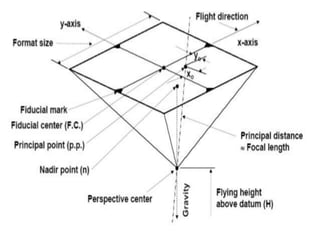
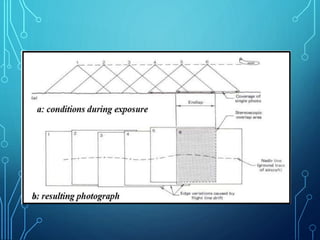
This document discusses aerial photography and how to determine flight direction from aerial photographs. It begins by defining aerial photography and noting that quality is determined by factors like the camera lens and material. Aerial photographs are classified by camera orientation and focal length. Annotations on photographs like fiducial marks, principal points, and X/Y coordinates are used to determine flight direction by finding matching or conjugate points between overlapping photographs. Careful planning of factors like scale, camera format, and overlap is needed to acquire the photographs and cover the study area.