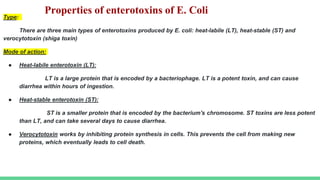
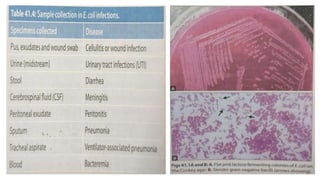
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a common bacterium found in the intestines that can cause illness when it enters other parts of the body. Certain pathogenic strains produce virulence factors like toxins and surface antigens that allow it to cause infections. E. coli is the most common cause of urinary tract infections and can lead to diarrhea through the action of different enterotoxins. Diagnosis involves culturing samples from sites of infection to identify E. coli and test for antibiotic susceptibility. Treatment depends on the antimicrobial susceptibility results and may include antibiotics like aminocillins, cephalosporins, or carbapenems.