Embed presentation
Downloaded 191 times











This document provides information about Escherichia coli (E. coli): - E. coli is commonly found in the lower intestine of humans and animals and is usually harmless, though some pathogenic strains can be transmitted via feces and cause disease. - It has a rod shape, is gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, and motile with flagella. Laboratory diagnosis involves examining samples under a microscope, culturing on blood and MacConkey agar to observe colony morphology and color, and conducting biochemical tests like catalase, oxidase, and API tests. Serotyping may also be done for epidemiological purposes.













Overview of the presentation on E. coli prepared by Samira Fattah, detailing lab work for health sciences.
E. coli is found in the lower intestine; most strains are harmless, with disease caused by pathogenic strains through fecal-oral transmission.
Describes E. coli as rod-shaped, gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, motile with peritrichous flagella, and encapsulated in some strains.
Specimens for diagnosis of E. coli include urine, pus, blood, stool, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and sputum.
Using a microscope and gram stain, E. coli appears as gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria.
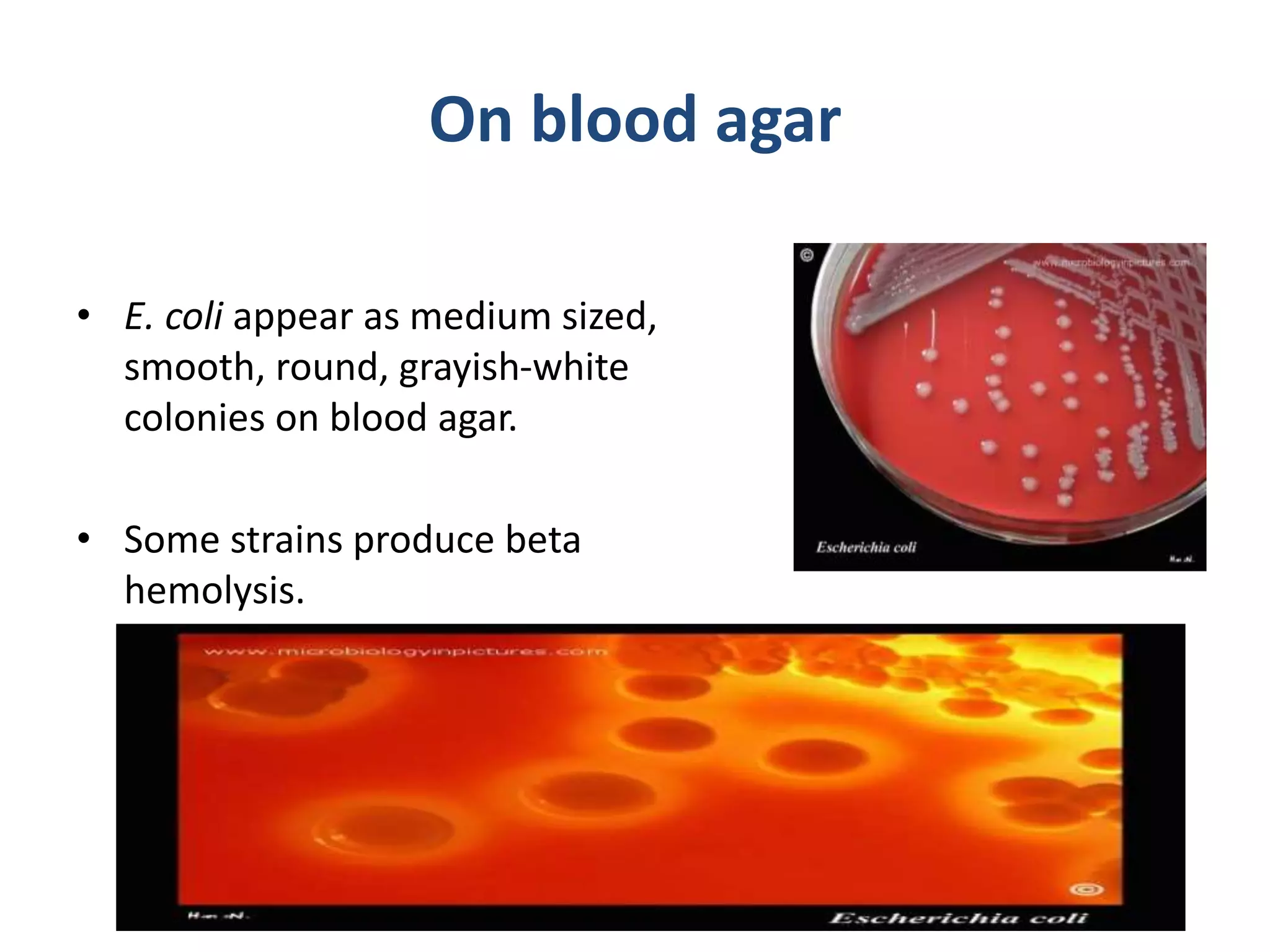
On blood agar, E. coli forms medium sized, smooth, round, grayish-white colonies, with some strains showing beta hemolysis.
