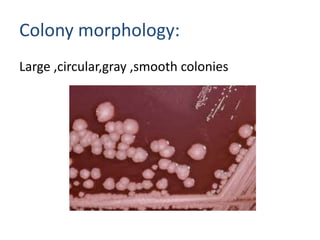
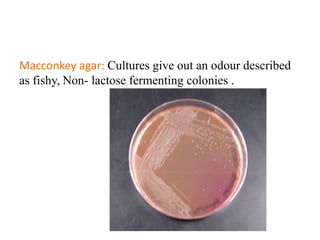
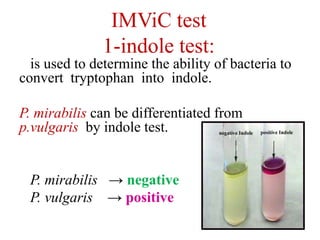
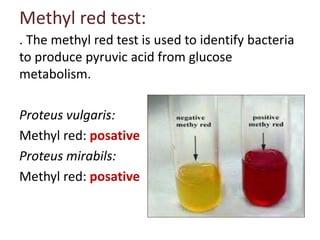
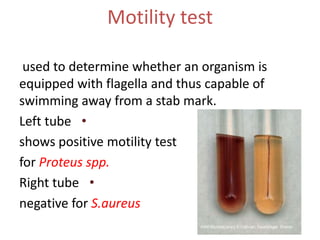
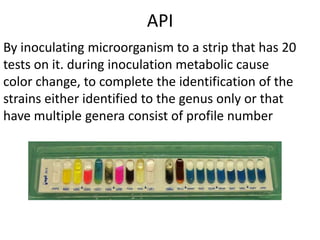
Proteus spp. are gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, motile bacilli commonly found in the human intestinal tract. The two main species of medical importance are P. mirabilis and P. vulgaris. They can cause various infections opportunistically. Diagnostic tests include gram stain showing gram-negative rods, growth on blood agar showing swarming motility, and positive reactions in the TSI test and oxidase test. Identification of species involves examining reactions in IMViC tests and analyzing biochemical profiles using systems like API or Vitek.