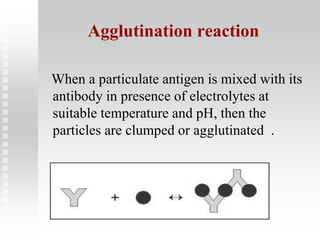
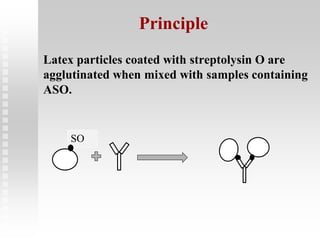
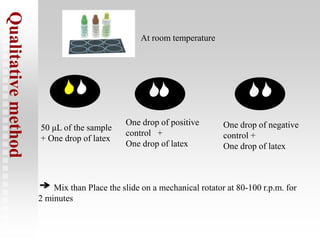
This document discusses agglutination tests, which cause antigens and antibodies to clump together when mixed. It focuses on agglutination tests using latex particles or other carriers coated with antigens. These qualitative or quantitative tests can identify bacteria, diagnose infections like typhoid, and detect antibodies. For example, the ASO latex slide agglutination test detects antibodies to streptolysin O, an exotoxin from streptococci bacteria that causes sore throats and other diseases. The test involves mixing serum samples with latex particles coated in streptolysin O, and observing for agglutination which indicates the presence of antibodies.