This document discusses several key concepts related to dispersion and variability in distributions:
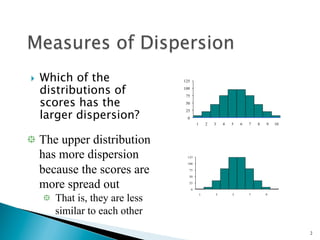
- Dispersion refers to how scattered or varied scores are around the central value. Greater dispersion means scores are less similar and more spread out.
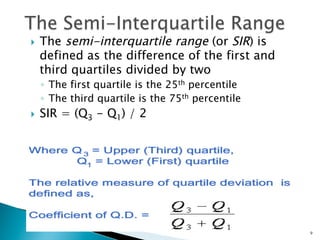
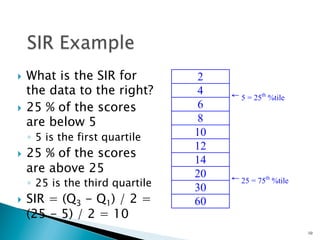
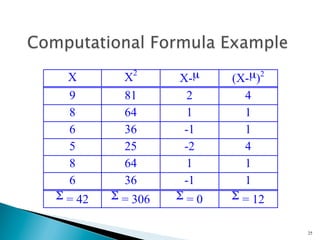
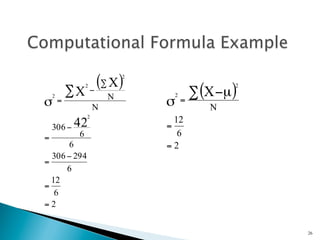
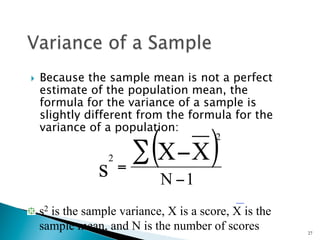
- Common measures of dispersion include the range, semi-interquartile range (SIR), variance, and standard deviation. Variance and standard deviation account for all scores rather than just the extremes.
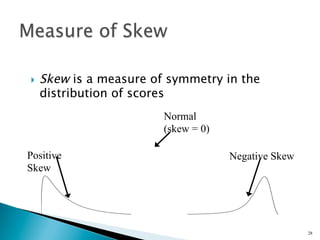
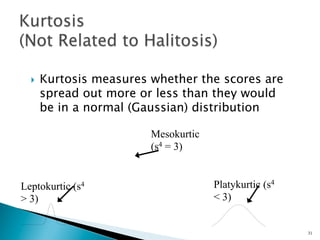
- Other concepts discussed include skew, which measures symmetry, and kurtosis, which compares a distribution's spread to a normal distribution. These provide additional information about a distribution's shape beyond just dispersion.