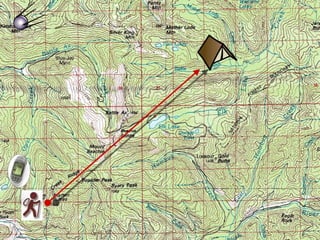
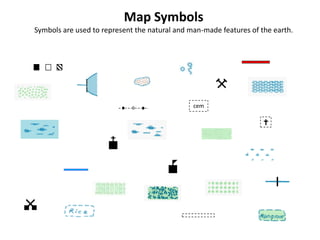
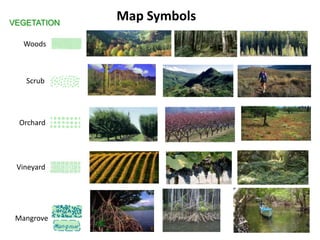
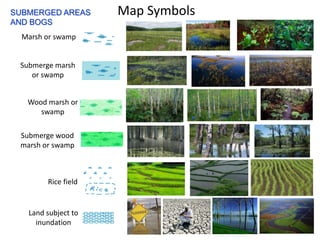
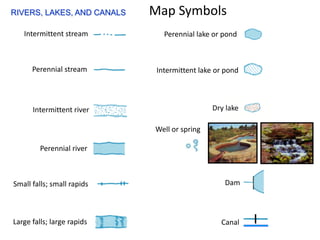
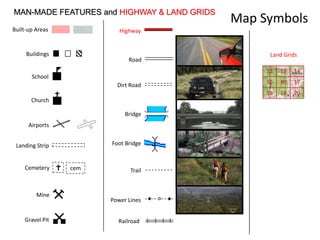
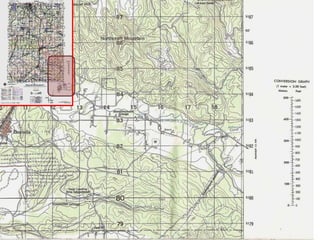
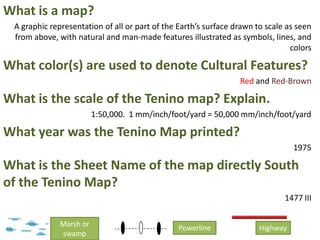
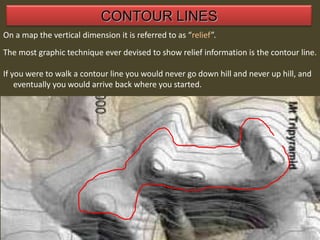
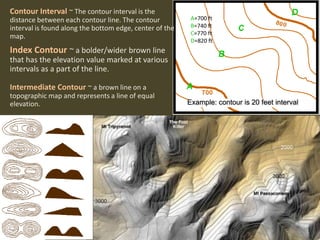
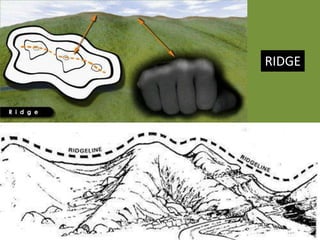
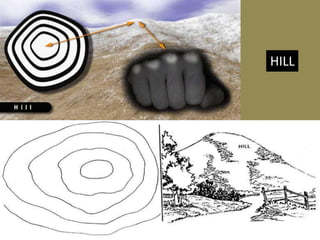
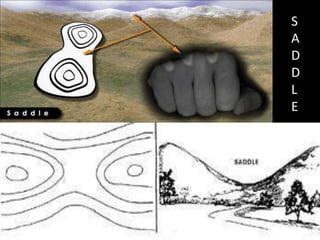
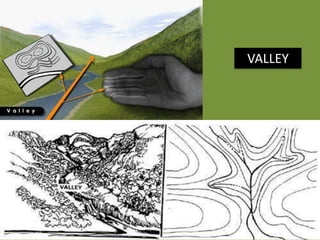
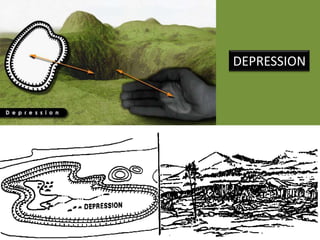
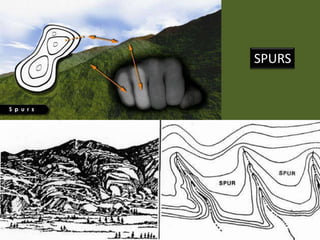
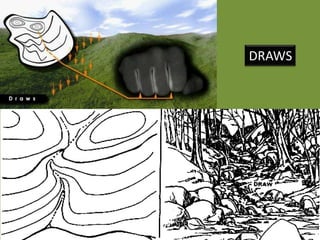
