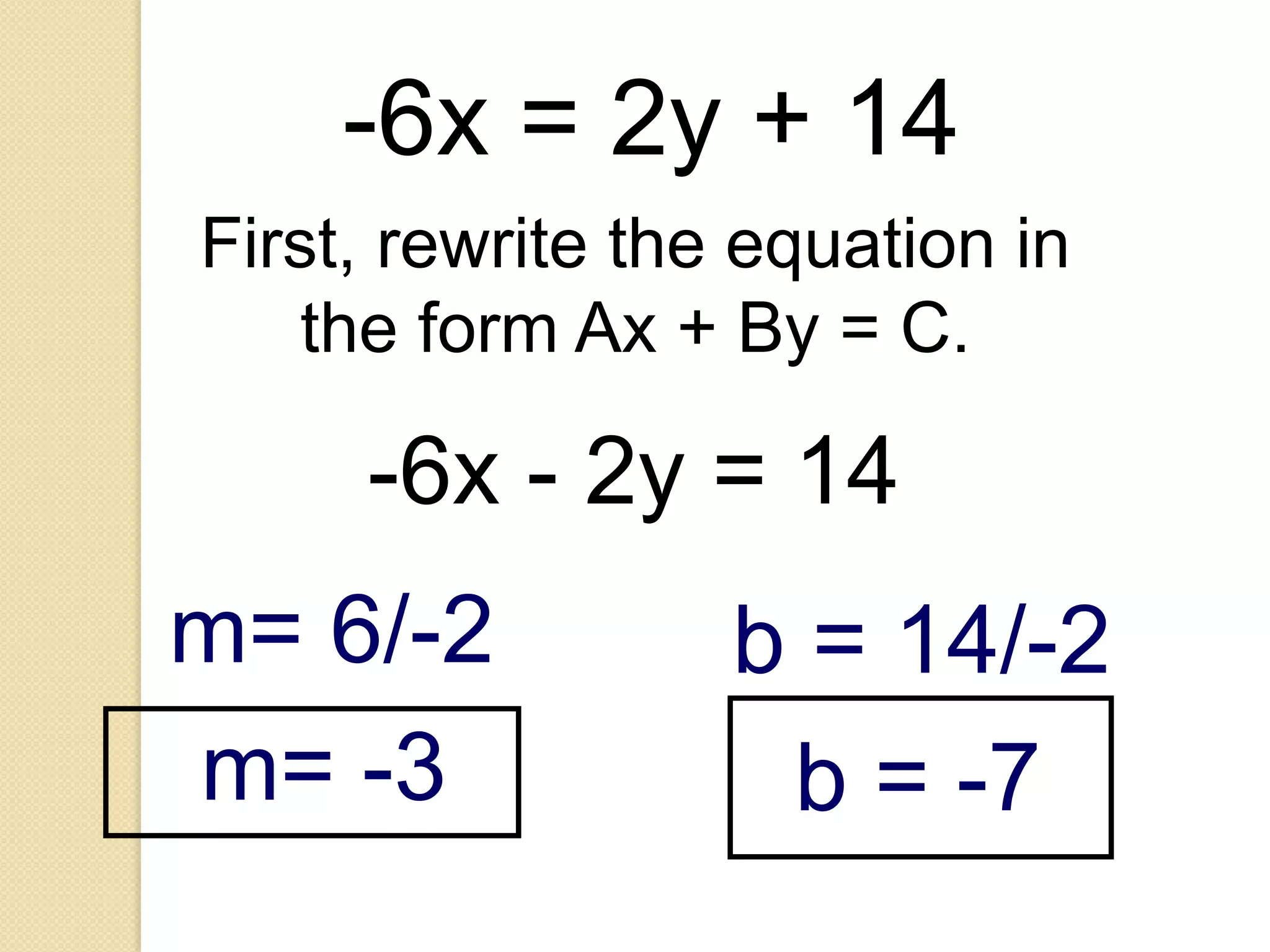
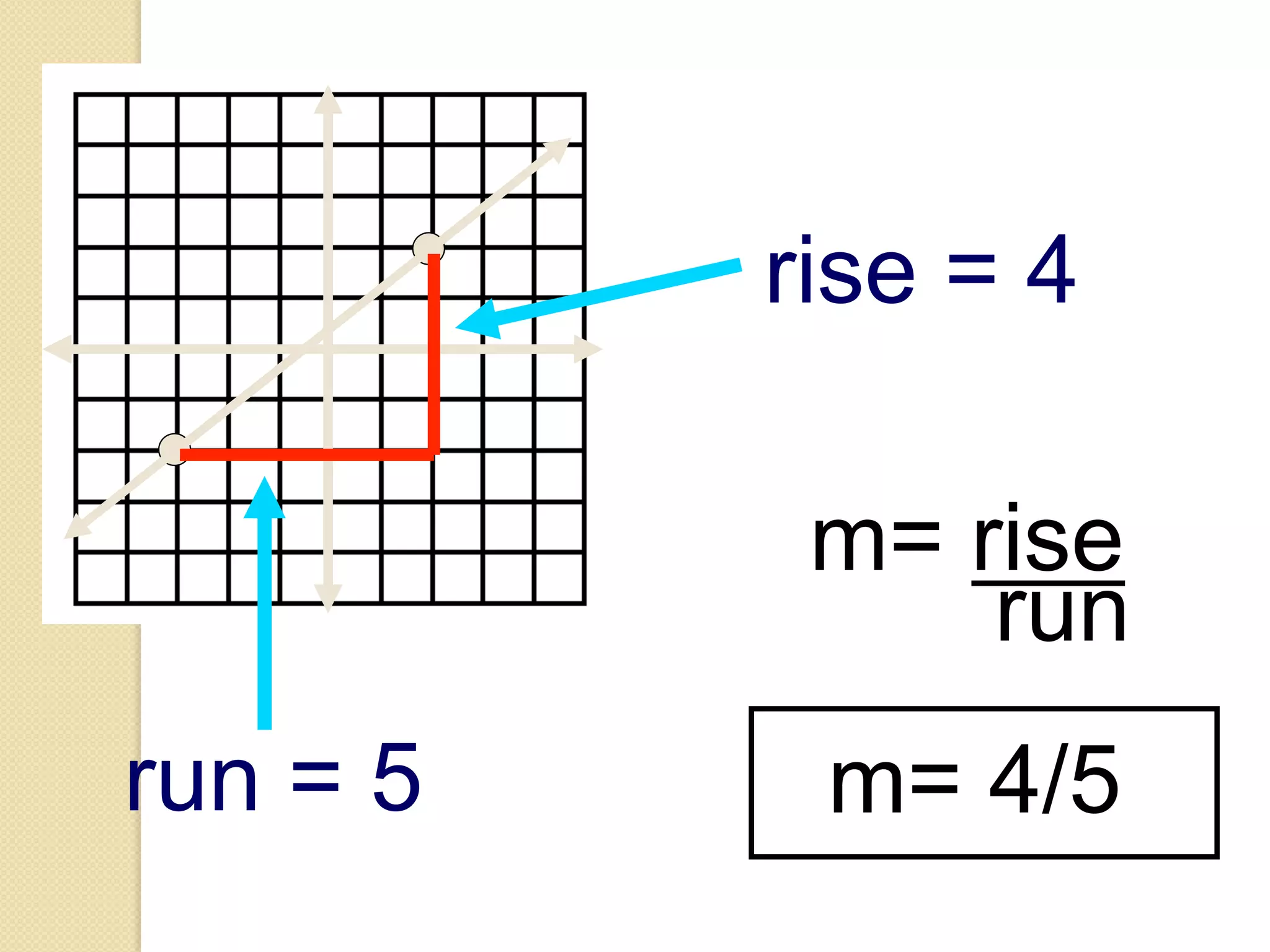
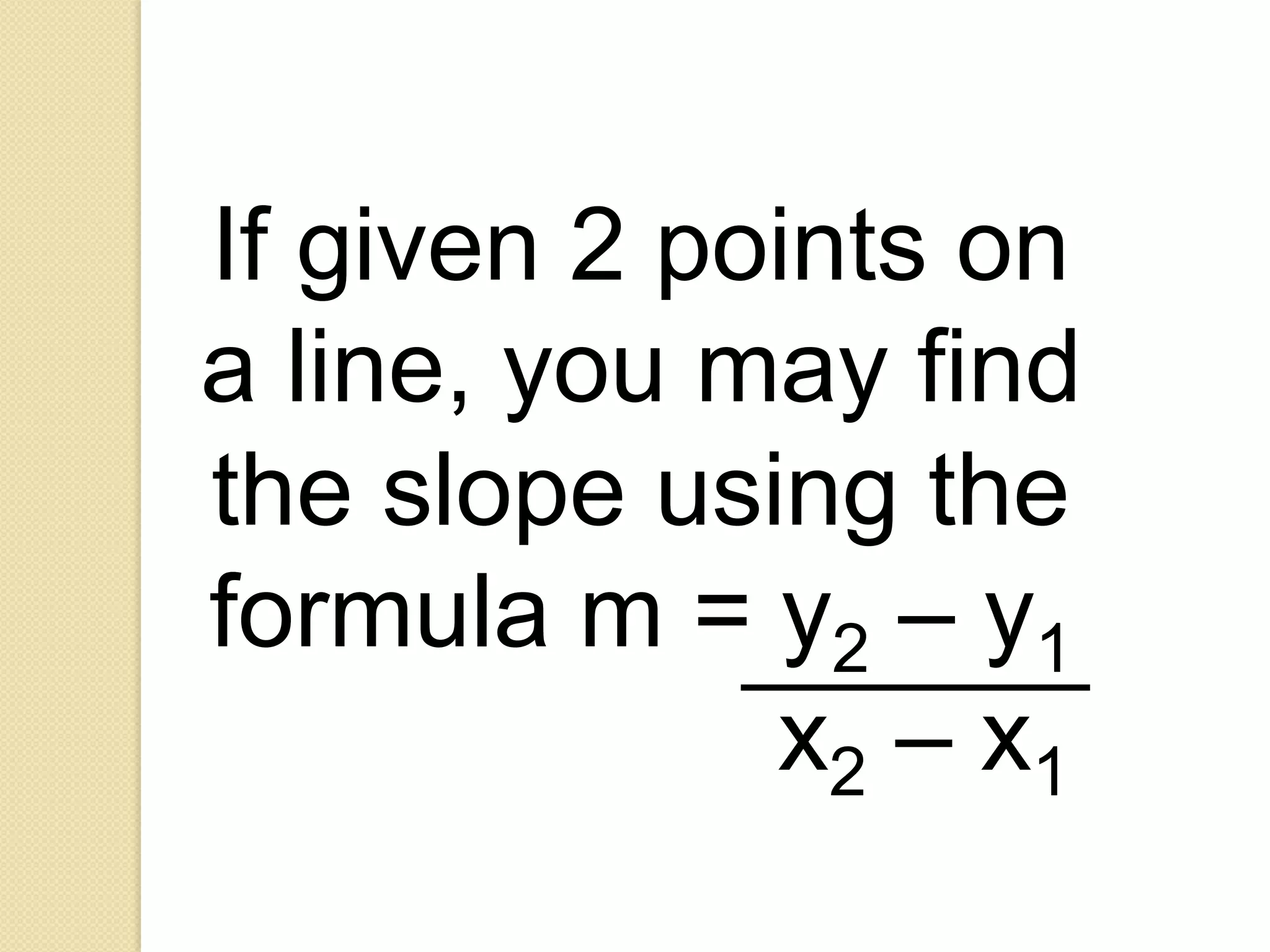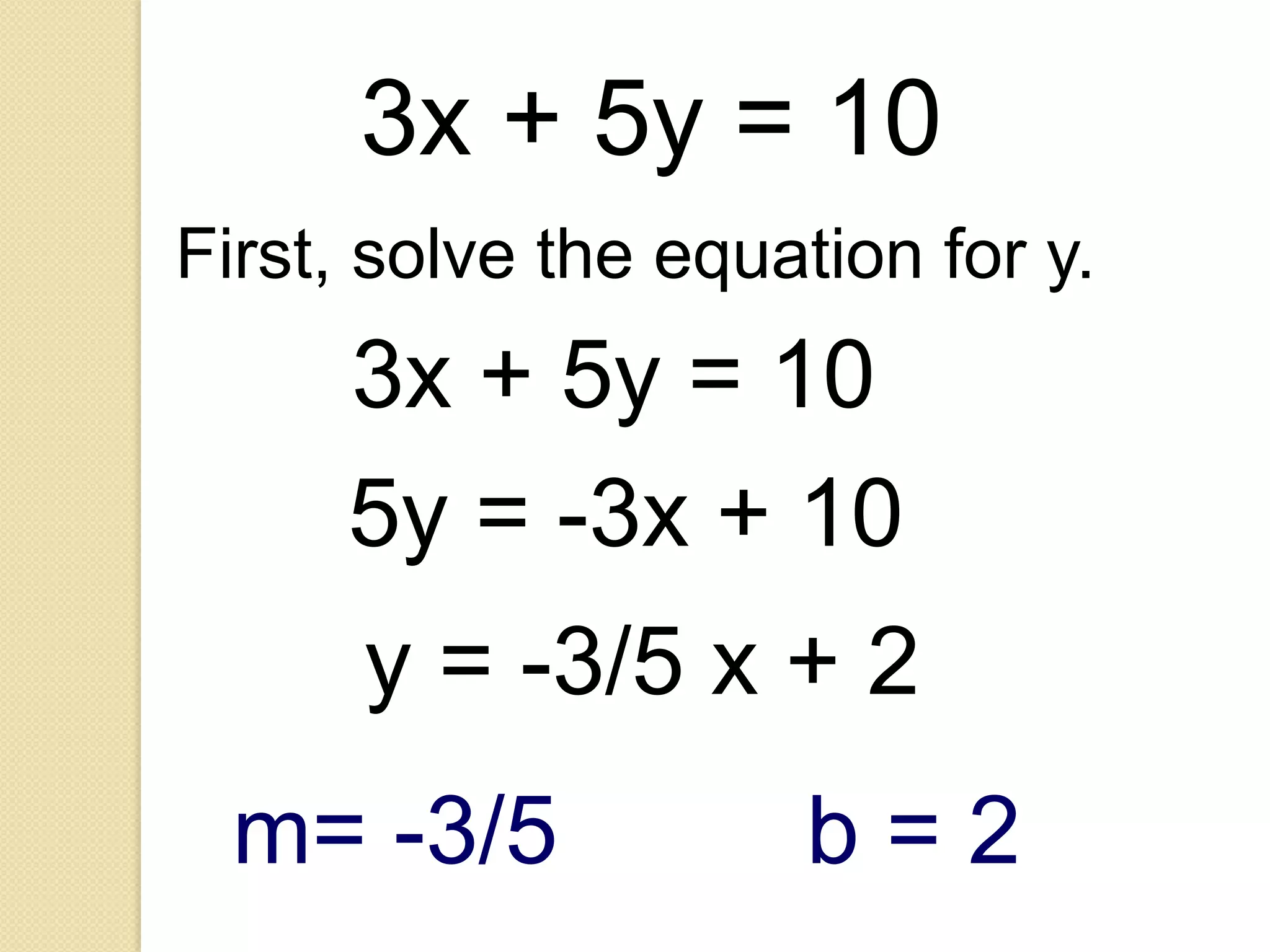This document provides an overview of frequency distributions and how to construct a frequency distribution table from a set of data. It discusses the key steps: 1) determining the range of the data, 2) choosing the number of classes, 3) calculating the class width, and 4) tallying the frequency of observations within each class interval to populate the table. Guidelines for constructing frequency tables are also outlined, such as using mutually exclusive and exhaustive class intervals of uniform width. An example of constructing a 7-class frequency table from a set of 50 observations is shown to demonstrate the process.