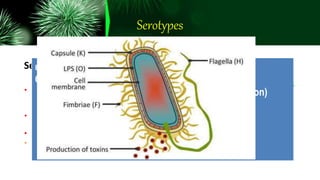
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a rod-shaped, facultatively anaerobic, Gram-negative bacterium commonly found in the intestines of humans and animals. E. coli can be either commensal or pathogenic. Pathogenic types include enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC), enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC), enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC), enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC), and enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC) which cause diseases like diarrhea, hemorrhagic colitis, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. E. coli is typically identified through culture and biochemical