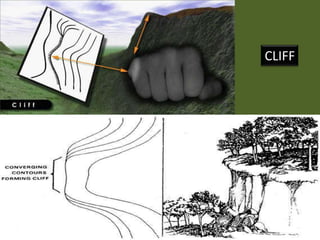
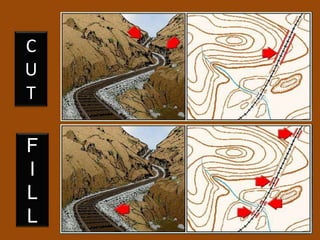
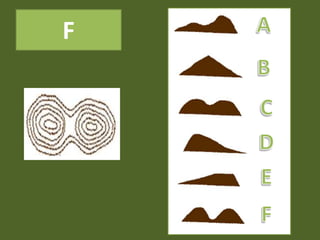
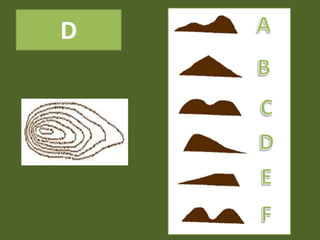
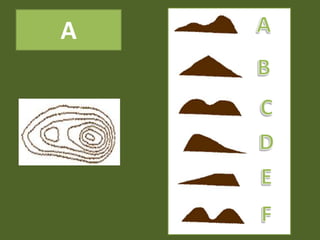
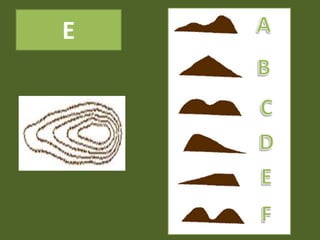
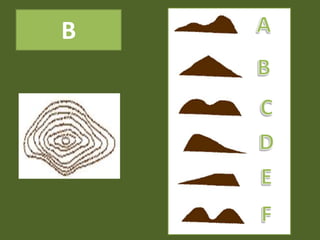
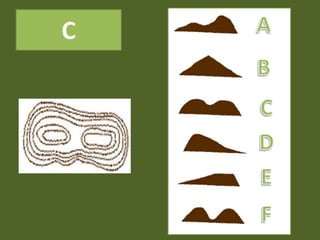
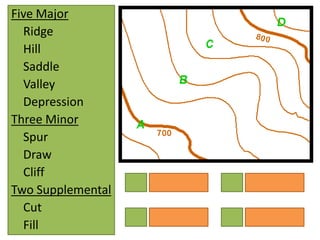
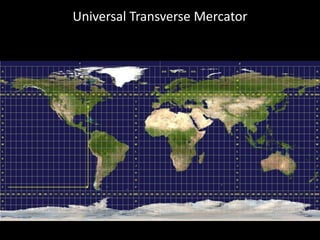
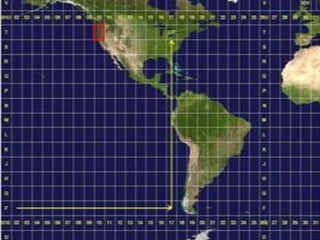
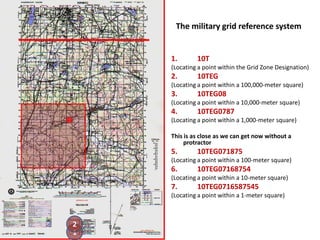
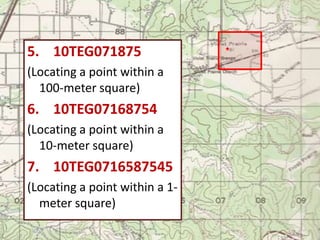
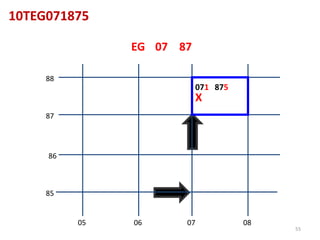
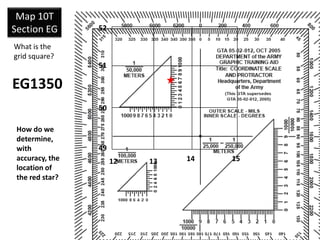
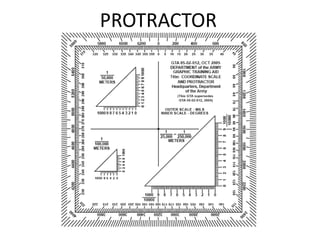
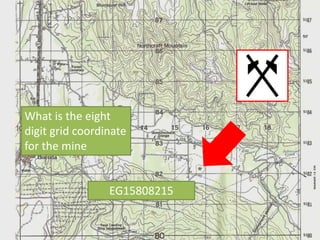