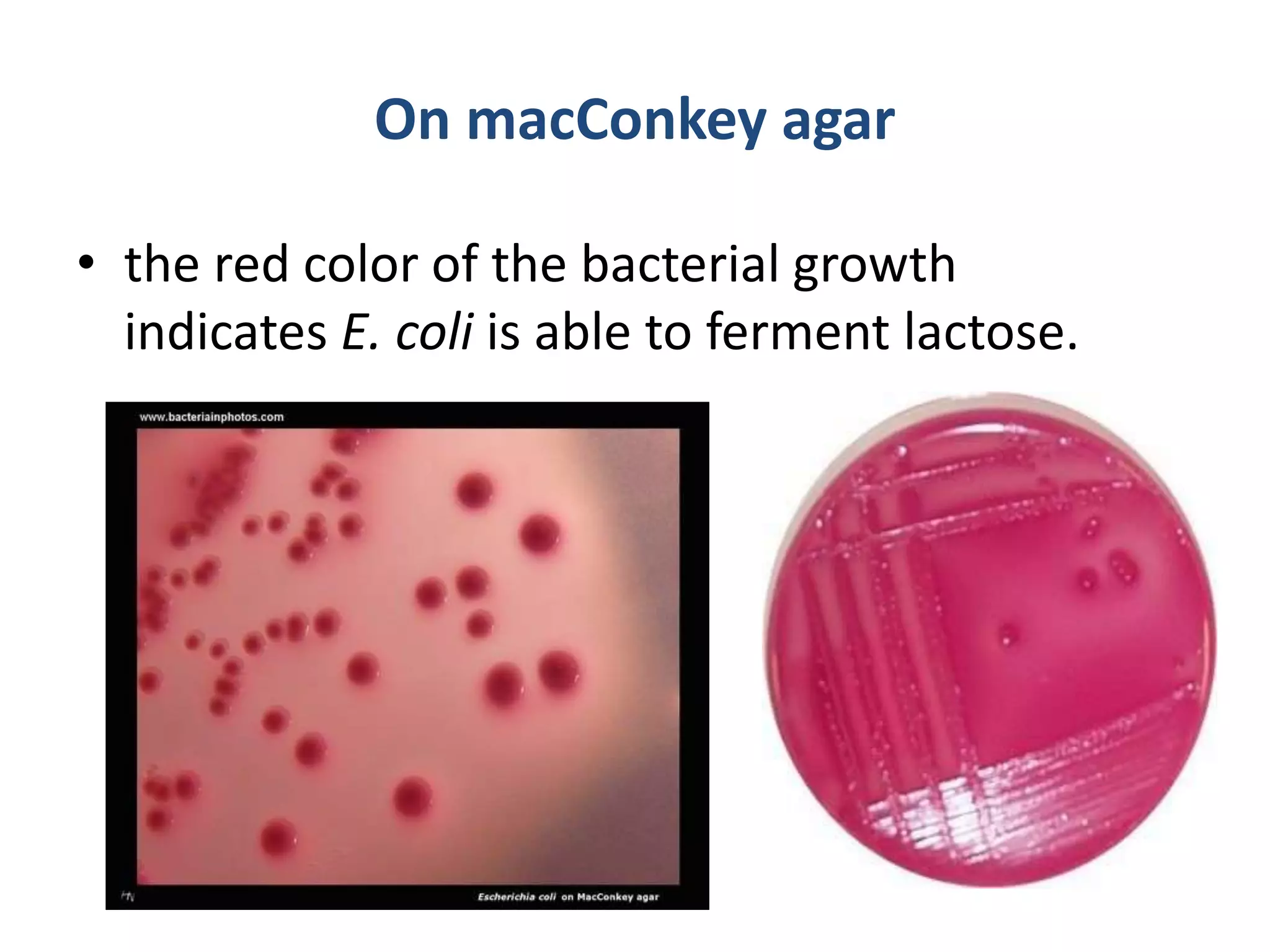
E. coli ferments lactose, indicated by red coloration in colonies on MacConkey agar.
On EMB agar, E. coli produces blue-black colonies with a greenish metallic sheen, confirming lactose fermentation.
Introduction to biochemical tests performed for E. coli identification.
E. coli is oxidase-negative, catalase-positive with bubble formation during testing.
Motility test results show E. coli is highly motile, displaying turbidity in the test medium, unlike Klebsiella pneumoniae.
API test results indicate E. coli is indole positive, gelatinase negative, urease negative, and does not produce H2O.
Serologic tests are used for E. coli serotyping, providing important epidemiologic information.