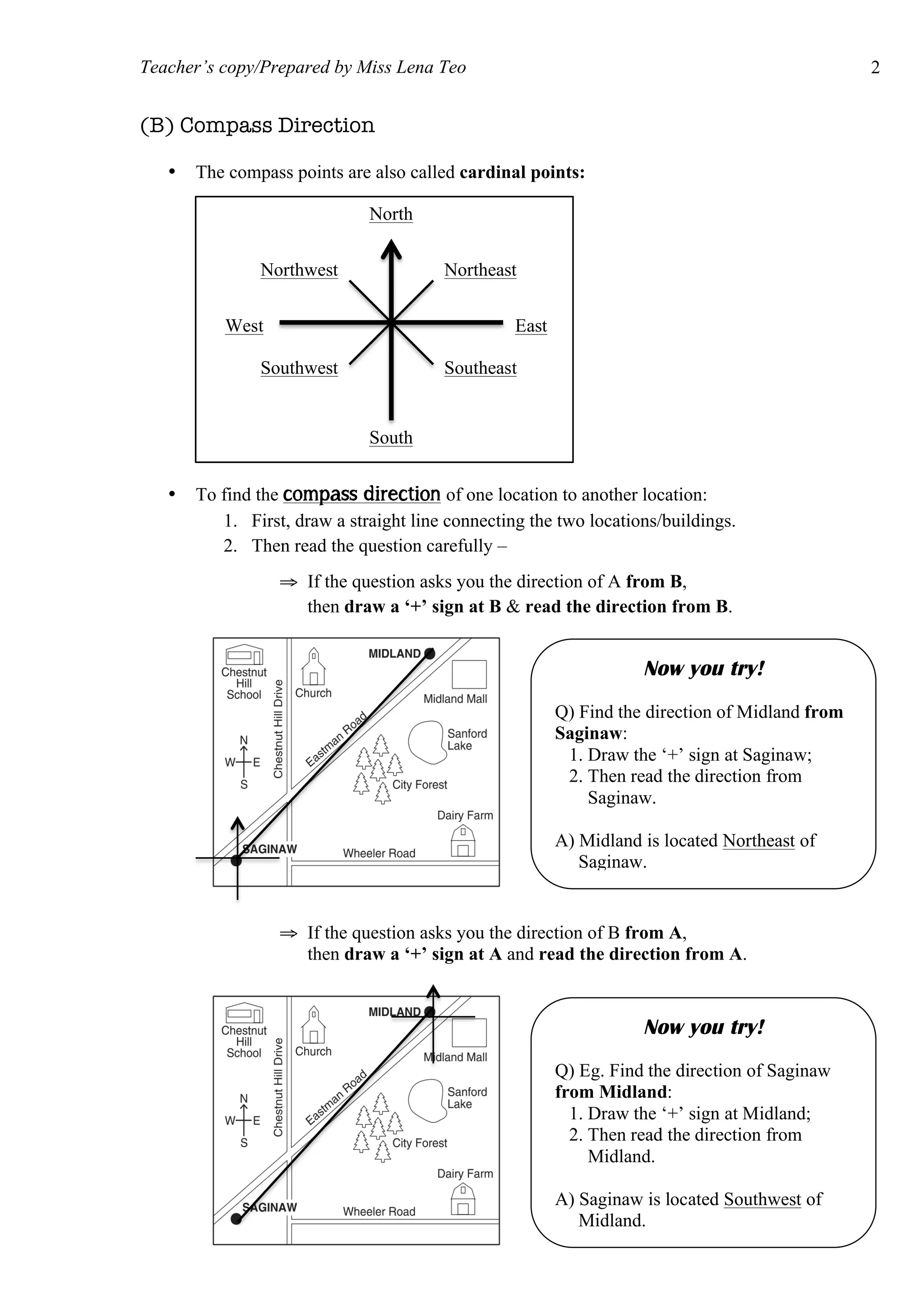
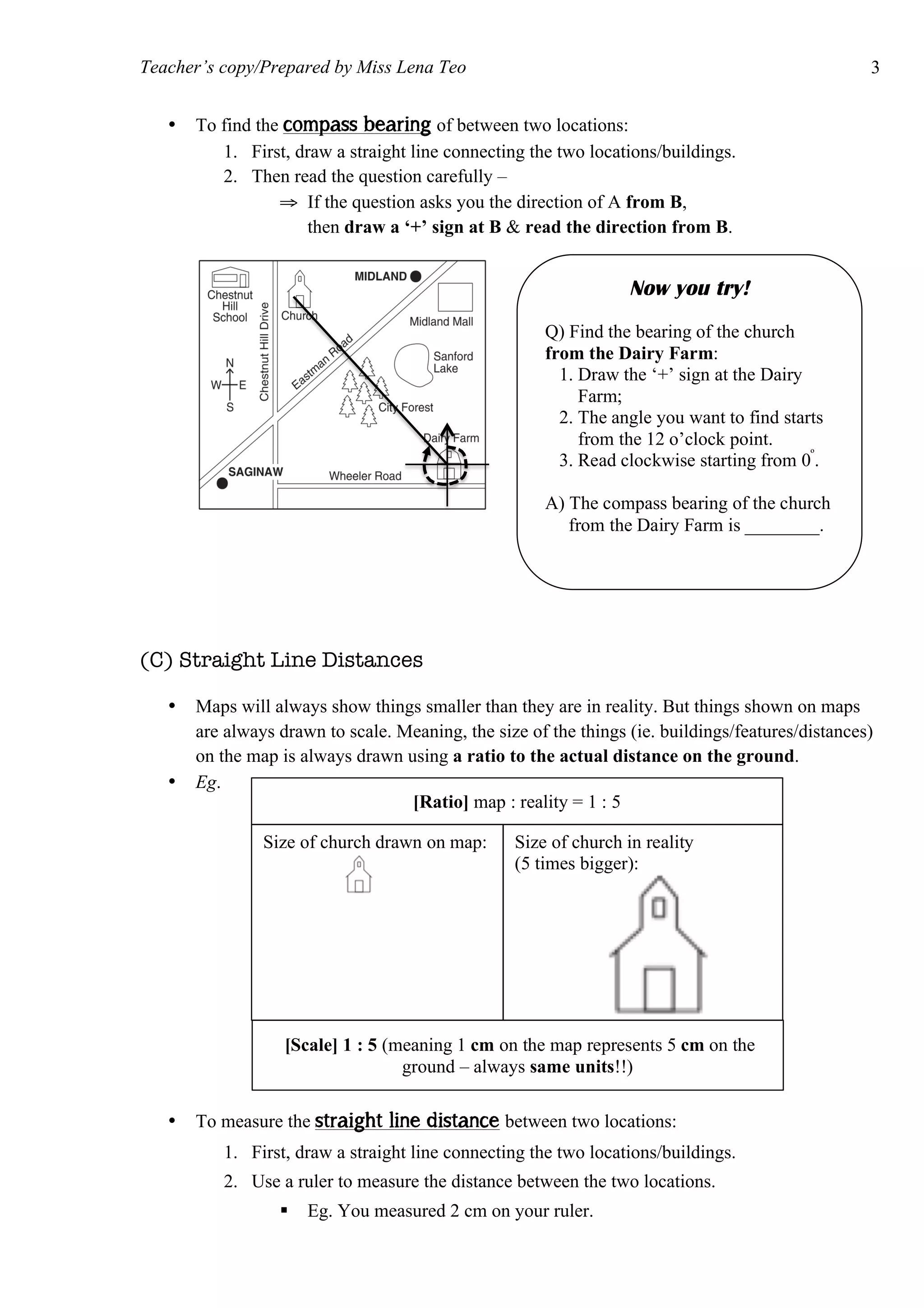
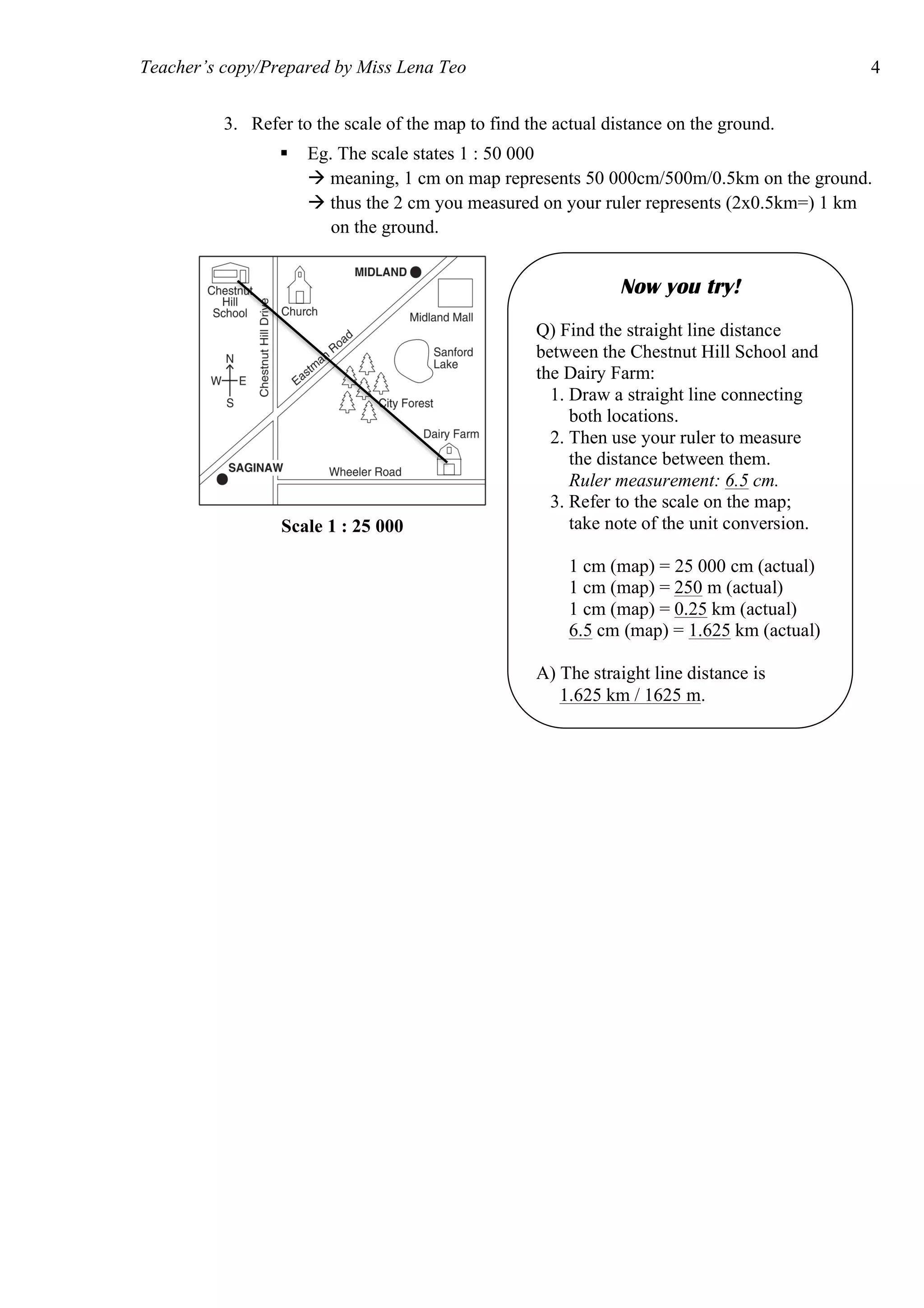
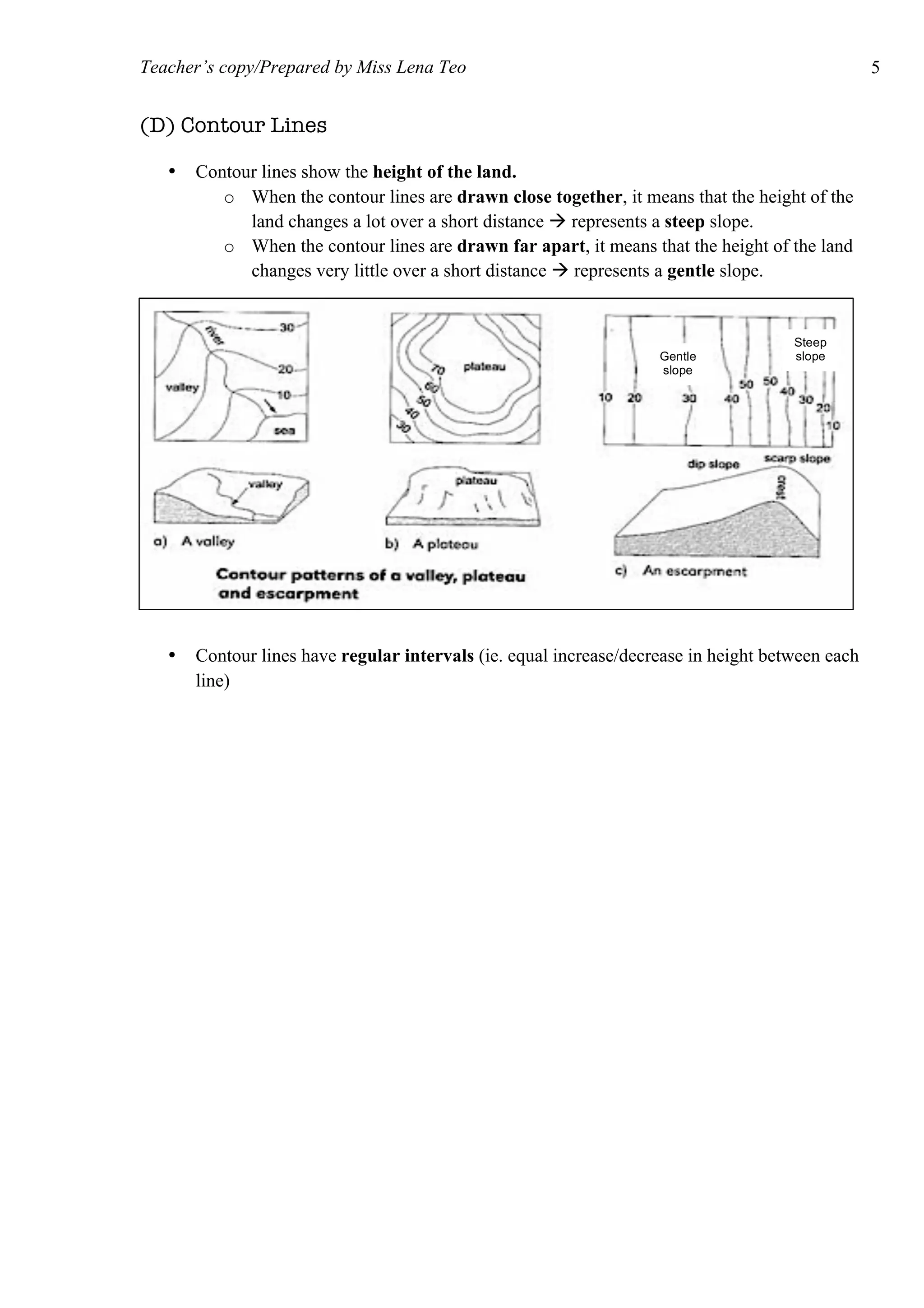
The document provides information on how to read and interpret topographical maps. It discusses key elements of maps including symbols, scale, contour lines, and compass use. Maps are representations of land or sea that use symbols to denote physical and human features. Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, with closer lines indicating steeper slopes. A compass is used to find cardinal and intercardinal directions as well as compass bearings between points in degrees. Scale relates distances on a map to actual ground distances using ratio or linear scales.