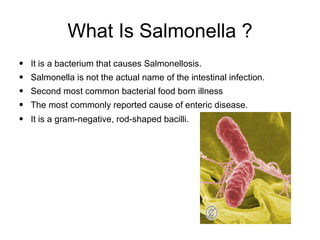
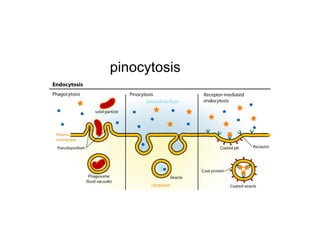
Salmonella was discovered in 1885 by Theobald Smith in pigs. It is a bacterium that causes salmonellosis, the second most common bacterial foodborne illness. Salmonella are rod-shaped bacteria that invade intestinal cells and multiply within them, causing inflammation. Symptoms include diarrhea, fever, and abdominal pain within 12-72 hours. While most cases resolve in a few days, some severe cases can be fatal, especially in young children, the elderly, and those with weak immune systems. Salmonella spreads through contact with contaminated animal feces or raw foods like meat and eggs.