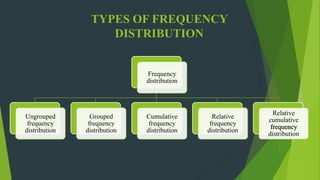
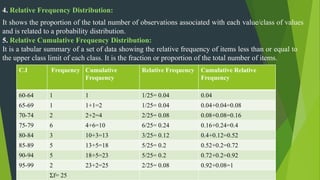
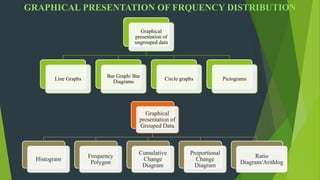
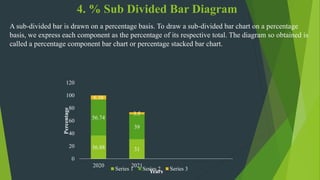
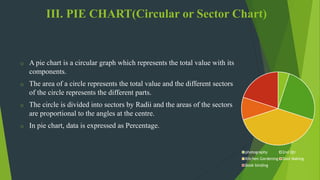
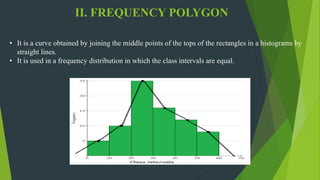
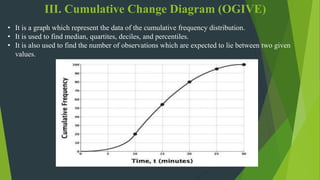
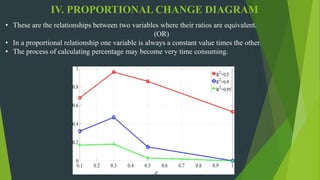
The document discusses frequency distribution in biostatistics, outlining its significance in summarizing observations across various classes or categories. It details different types of frequency distributions including ungrouped, grouped, cumulative, relative, and relative cumulative, along with examples and graphical representations such as histograms, bar diagrams, and pie charts. Additionally, the document explains how to visually present data through methods like line graphs and pictograms.