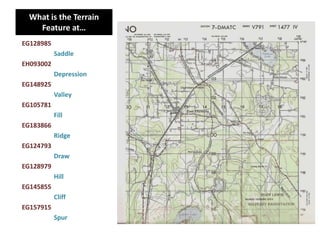
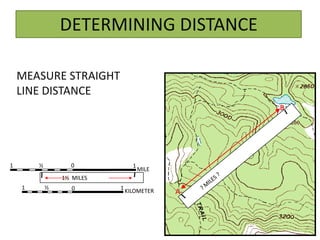
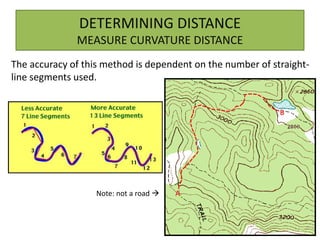
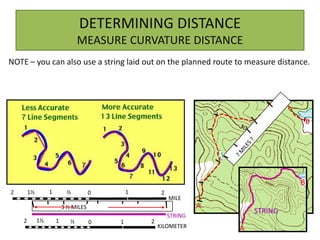
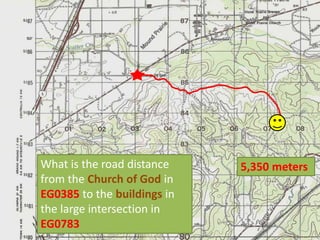
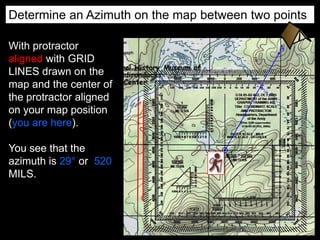
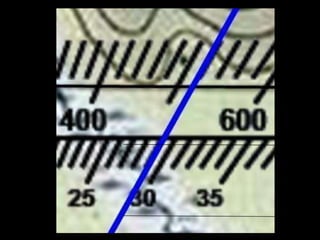
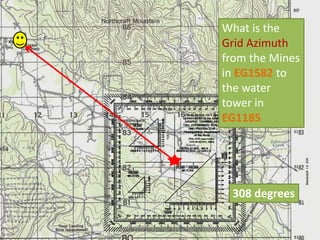
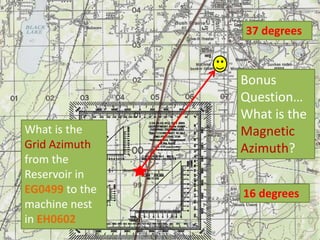
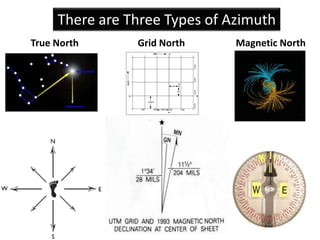
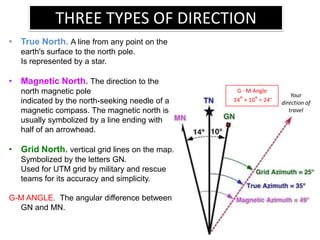
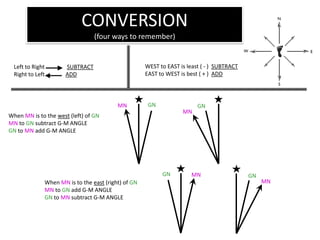
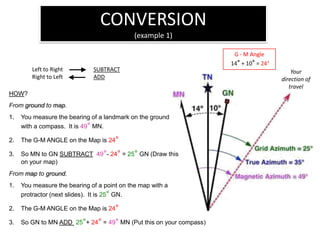
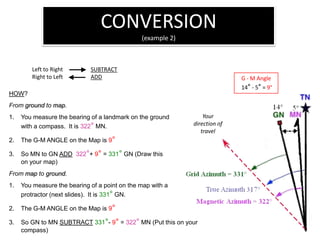
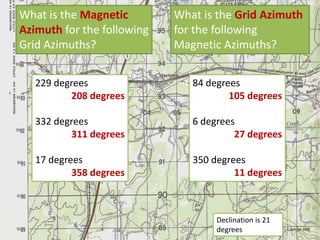
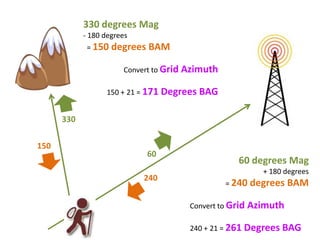
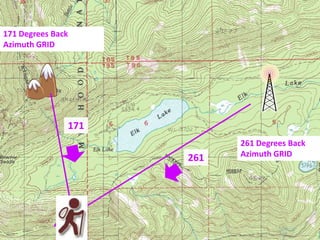
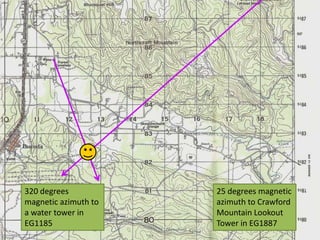
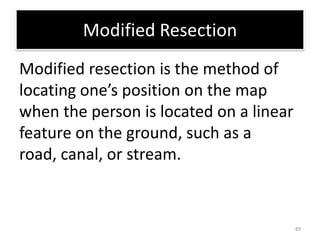
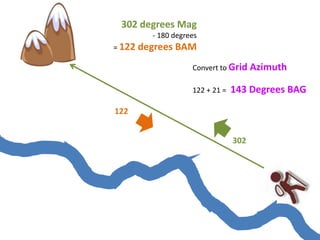
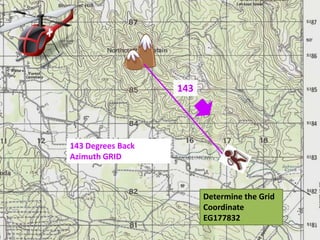
The document outlines a comprehensive land navigation training program for military personnel, focusing on essential skills such as identifying topographic symbols, determining grid coordinates, measuring distances, and converting azimuths. It establishes specific learning objectives, conditions for practical exercises, and standards for successful completion, emphasizing navigation both during day and night. Overall, it aims to equip participants with the necessary competencies to accurately navigate and locate points on military maps.